Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a frequent complication in progressive systemic sclerosis (SSc), being present in 25% to 90% of cases.
ObjectivesTo evaluate whether serum levels of procollagen type I and III aminoterminal propeptide (PINP and PIIINP) correlate with severity and patterns of ILD in Mexican women with SSc.
MethodsThirty-three SSc patients were assessed for disease characteristics and anti-topoisomerase antibodies (topo I), and also underwent pulmonary function tests and high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT). Nineteen patients had ILD+SSc, and 14 had no lung involvement (no ILD-SSc); data were compared with those from 45 healthy controls. PINP and PIIINP were assessed in all 3 groups.
ResultsPatients with SSc had higher PINP and PIIINP vs controls (P=.001, P<.001, respectively). Compared to no ILD-SSc patients, those with ILD+SSc had longer disease duration in years (P=.005), higher modified Rodnan skin score (P<.001), higher Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index scores (P<.001), higher topo I U/mL (P<.001), PINP (49.28±28.63 vs 32.12±18.58μg/L, P=.05), and PIIINP (4.33±1.03 vs 2.67±1.26μg/L, P<.001) levels. ILD severity based on total HRCT correlated with PINP (r=.388, P=.03) and PIIINP (P=.594, P<.001). On adjusted analysis, ILD severity was associated with disease duration (P=.037), PIIINP (P=.038), and topo I (P=.045).
ConclusionsPINP and PIIINP are useful markers for severe ILD+SSc, suggesting they could play a role in the follow-up of this complication in SSc.
La enfermedad pulmonar intersticial (EPI) es una complicación frecuente en la esclerosis sistémica (ES) progresiva, presente en el 25–90% de los pacientes.
ObjetivoEvaluar si los niveles séricos de propéptido aminoterminal de procolágeno tiposi y iii (PINP y PIIINP) se correlacionan con la gravedad de la EPI en mujeres mexicanas con ES.
MétodosEn 33 pacientes con ES se evaluaron las características de la enfermedad, anticuerpos antitopoisomerasa (topoi), pruebas de función pulmonar y tomografía computarizada de alta resolución (TCAR). Diecinueve pacientes tenían ES+EPI y 14 no presentaban afectación pulmonar (ES sin EPI). Se compararon con 45 controles sanos. Se evaluaron PINP y PIIINP en los 3 grupos.
ResultadosEl grupo ES tuvo mayores niveles de PINP y PIIINP que el control (p=0,001 y p<0,001, respectivamente). Las pacientes ES+EPI habían presentado la enfermedad más años que las ES sin EPI (p=0,005), tenían mayor puntuación en el índice modificado de Rodnan (p<0,001), puntuación alta en el índice de evaluación de discapacidad (p<0,001), mayores niveles de antitopoisomerasa i (p<0,001), PINP (49,28±28,63 vs. 32,12±18,58μg/l, p=0,05), y PIIINP (4,33±1,03 vs. 2,67±1,26μg/l, p<0,001). La gravedad de la EPI en TACAR se correlacionó con los niveles de PINP (r=0,388, p=0,03) y PIIINP (p=0,594, p<0,001). En el análisis ajustado, la gravedad de la EPI se asoció con la duración de la enfermedad (p=0,037) y con los niveles de PIIINP (p=0,038) y de antitopoisomerasai (p=0,045).
ConclusionesEl PINP y el PIIINP son marcadores útiles para la ES+EPI grave. Esto apoya su uso clínico para el seguimiento de esta complicación.
Progressive systemic sclerosis (SSc) is characterized by the excessive accumulation of collagen in tissues such as the skin, subcutaneous tissues, the lungs, and other internal organs.1 Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a common complication of SSc that occurs in 25%–90% of cases, depending on the method used for diagnosis.2 As ILD progresses, abnormalities develop in excellular matrix remodeling processes. ILD is similar to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: common manifestations include fibroblast proliferation, excessive collagen deposits and, in the early stages, abundant myofibroblasts.3 These myofibroblasts have been shown in in vitro studies to increase the synthesis of type I collagen.4
Pulmonary fibrosis is one of the most common causes of death in SSc. Nagy and Czirják,5 in a prospective cohort study, found that increased procollagen type III aminoterminal propeptide (PIIINP) levels were associated with poor SSc prognosis, and lung involvement was associated with poor prognosis in the Kaplan–Meier analysis. Increased collagen synthesis is associated with high levels of PIIINP and procollagen type I aminoterminal propeptide (PINP) that are released into the bloodstream in SSc associated with ILD. Of these biomarkers, PIIINP has received most attention to date.6–8
Findings regarding PINP levels in SSc are contradictory, and some authors have reported no changes, or normal values.9,10 A systematic review concluded that current evidence is insufficient for supporting the use of serum markers associated with collagen turnover in the evaluation of disease activity or SSc severity. The authors underlined the need for performing standardized evaluations in future studies.11 Moreover, the utility of these potential markers must be determined in specific types of SSc. It is not yet known if serum levels of procollagen type I and III propeptides are correlated with SSc severity when this entity is complicated by ILD. Thus, the objective of this study was to determine if procollagen type I and III propeptide levels in serum correlate with the clinical characteristics, patterns of ILD involvement detected on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) and pulmonary function tests.
Material and MethodsPatients and Study DesignWomen with SSc attending a rheumatology outpatient clinic in Guadalajara, Mexico, were consecutively screened for inclusion in this cross-sectional study. To be eligible, patients had to be at least 18 years old and meet the American College of Rheumatology criteria for SSc (1980).12 Patients with localized scleroderma or overlap syndrome, a history of hepatic or cardiac disease, active respiratory infection or asthma were excluded. Pregnant patients were also excluded. Patients with SSc were then divided into two subgroups: those with normal results on lung HRCT were included in the “no interstitial lung disease” group (SSc-no ILD, n=14) and those with conclusive findings of ILD on HRCT formed the SSc+ILD group (n=19).
A control group was also included, comprising of women blood donors of the same age without infections or indicators of systemic rheumatic disease or other autoimmune disorders. The same exclusion criteria described for patients with SSc were also applied to the selection of control group, which included 45 women.
Clinical Evaluation of Systemic SclerosisAll patients completed a structured questionnaire, evaluating the demographic and clinical variables related with rheumatic disease, including disease duration, time of rheumatological control, comorbidities and medication history. Clinical evaluation was performed by a rheumatologist and SSc subtypes were classified according to the definitions of LeRoy et al.13 Parameters included skin thickness, according to the modified Rodnan index (mRSS),14 maximum mouth opening, finger-palm distance, visual analog scale (VAS) for evaluating disease severity as perceived by the patient and function according to the Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index HAQ-DI, validated for SSc.15
Quality of Life in Systemic Sclerosis PatientsThree indices were used to evaluate the impact of ILD on the cardiopulmonary system. The first was a Spanish version of the Saint George Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ), a specific health-related quality of life (HRQoL) index for patients with chronic lung disease. This 50-item questionnaire evaluates three HRQoL-related domains: symptoms, activity and disease impact, which are summarized in an overall score.16 The second index was the 6-min walk test (6MWT), used to evaluate cardiopulmonary function, according to the guidelines of the American Thoracic Society.17 The third instrument was the modified Borg scale for evaluating dyspnea and fatigue (ATS guidelines).18
Respiratory Function Test ScreeningThe three groups (SSc+ILD, SSc-no ILD and controls) performed spirometric testing with a portable SpiroPro spirometer (SensorMedics version 2.0) according to the recommendations of the American Thoracic Society and the European Respiratory Society (2005).18 Forced expiratory volume in 1s (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC) and FEV1/FVC ratio were determined in three measurements taken during the same evaluation to confirm a restrictive ventilatory pattern. Values obtained were expressed as percentages of the predicted value for subjects of the same sex, age, weight and height. The restrictive pattern was defined from the results of the respiratory function tests, when FVC<80 and FEV1/FVC>80%.18
Patients with overlap syndrome, pregnancy, active infection, grade III or IV heart failure, chronic obstructive lung disease, asthma or pulmonary tuberculosis were excluded.
High-Resolution Computed TomographyHRCT was performed in all patients using the same scanner (fourth generation SOMATOM AR.T., Siemens®). Slices of 1–2mm (10mm intervals) were obtained with the patient in a prone position. Images were reconstructed using a high-resolution algorithm, bone filter and standard lung window (WL-700, WW 1.000–1.500HU). Criteria for classifying ILD were determined prospectively in consensus by 2 pulmonologists (JP, MM), 2 rheumatologists (LGL, JIGN) and a radiologist (JFN). The definitive diagnosis of SSc associated with ILD (SSc+ILD) required the observation on HRCT of defined bilateral peripheral reticular opacities, with or without subpleural honeycomb pattern or evidence of ground glass opacities. As mentioned above, patients with SSc were divided into two groups, depending on HRCT results: group 1, SSc+ILD, and group 2, SSc-no ILD.
Using the method put forward by Kazerooni et al.,19 the presence or absence of two characteristics was recorded on a standardized form: (a) ground glass opacity (operatively equivalent to alveolar score), defined as a more attenuated area; and (b) honeycomb pattern (operatively equivalent to interstitial score), defined as clustered subpleural cystic air spaces with defined walls of 3–25mm in diameter. The three lobes of both lungs were scored on a scale of 0–5, as follows: for the alveolar scale, no evidence of alveolar involvement=0; ground glass opacities in <5% of the lobe=1; in >25%=2; in 50%–75%=4; in >75% of the lobe=5. The sum for each pattern was calculated from the score of the sections evaluated. Operatively, the total HRCT score was calculated by adding the alveolar and interstitial scores and dividing by 2.
Evaluation of Pulmonary Arterial Pressure by EchocardiographyAn experienced cardiologist and echocardiographer, blinded to the clinical characteristics and laboratory test results of the patients, performed an echocardiogram in all participants using a Philips 7500 device with a 2.5MHz transducer. Tricuspid regurgitation was studied using color Doppler and the regurgitation jet was recorded using continuous wave Doppler. Regurgitation peak velocity was used to calculate transvalvular pressure gradient with the modified Bernoulli equation (4V2). Right atrium pressure was estimated using the maximum diameter of the inferior vena cava, as described by Denton et al.20 Finally, systolic pulmonary arterial pressure (SPAP) was taken as the sum of the pressure gradient through the tricuspid valve plus right atrium pressure.
Serum MarkersVenous blood samples were obtained at the time of the clinical evaluation. Serum was collected in a cold tube (4°C) after whole blood was centrifuged at 2000rpm for 15min at 4°C. Serum aliquots were stored at −20°C for up to 5 months. These samples were used for determination of PINP and PIIINP by radioimmunoassay, using the Risteli technique in commercially-available kits.21,22 Levels of PINP and PIIINP, expressed as μg/dl, were determined in the controls. Technicians performing the tests were blinded to the clinical data of the patients.
Statistical AnalysisQuantitative variables are expressed as mean and standard deviation and qualitative variables as frequencies and percentages. The Student's t-test was used for comparing quantitative variables between SSc+ILD patients and SSc-no ILD patients. Qualitative variables between these groups were compared using the Chi-squared test (or Fisher's exact test, if necessary). Correlations between alveolar and interstitial scores and total HRCT scores and clinical characteristics, HRQoL, cardiopulmonary indices, and PINP and PIIINP levels were analyzed using the Pearson r test. Multivariate regression analysis was conducted to identify factors associated with the ILD score on HRCT, and variables included in this analysis were selected according to two criteria: (a) if they were statistically significant on the univariate analysis, and (b) if they were considered confounding factors. After attempting several models, the following variables were included in the final model: age, duration of disease, PINP and PIIINP levels, and antitopoisomerase antibody titers. A logistic regression analysis was also performed using the presence of ILD with SSc as a dependent variable, and sex, age, disease duration and PINP and PIIINP levels as covariables. Statistical significance was set a 0.05. All analyses were performed using SPSS version 8.0.
EthicsThe study was approved by the Hospital Institutional Review Board of the Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social (IMSS) (authorization number IMSS R-2005-1303-93). All participants gave their informed consent in writing.
ResultsThere were no differences between patients with SSc (n=33) and the healthy control group (n=45) in terms of age (52.55±11.48 vs 49.47±7.25, respectively, P=.15), frequency of exposure to solvents (15.2% vs 8.9%, respectively, P=.48), exposure to smoke (45.5% vs 26.7%, respectively, P=.98), smoking history (24.4% vs 15.6%, respectively, P=.39), use of alcohol (3.0% vs 2.2%, respectively, P=1.00) or contraceptives (39.4% vs 44.4%, respectively, P=.13). Differences between patients and controls were found in all pulmonary function test parameters evaluated (FVC%, FEV1, FEV1/FVC) (P<.001). Mean 6MWT was significantly lower in the SSc group compared to the controls (372.87±112.14 vs 563.84±131.34, respectively, P<.001). PINP serum levels were significant higher in the SSc group compared to the control group (PINP, 42.0 vs 26.58, respectively, P=.001). Similarly, PIIINP levels were significantly higher in the SSc group than in the controls (3.67 vs 2.32, respectively, P<.001).
Four of the controls were active smokers (8.9%). Patients with SSc reported pulmonary symptoms as follows: cough (n=15, 45.5%), phlegm (n=10, 30.3%), wheezing (n=3, 9.1%), bilateral crackles on inhalation and exhalation (n=23, 69.7%) and dyspnea (n=15, 45.5%). Moreover, 22 (66.7%) patients with SSc showed a restrictive pattern on their pulmonary function tests (PFTs). Modified Borg scale results before 6MWT showed significant worsening in the SSc group compared to the control group (1.17 vs 0, respectively, P<.001). A similar difference in Borg scale values after 6MWT was seen between the SSc group and the controls (2.62 vs 0, respectively, P<.001). SGRQ scores in each domain were also significantly higher in patients with SSc compared to controls, indicating poorer symptom-related quality of life (15.42 vs 0, respectively, P<.001), activity (17.67 vs 0, respectively, P<.001), and impact (10.39 vs 0, respectively, P<.001).
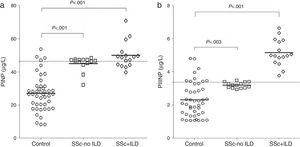
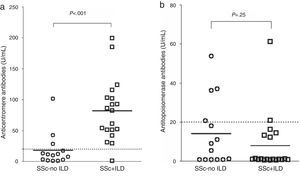
Serum Marker LevelsPINP and PIIINP levels in controls, SSc-no ILD and SSc+ILD patients are shown in Fig. 1. SSc-no ILD and SSc+ILD groups had higher PINP levels (Mann–Whitney U test) than the control group (Fig. 1a, with P<.001 for both comparisons). Higher PIIINP levels were also found in SSc-no ILD (P=.003) and SSc+ILD patients compared to the control group (Fig. 1b). In a subanalysis not shown in this figure, mean PINP and PIIINP levels were compared among the three study groups: SSc+ILD patients had significantly higher PINP levels than the control group (49.28±28.63 vs 26.58±11.12, respectively, P<.001), although there were no differences in PINP levels between the SSc-no ILD group and the control group (32.12±18.59 vs 26.58±11.12, respectively, P=.061). Moreover, SSc+ILD patients had significantly higher levels of PIIINP than controls (4.33±1.03 vs 2.32±1.04, respectively, P<.001), while there were no differences in PIIINP levels between the SSc-no ILD group and the control group (2.67±1.26 vs 2.32±1.04, respectively, P=.058). Antitopoisomerase I and anticentromere antibodies levels in SSc-no ILD and SSC+ILD patients are compared in Fig. 2. SSc+ILD patients had significantly higher antitopoisomerase antibody levels than those without ILD (P<.001; Fig. 2a), but no differences were found in anticentromere antibody titers between the two groups (P=.25; Fig. 2b).
Comparison of PINP and PIIINP levels between groups. (a) Comparison of procollagen type I propeptide (PINP) in healthy controls, in patients with systemic sclerosis without interstitial lung disease (SSc-no ILD) and in patients with systemic sclerosis with interstitial lung disease (SSc+ILD). (b) Comparison of serum levels of procollagen type III propeptide (PINP) in healthy controls, in SSc-no ILD patients and SSc+ILD patients. P-values were calculated with the Mann–Whitney U test.
(a) Comparison of antitopoisomerase I antibody titers in patients with systemic sclerosis without interstitial lung disease (SSc-no ILD) and patients with systemic sclerosis with interstitial lung disease (SSc+ILD). (b) Comparison of anticentromere antibody titers in SSc-no ILD patients and SSc+ILD patients. P-values were calculated with the Mann–Whitney U test.
Differences in median PINP and PIIINP levels were compared between SSc-no ILD and SSC+ILD patients, although the data are not shown in the tables (Mann–Whitney U test). Significant differences in PINP levels were found between both SSc groups compared to the control group (P<.001 for both groups), and this was also the case for PIIINP (P=.003 and P<.001 in SSc-no ILD). SSc+ILD patients had significantly higher levels of antitopoisomerase levels than SSc-no ILD patients (P<.001), but no differences in anticentromere antibody levels were observed between SSc+ILD and SSc-no ILD groups (P=.25).
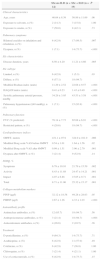
Comparison Between the two SSc Groups: SSc+ILD vs SSc-no ILDTable 1 shows the comparison between the HRCT results of the SSc+ILD and the SSc-no ILD groups in terms of clinical characteristics, cardiopulmonary index scores, FVC results, propeptide serum levels and frequency of positive antinuclear, antitopoisomerase I and anticentromere antibody results. SSc+ILD patients had had the disease for a longer time (P=.005), presented a higher rate of diffuse SSc (P=.03) and had higher mRSS scores (P<.01) in the HAQ-DI (P<.001). As expected, FVC was significantly lower in patients with SSc+ILD compared with those who did not have ILD (P<.001).
Comparison of Selected Characteristics Between Patients With Progressive Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) With Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (SSc+ILD) vs Patients With SSc Without ILD (SSc-no ILD).
| SSc-no ILD (n=14) | SSc+ILD (n=19) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical characteristics | |||
| Age, years | 46.64±8.39 | 56.89±11.69 | .06 |
| Exposure to solvents, n (%) | 2 (14.3) | 3 (15.8) | 1.00 |
| Exposure to smoke, n (%) | 7 (50.0) | 8 (42.1) | .73 |
| Pulmonary symptoms | |||
| Bilateral crackles on inhalation and exhalation, n (%) | 6 (42.9) | 17 (89.5) | .007 |
| Dyspnea, n (%) | 1 (7.1) | 14 (73.7) | <.001 |
| SSc characteristics | |||
| Disease duration, years | 6.50±4.20 | 11.21±4.66 | .005 |
| SSc subtype | |||
| Limited, n (%) | 6 (42.9) | 1 (5.3) | .03 |
| Diffuse, n (%) | 8 (57.1) | 18 (94.7) | |
| Modified Rodnan index (units) | 11.29±2.52 | 22.68±9.57 | <.001 |
| HAQ-DI index (units) | 0.41±0.23 | 1.43±0.49 | <.001 |
| Systolic pulmonary arterial pressure, mmHg | 34.29±3.95 | 43.53±3.58 | <.001 |
| Pulmonary hypertension (≥40mmHg), n (%) | 1 (7.1) | 15 (93.8) | <.001 |
| Pulmonary function | |||
| FVC (% predicted) | 78.14±7.73 | 65.68±6.91 | <.001 |
| Restricted pattern, n (%) | 4 (28.6) | 18 (94.7) | <.001 |
| Cardiopulmonary indices | |||
| 6MWT, meters | 431.1±97.9 | 324.9±101.9 | .006 |
| Modified Borg scale VAS before 6MWT | 0.54±1.01 | 1.64±1.56 | .02 |
| Modified Borg scale VAS after 6MWT | 0.99±1.51 | 3.96±2.79 | .001 |
| Dyspnea after 6MWT, n (%) | 3 (21.4) | 9 (52.9) | .14 |
| SGRQ, % | |||
| Symptoms | 6.79±10.10 | 21.79±15.59 | .002 |
| Activity | 8.43±11.88 | 24.47±14.21 | .001 |
| Impact | 4.07±6.88 | 15.05±9.71 | .001 |
| Total | 8.71±11.06 | 25.32±15.17 | .001 |
| Collagen metabolism markers | |||
| PINP (μg/l) | 32.12±18.58 | 49.28±28.63 | .05 |
| PIIINP (μg/l) | 2.67±1.26 | 4.33±1.03 | <.001 |
| Autoantibody profile | |||
| Antinuclear antibodies, n (%) | 12 (85.7) | 18 (94.7) | .56 |
| Antitopoisomerase antibodies, n (%) | 3 (21.4) | 18 (94.7) | <.001 |
| Anticentromere antibodies, n (%) | 4 (28.6) | 2 (10.5) | .36 |
| Treatment | |||
| D-penicillamine, n (%) | 9 (64.3) | 14 (73.7) | .71 |
| Azathioprine, n (%) | 6 (42.9) | 11 (57.9) | .49 |
| Colchicine, n (%) | 6 (42.9) | 7 (36.8) | 1.00 |
| Chloroquine, n (%) | 3 (21.4) | 4 (21.1) | 1.00 |
| Use of corticosteroids, n (%) | 6 (42.9) | 14 (73.7) | .15 |
6MWT, 6min walk test; FVC, forced vital capacity; HAQ-DI, Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index; PIIINP, procollagen III animoterminal propeptide; PINP, procollagen I animoterminal propeptide; SGRQ, Saint George Respiratory Questionnaire; VAS, visual analog scale.
Qualitative variables are expressed in frequency (%); quantitative variables are expressed as mean±standard deviation. Proportions were compared with the Chi-squared test or Fisher's exact test. Means were compared with the unpaired Student t-test.
The correlation between ILD severity scores on HRCT and series of selected characteristics in 33 patients with SSc is shown in Table 2. The total HRCT score was correlated with age (P=.03), disease duration (P<.001), mRSS score (P<.001), finger–palm distance (P=.04), mouth-opening (negative correlation, P=.02), HAQ-DI score (P<.001), all SGRQ domains (P<.001), 6MWT (negative correlation, P=.01), modified Borg scale before 6MWT (P=.03), modified Borg scale after 6MWT (P=.001), PINP (P=.03) and PIIINP levels (P<.001). SPAP correlated significantly with PINP (r=0.422, P=.014) and PIIINP levels (r=0.476, P=.005). These data are not shown in the table.
Correlation Between Interstitial Lung Disease Severity Scores on High-Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT) and Selected Characteristics of Women With Progressive Systemic Sclerosis (SSc).
| Alveolar score | Interstitial score | Total HRCT score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | P | r | P | R | P | |
| Age, years | 0.341 | .05 | 0.362 | .04 | 0.373 | .03 |
| Disease duration, years | 0.582 | <.001 | 0.653 | <.001 | 0.665 | <.001 |
| SSc characteristics | ||||||
| Modified Rodnan index (units) | 0.866 | <.001 | 0.850 | <.001 | 0.922 | <.001 |
| Finger-palm distance (cm) | 0.236 | .19 | 0.460 | .007 | 0.368 | .04 |
| Mouth-opening (cm) | −0.283 | .110 | −0.502 | .003 | −0.410 | .02 |
| HAQ-DI score (units) | 0.665 | <.001 | 0.723 | <.001 | 0.743 | <.001 |
| Pulmonary function | ||||||
| FVC (% predicted) | −0.858 | <.001 | −0.851 | <.001 | −0.914 | <.001 |
| Health-related quality of life | ||||||
| SGRQ, Symptoms | 0.749 | <.001 | 0.830 | <.001 | 0.840 | <.001 |
| SGRQ, Activity | 0.617 | <.001 | 0.752 | <.001 | 0.723 | <.001 |
| SGRQ, Impact | 0.663 | <.001 | 0.773 | <.001 | 0.764 | <.001 |
| SGRQ, Total | 0.611 | <.001 | 0.775 | <.001 | 0.713 | <.001 |
| Cardiopulmonary indices | ||||||
| Modified Borg scale VAS before 6MWT | 0.383 | .03 | 0.302 | .09 | 0.372 | .03 |
| 6MWT, meters | −0.469 | .008 | −0.376 | .04 | −0.453 | .01 |
| Modified Borg scale VAS after 6MWT | 0.556 | .001 | 0.519 | .003 | 0.572 | .001 |
| Collagen markers | ||||||
| PINP (μg/dl) | 0.200 | .26 | 0.550 | .001 | 0.388 | .03 |
| PIIINP (μg/dl) | 0.521 | .002 | 0.582 | <.001 | 0.594 | <.001 |
6MWT, 6min walk test; FVC, forced vital capacity; HAQ-DI, Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index; PIIINP, procollagen III animoterminal propeptide; PINP, procollagen I animoterminal propeptide; SGRQ, Saint George Respiratory Questionnaire; VAS, visual analog scale.
Results from the multivariate linear regression analysis including variables associated with alveolar, interstitial and total HRCT scores from 33 patients with SSc are shown in Table 3. After adjusting for age and disease duration, variables associated with a higher alveolar score were PINP (P=.029), PIIINP (P=.050) and antitopoisomerase antibodies (P=.023). No significant associations were identified for interstitial score. Total HRCT score was associated with disease duration (P=.037), PIIINP levels (P=.038), and antitopoisomerase antibody levels (P=.045). A log regression analysis was performed to evaluate if PINP and PIIINP levels were associated with SSc+ILD. After adjusting for age and disease duration, PIIINP levels were still significantly associated (OR=9.74, 95% CI: 1.20–78.78, P=.03), while PINP levels were no longer significant in this model (data not shown in the table).
Factors Determining Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) in Multivariate Regression Analysis.
| Variable | β Coefficient | Partial R2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alveolar score | |||
| Age, years | 0.090 | 0.116 | .538 |
| Disease duration, years | 0.752 | 0.340 | .074 |
| PINP (μg/dl) | −0.143 | 0.347 | .029 |
| PIIINP (μg/dl) | 1.983 | 0.487 | .050 |
| Anti-topoisomerase antibodies (U/ml) | 0.085 | 0.578 | .023 |
| Interstitial score | |||
| Age, years | 0.057 | 0.131 | .675 |
| Disease duration, years | 0.689 | 0.430 | .076 |
| PINP (μg/dl) | 0.054 | 0.505 | .350 |
| PIIINP (μg/dl) | 1.976 | 0.599 | .060 |
| Anti-topoisomerase antibodies (U/ml) | 0.034 | 0.615 | .298 |
| Total HRCT score | |||
| Age, years | 0.067 | 0.139 | .587 |
| Disease duration, years | 0.748 | 0.445 | .037 |
| PINP (μg/dl) | −0.053 | 0.452 | .321 |
| PIIINP (μg/dl) | 2.000 | 0.531 | .038 |
| Anti-topoisomerase antibodies (U/ml) | 0.062 | 0.647 | .045 |
HRCT, high-resolution computed tomography; PIIINP, procollagen III animoterminal propeptide; PINP, procollagen I animoterminal propeptide.
Multivariate regression analysis of interstitial lung disease severity according to HRCT markers with clinical and procollagen aminoterminal propeptides in women with progressive systemic sclerosis. Beta values are non-standardized coefficients. R2 is the total variance explained in the model.
In this study, patients with ILD associated with SSc had higher concentrations of PINP and PIIINP compared to those with SSc with no lung involvement. Increased PIIINP was correlated with severity and extent of alveolar and interstitial damage and with the total HRCT score, while PINP levels were only correlated with interstitial involvement and total HRCT severity score.
Procollagen types I and III aminoterminal propeptides are an indication of the formation of collagen, and as such, are a useful marker of fibrogenesis in many organs. The fibrotic process that occurs in skin and other organs in SSc increases type I collagen production, causing high PINP levels in blood. In this study, we found that PINP serum levels were significantly higher in patients than in controls, a finding that differs from those of some other authors.10 High quantities of type III collagen are found in the architecture of the lung under normal conditions, and PIIINP levels reflect type III collagen production in the lungs and other organs. In lung diseases, increased PIIINP can be found in the presence of alveolar and interstitial damage, and is associated with active type III collagen production. Thus, increased serum levels of PIIINP may be an indication of the excessive type III collagen formation that has previously been described in SSc.9 Increased PIIINP has also been associated with poor prognosis in SSc patients.5
To date, the utility of PINP serum levels in the evaluation of the organ involvement of SSc has not been as widely evaluated as PIIINP. Diot et al.23 reported that high PIIINP levels were associated with lung involvement in SSc, but could not identify any correlation with severity. Scheja et al.9 showed that higher levels of PIIINP in SSc were associated with a loss of carbon monoxide diffusion capacity, but these authors did not perform any radiological studies to determine ILD.
Increased PIIINP serum levels have been related with the development of alveolitis, a condition that can lead to pulmonary fibrosis. Lammi et al.24 found increased PIIINP in the bronchoalveolar lavage of 18 patients with fibrosing alveolitis of different origins, mainly idiopathic. This supports the notion that PIIINP is a potential marker of active ILD. Lee et al.25 found that patients with SSc and FVC<80% had higher PIIINP levels, suggesting that this biomarker could be used to identify patients with a restrictive pattern on pulmonary function tests.
To our knowledge, no other study has examined the correlation between ILD severity, according to HRCT results in SSc patients, and serum levels of PINP and PIIINP. We are equally unaware of any multivariate analysis exploring the association of these propeptides with ILD severity and patterns. We found that more severe ILD on HRCT is correlated with higher PIIINP levels, and that these levels are associated with greater interstitial and alveolar involvement. These data support the role of PIIINP not only in the detection of SSc+ILD, but also as a biomarker for determining the severity of lung involvement. Hunzelmann et al.10 evaluated PINP serum levels in patients with SSc, but did not find any correlation between the skin score and levels of this biomarker. In contrast, we found that patients with ILD had significantly higher levels of PINP, compared to healthy controls. Furthermore, Scheja et al.9 found a correlation between PINP levels and vital capacity on spirometry.
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a significant complication of SSc. Echocardiography can be used to detect PH, and SPAP can often be estimated by Doppler echocardiography. In this study, SPAP was seen to correlate significantly with PINP (r=0.422, P=.014) and PIIINP levels (r=0.476, P=.005). Denton et al.20 reported a correlation between Doppler echocardiography and right heart catheterization.
One limitation of our study is that, although our patients with severe ILD had higher PIIINP levels, we were not able to determine if these patients have an increased risk of poor prognosis. For example, Nagy and Czirják5 found that patients with higher PIIINP levels were more likely to have a poor prognosis. Another limitation is that no men with SSc were included in our series. The reason for this is that the population of men with this disease in our clinic is so small that the sample would be insufficient for statistical analysis. This limitation means that our results can only be generalized to women with SSc, and future studies should be designed to confirm our findings in a series that includes both sexes. Yet another limitation of our study is that there is no statistical association in the linear regression analysis between PINP or PIIINP and reticular pattern findings. This may be partially explained by the limited precision of our HRCT score for identifying some of the less severe cases of ILD (false negatives) that may have been wrongly classified. These problems must be taken into account in future studies, and a combination of diagnostic methods should be used for better detection of interstitial involvement, to increase the sensitivity of the ILD diagnosis. Another limitation is that these propeptides cannot be considered highly specific ILD markers; other disease characteristics and comorbidities are associated with increased serum levels of PINP and PIIINP and these must be taken into account. Other diseases associated with higher PINP levels include osteoporosis,26,27 systemic lupus erythematosus,28 breast cancer bone metastases29 and chronic renal failure.30 Moreover, increased levels of both PINP and PIIINP are associated with acute respiratory failure.31 To minimize possible confounding factors, we excluded patients with overlap syndrome, localized scleroderma and history of cardiac or hepatic disease, all of which are associated with increased levels of these propeptides. However, our patients did not undergo a formal evaluation of osteoporosis with bone density studies, so this must be considered another limitation of our study, particularly in the case of PINP levels. None of our patients had creatinine serum levels >1.5mg/dl, so this variable probably did not affect the PINP and PIIINP increases in serum found in patients with SSc+ILD. Although chronic renal failure was not a confounding factor in our study, PINP or PIIINP level as markers for SSc+ILD may be less useful in patients with significant renal impairment. Finally, a well-founded evaluation of the correlation between pulmonary function tests and PINP or PIIINP level in serum was not possible with the methodology used to explore lung function in our study.
One of the strengths of our study is that the methodology used for evaluating lung involvement in SSc was based on a validated definition of ILD findings on HRCT and a validated index of the severity of the involvement. The main contribution of this study is not only that SSc complicated by ILD is associated with propeptide serum levels, but also that these levels increase in line with the severity of the lung involvement on the HRCT score. Another strength of this study that that the multivariate analysis was performed adjusting for confounding factors, and PIIINP levels were maintained as a factor associated with ILD severity. Our study was not designed to evaluate the role of PINP or PIIINP concentrations as an indication of prognosis in these patients. Nonetheless, the results from some patients in whom these biomarkers were increased, even in the absence of ILD as a complication, suggest that there is a need for longitudinal studies to determine if there are any clinically significant differences in disease course that can be predicted by propeptide levels.
In conclusion, we provide evidence that PINP and PIIINP are markers of ILD severity in SSc, and that these markers are correlated with changes in HRCT scores of these patients. PIIINP is also associated with interstitial and alveolar involvement in ILD, supporting the suggestion that this marker may be useful in evaluating disease severity. Further studies in well-controlled cohorts are required to explore these findings in greater depth.
FundingThis project was co-funded by two research grants: the Mexican Social Security Institute IMSSFOFOI-2005/1/I/065, and the National Science and Technology Council (CONACYT) mixed funds, Government of the State of Michoacán, MICH-2003 C01-12442.
Contributions of the AuthorsConcept and design: Laura Gonzalez-Lopez, Araceli Garcia-Gonzalez, Alberto D. Rocha-Muñoz, Jorge I. Gámez-Nava.
Data analysis and interpretation: Laura Gonzalez-Lopez, Alberto D. Rocha-Muñoz, Arnulfo H. Nava-Zavala, Jorge I. Gámez-Nava, Eva M Olivas-Flores.
Manuscript preparation: Jorge I. Gamez-Nava, Alberto D. Rocha-Muñoz, Eva M Olivas-Flores, Laura Gonzalez-Lopez, Mayra Mejía, Soraya A Zavaleta-Muñiz, Mónica Vázquez-del Mercado, Ernesto G. Cardona-Muñoz, Benjamín Trujillo-Hernández.
Critical review of the important intellectual content of the article: Araceli Garcia-Gonzalez, Arnulfo H. Nava-Zavala, Alberto I. Villa-Manzano, Soraya A. Zavaleta-Múñiz, Mónica Vázquez-del Mercado, Ernesto G. Cardona-Muñoz, Benjamín Trujillo-Hernández, Mario Salazar-Paramo, Ana Peguero.
Supply of study patients or materials: Laura González-López, Juan Flores-Navarro, Alberto I. Villa-Manzano, Pablo Juárez-Contreras.
Administrative, technical or logistical support: Mario Salazar-Paramo, Ana Peguero, Juan Flores-Navarro, Pablo Juárez-Contreras, Mayra Mejía.
Final approval of the article: Laura González-López, Alberto D. Rocha-Muñoz, Eva M. Olivas-Flores, Araceli García-Gonzalez, Ana Peguero, Juan Flores-Navarro, Alberto I. Villa-Manzano, Soraya A. Zavaleta-Muñiz, Mario Salazar-Paramo, Mayra Mejía, Pablo Juárez-Contreras, Mónica Vázquez-del Mercado, Ernesto G. Cardona-Muñoz, Benjamín Trujillo-Hernández, Arnulfo Nava, Jorge I. Gámez-Nava.
Conflict of InterestsAll authors declare that they have no conflict of interests with regard to the publication of this article.
Please cite this article as: Gonzalez-Lopez L, Rocha-Muñoz AD, Olivas-Flores EM, Garcia-Gonzalez A, Peguero-Gómez AR, Flores-Navarro J, et al. Niveles de propéptido aminoterminal de procolágeno tipos i y iii y gravedad de la enfermedad pulmonar intersticial en mujeres mexicanas con esclerosis sistémica progresiva. Arch Bronconeumol. 2015;51:440–448.