Emphysema has been associated with decreased VEGF and VEGFR-2 expression and the presence of high numbers of apoptotic alveolar cells. Keratinocyte growth factor stimulates VEGF synthesis which in turn confers normal lung structure maintenance via the Akt pathway. In this study the potential role of rHuKGF in the improvement of deregulated Akt mediated cell survival pathway in emphysematous mice was investigated.
MethodsThree experimental groups, i.e., emphysema, treatment and control groups, were prepared. Lungs of mice were treated on 3 occasions by oropharyngeal instillation of 10mg rHuKGF per kg body weight after induction of emphysema with porcine pancreatic elastase. Subsequently, lung tissues from mice were collected for histopathology and molecular biology studies.
Results and discussionHistopathology photomicrographs and destructive index analysis have shown that elastase-induced airspace enlargement and loss of alveoli recovered in the treatment group. rHuKGF stimulates VEGF production which in turn induces the Akt mediated cell survival pathway in emphysematous lungs. mRNA expression of VEGF, VEGFR, PI3K and Akt was significantly increased while Pten, Caspase-9 and Bad was notably decreased in treatment group when compared with emphysema group, being comparable with the control group. Moreover, VEGF protein expression was in accordance with that found for mRNA.
ConclusionTherapeutic rHuKGF supplementation improves the deregulated Akt pathway in emphysema, resulting in alveolar cell survival through activation of the endogenous VEGF-dependent cell survival pathway. Hence rHuKGF may prove to be a potential drug in the treatment of emphysema.
El enfisema se ha asociado a una disminución de la expresión de VEGF y VEGFR-2 y a la presencia de un número elevado de células alveolares apoptósicas. El factor de crecimiento queratinocítico estimula la síntesis de VEGF, lo cual proporciona, a su vez, un mantenimiento de la estructura pulmonar normal a través de la vía de Akt. En este estudio hemos investigado el posible papel del rHuKGF en la mejora de la falta de regulación de la vía de supervivencia celular mediada por Akt en ratones enfisematosos.
MétodosSe establecieron 3 grupos experimentales: grupos de enfisema, tratamiento y control. Los pulmones de los ratones se trataron terapéuticamente en 3 ocasiones mediante la instilación orofaríngea de 10mg de rHuKGF/kg de peso corporal tras la inducción del enfisema mediante elastasa pancreática porcina. Posteriormente, se obtuvo tejido pulmonar de los ratones para la realización de exámenes de histopatología y biología molecular.
Resultados y discusiónLas microfotografías de histopatología y el análisis del índice de destrucción han mostrado que el agrandamiento del espacio aéreo inducido por la elastasa y la pérdida de alvéolos se recuperaron en el grupo de tratamiento. El rHuKGF estimula la producción de VEGF, que a su vez induce la vía de supervivencia celular mediada por Akt en los pulmones enfisematosos. Se produjo un aumento significativo de la expresión de mRNA de VEGF, VEGFR, PI3K y Akt, mientras que hubo una disminución notable de Pten, caspasa-9 y Bad en el grupo de tratamiento en comparación con el grupo de enfisema, y los resultados fueron comparables a los del grupo de control. Además, la expresión de VEGF a nivel proteico concordaba con la observada a nivel de mRNA.
ConclusiónLos suplementos terapéuticos de rHuKGF mejoran la mala regulación de la vía de Akt en el trastorno del enfisema, dando lugar a una supervivencia celular alveolar a través de una activación de la vía de la supervivencia celular dependiente de VEGF endógena. Así pues, el rHuKGF podría ser un posible fármaco para el tratamiento del enfisema.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a major healthcare burden worldwide, and the only leading cause of death that is increasing in prevalence.1 In the United States, it accounts for a morbidity of 4%, and is the fourth leading cause of death.1 Pulmonary emphysema, which comes under COPD, is an anatomic pathological diagnosis defined by permanent destructive enlargement of airspaces distal to the terminal bronchioles, contributing to airflow limitation. It is thought to be irreversible.2 As yet, no effective treatment is available to re-establish normal gas exchanging lung parenchyma after emphysematous changes have been established. Although promising results with All-trans-retinoic acid therapy have been reported in rodent models of emphysema,3 there is no proven clinically effective treatment to promote recovery from established emphysema.4,5 Hence, the induction of alveolar regeneration is still a major challenge in the development of novel therapies for emphysema.6
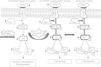
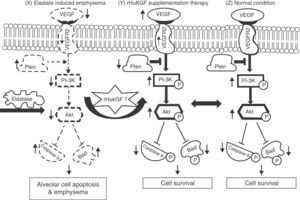
Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) is a potent mitogen for different types of epithelial cells and assists in the repair of the skin, cornea and gastrointestinal lining by stimulating cells division and growth.7–9 This repair action has sparked interest in its potential use to treat epithelial injury in acute lung injury (ALI).10 KGF modulates several mechanisms known to be important in alveolar epithelial repair, and has therefore been targeted as a possible therapeutic intervention in ALI. The first study on the protective effect of exogenous KGF in a rodent model with ALI was reported by Panos et al.,11 who found that intratracheal administration of rHuKGF stimulated in vivo alveolar epithelial type 2 (AE2) cell proliferation and reduced hyperoxia-induced lung injury in rats. Subsequently, exogenous KGF has been extensively studied to protect lung tissue against experimental lung injury, including bleomycin,12,13Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia,14 hydrochloric acid,15,16 oleic acid,17 and radiation- and bleomycin-induced lung injury.18 Recently, data from a human ex vivo lung perfusion model of endotoxin-induced lung injury showed that KGF treatment improved lung endothelial and epithelial barrier function and improved the rate of alveolar fluid clearance, hence reducing alveolar oedema.19 Interestingly, supplementation of rHuKGF into emphysematous lungs shows regeneration of alveolar epithelium and capillary endothelium as well as interstitial tissue formation and maintenance.20 In addition, KGF has a tendency to stimulate vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) production in human keratinocytes.21–23 VEGF is an endothelial cell (EC)-specific mitogen and is involved in wound repair, angiogenesis, microvascular permeability and vascular protection. However, its expression in cells is strictly regulated by growth factors.22 These growth factors do not normally stimulate angiogenesis directly, but can modulate angiogenesis by modulating VEGF expression in specific cell types, and thus exert an indirect angiogenic or anti-angiogenic effect.24 Among these, fibroblast growth factor 4 (FGF-4),25 KGF,26 PDGF27 and transforming growth factor β (TGF-β)28 can potentiate VEGF production, which in turn activates the phosphatidylinositide-3′-OH kinase (PI3K)-Akt pathway.29 Particularly in the lung, the PI3K-Akt pathway regulates multiple cellular processes, including alveolar cell proliferation, survival, growth, and motility.30,31 Hence, in this study, we investigated the potential role of exogenous supplementation of KGF in inducing Akt-mediated cell survival pathway by activating the PI3K and its downstream targets in emphysema (Fig. 1).
Hypothesised mechanism of rHuKGF induced Akt-mediated survival signalling in emphysematous condition. Elastase-induced emphysema decreases vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and VEGFR2 levels, thereby altering survival signalling via PI-3K/Akt. Growth factors (such as VEGF, KGF etc.) and survival factors activate receptors that recruit PI3K to the membrane, which in turn activates the kinase Akt. The antagonist PTEN suppresses cell survival by down-regulating (shown by down arrow) the Akt pathway through dephosphorylation. Akt phosphorylates and compromises the function of caspase-9 and Bad, proteins involved in cell death pathways. The hypothesis here shows the deregulation of Akt Mediated Cell Survival in elastase induced emphysema group (X). Various molecules, such as several growth factors, are known to play a key role in lung repair, development, and cell survival. In this case, rHuKGF supplementation (Y) is thought to induce the Akt-Mediated Cell Survival pathway in emphysema, and should be identical to the healthy group (Z). VEGF=vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR2=VEGF receptor; PI3K=Phosphatidylinositide-3′-OH kinase; Akt=Ak-mouse strain; t-thymoma; PTEN=Phosphatase and Tensin homolog on chromosome 10; Bad=Bcl-2-associated death promoter.
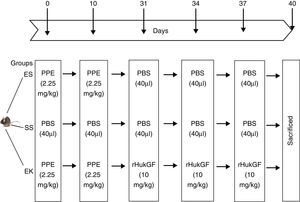
All animal experiments were performed according to institutional guidelines that comply with national and international regulations, and have been approved by the regional government (IAEC, Ministry of Environment and Forests, India). All experimental animal models were prepared as described by Yildirim et al.20 Pathogen-free 8 week old C57BL male mice with a body weight of around 20g were randomly assigned to 3 different experimental groups. Mice were maintained under anaesthesia by isofluran and were given either elastase or rHuKGF/saline by oropharyngeal instillation. The development of the experimental models is described in detail below and Fig. 2:
- -
Control model (saline+saline=SS, n=8): Oropharyngeal instillation was used to deliver 40μl saline at day 1, 10, 31, 34 and 37.
- -
Emphysema model (elastase+saline=ES; n=8): Emphysema was induced by oropharyngeal instillation of porcine pancreatic elastase [PPE; 2.25mg/kg b.w] into lungs of mice at day 1 and 10. However, elastase-treated lungs received saline at day 31, 34 and 37.
- -
Therapeutic model for emphysema (elastase+rHuKGF=EK; n=8): Elastase treated lungs received 10mg/kg b.w of recombinant human keratinocyte growth factor (rHuKGF) per oropharyngeal instillation at day 31, 34 and 37, respectively.
Schematic outline of the experimental setup. On day 0 and day 10, mice received an oropharyngeal instillation of 40μl of saline with or without porcine pancreatic elastase (2.5mg/kg body weight). On day 31, 34 and 37, animals received an oropharyngeal instillation of 40μl of saline or with rHuKGF (10mg/kg body weight). At day 40, animals were sacrificed and lungs removed for analysis by histopathology and molecular biology. ES=Elastase–saline (emphysema group); SS=Saline–saline (healthy group); EK=Elastase–rHuKGF (therapy group).
At day 40, animals were sacrificed by cervical dislocation. Lungs were artificially ventilated and perfused with sterile phosphate buffer saline to remove blood. The right lung was used for histopathology analyses, whereas the left lung tissues were dipped immediately in liquid nitrogen tank and stored at −80°C until used for molecular biology based studies.
Lung FixationRight lungs were fixed by airway instillation with 6% phosphate-buffered paraformaldehyde at a pressure of 20cm fluid column, and were stored overnight in the refrigerator. Dehydration, clearing, and infiltration were performed using standard protocols. The processed tissue slices were placed in a block of molten paraffin and allowed to cool and solidify before slicing. Subsequently, tissue was deparaffinised 3 times by Xylene and rehydrated with different concentrations of ethanol. Using a microtome (Spencers rotary microtome, India), 5μm tissue sections were cut. The sliced tissue sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain.
MorphometryParenchymal destruction: A microscopic point count technique known as destructive index analysis was used to determine the degree of parenchymal destruction.32 A transparent sheet with 83 counting points was laid on an A4-size print of microscopic images from the stained sections. From each lung specimen, an average of 3 different sections were used. From these sections, 3 representative non-overlapping fields were usually selected. Destruction was evaluated by counting the points overlapping alveolar and duct spaces, as discussed by Robbesom et al.33 The percentage of all the points falling into the different categories of destroyed air spaces was computed to reveal the Destructive Index, using the formula [D/(D+N)]×100%, where D=destroyed, and N=normal. Differences in DI between emphysema and therapy groups were calculated with respect to control (100%).
Isolation of Total RNA from the Left Lung Tissue and cDNA SynthesisTo investigate the relative mRNA expression in lung tissue, total RNA was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, New Delhi, India) with a minor modification in the protocol proposed by Muyal et al.34 The quantity and purity of total RNA was determined with Nanodrop (Thermo Scientific, USA), while the quality of total RNA integrity was assessed by analysing 18S and 28S ribosomal RNA on 1.2% ethidium-bromide stained agarose gel electrophoresis. First-strand cDNA was synthesised by introducing equal amounts of RNA (300ng) from each sample in a total reaction volume of 20μl using an Oligo dt primer (Qiagen, New Delhi, India) and Omniscript RT Kit (Qiagen, New Delhi, India) and their respective protocols. The reaction was incubated at 37°C for 1h in Thermoblock TB2 (Biometra, Goettingen, Germany).
Relative mRNA QuantificationReal-time PCR for determining the amplification factor of the target genes (see Table 1) was performed in a 96-well format Stratagene Mx 3005P (Agilent Technologies, Inc., USA) in 20μl total reaction volume using 10μl an QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR Kit (Qiagen, New Delhi, India), 1μl each of sequence-specific forward and reverse oligonucleotide primers (10pmol), 7μl water, and 1μl cDNA. The thermal cycle conditions used for all reactions were as follows: Step 1: 95°C for 15min; at 30 cycles of Step 2 (95°C for 45s), Step 3 (annealing temperature of the sequence-specific oligonucleotide primer, see Table 1, for 35s) and Step 4 (72°C for 45s), followed by step 5 (performed once): 72°C, 5min.
Primer Details: Sequence and Amplicon Size of Target Sequences.
| Gene name | Left primer [5′–3′] | Right primer [5′–3′] | Amplicon length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| VEGFA | CAGGCTGCTGTAACGATGAA | GCATTCACATCTGCTGTGCT | 140 |
| VEGFR2 | ACCAAGGCGACTATGTTTGC | GGGCAAGTCACTTCAATGGT | 160 |
| PI3K | CAAAGCGGAGAACCTATTGC | CCGGTGGCAGTCTTGTTAAT | 138 |
| Akt1 | GTGAAAGAGAAGGCCACAGG | GTCGTGGGTCTGGAATGAGT | 165 |
| Pten | AGACCATAACCCACCACAGC | TACACCAGTCCGTCCCTTTC | 127 |
| Caspase9 | GATGCTGTCCCCTATCAGGA | CGATGTACCAGGAGCCACTT | 151 |
| Bad | GGAGCTTAGCCCTTTTCGAG | GCTTTGTCGCATCTGTGTTG | 166 |
VEGF=vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR2=VEGF receptor; PI3K=Phosphatidylinositide-3′-OH kinase; Akt=Ak–mouse strain; t-thymoma; Pten=Phosphatase and Tensin homolog on chromosome 10; Bad=Bcl-2-associated death promoter.
Total protein was extracted from 100mg WLT using total protein extraction kit (Biochem Life Sciences, New Delhi, India). The VEGF western blot protocol was performed as described by Fehrenbach et al. for VEGFR2.20
Statistical Analysis of Relative mRNA QuantificationmRNA levels of target genes were determined relative to the endogenous control β-actin, according to the formula 2 to the power of delta cycle threshold (2ΔCt), where ΔCt=Ct, reference gene–Ct, test gene. Differences between experimental groups were tested for significance using nonparametric Mann–Whitney test (GraphPad Prism version 4, San Diego, USA). Levels of significance are indicated by *=P<.05; **=P<.01.
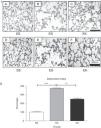
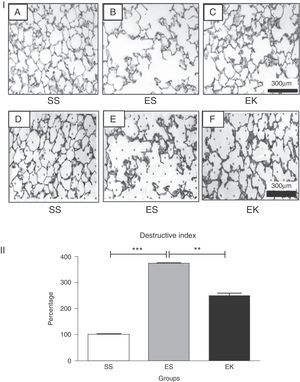
ResultsEffects of rHuKGF on Tissue ArchitectureOropharyngeal instillation of 2.25mg PPE/kg b.w. on 2 occasions (Days 0, 10) resulted in severe pulmonary emphysema, as shown in the photomicrograph generated from the histopathology study (Fig. 3I-B). However, the photomicrograph for rHuKGF-treated emphysematous lungs clearly shows the recovery of lost alveolar septa in the therapy group (EK, Fig. 3I-C), and was comparable to control (SS, Fig. 3I-A). Upon determination of destructive index (DI) of tissue slices from all 3 animal models (Fig. 3I-D–F), emphysematous mouse models showed significantly higher DI values than control models (P<.001). However, the DI was significantly reduced (P<.001) in therapy models i.e. rHuKGF-treated emphysematous lungs of mice (Fig. 3I).
(I) Histopathology of gas exchange area. Haematoxylin and Eosin staining tissue sections show (A) normal histology in control lungs, (B) rarefaction of alveolar septa with enlarged airspaces in emphysema lungs, and (C) increased airspaces with thickened alveolar septa in therapy lungs. All micrographs were taken at identical magnification. Determination of Destructive Index, a transparent sheet with 80 equally distributed points, is laid over the printed digitised image of a HE-stained section (D, E, F). The area surrounding each dot is determined according the criteria described in the ‘Methods’ section. (II) Statistical analysis of the Destructive Index. In contrast to the healthy group (SS), significant increase in percentage Destructive Index was seen in f emphysematous lungs (ES), while the same was reduced upon supplementation of rHuKGF in emphysematous lungs (EK). Graphs indicate mean values with standard deviation. Data were analysed by means of unpaired t-test to test for the effect of rHuKGF and elastase, respectively (Fig. 6I). ES=Elastase–saline (emphysema group); SS=Saline–saline (healthy group); EK=Elastase–rHuKGF (therapy group). *P<.05 versus the respective control group.
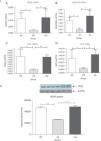
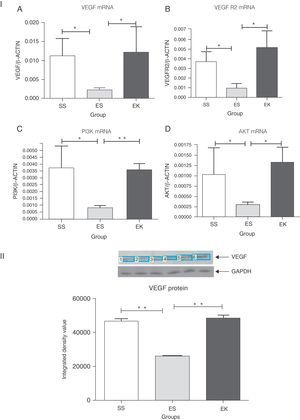
In normal condition, VEGF binds with VEGFR2 to activate the Akt signalling cascade downstream, which in turn mediates cell survival (Fig. 1). To determine whether supplementation of rHuKGF induces the Akt signalling cascade in emphysematous lungs, we evaluated the mRNA expression levels of VEGF, VEGFR 2, PI3K, and Akt, respectively. In contrast to emphysematous lungs, the therapy group (EK) showed good induction in the mRNA levels of VEGF (P<.05), VEGFR2 (P<.03), PI3K (P<.001), and Akt (P<.02), respectively. However, the expression of these genes was markedly more reduced in emphysematous lungs (ES) than in healthy ones (SS) (Fig. 4I). Furthermore, upon validation of VEGF expression at protein level, the western blot analysis for VEGF showed a similar pattern as that observed at mRNA level (Fig. 4II).
(I) Relative mRNA expression of VEGF, VEGFR2, PI3K and Akt (A–D) in whole lung tissue. VEGF, VEGFR2, PI3K and Akt were significantly more down-regulated in the emphysema group (ES) than the control group (SS). In contrast, VEGF, VEGFR2, PI3K and Akt were significantly up-regulated in the therapy group (EK) and were comparable with the control group. The mRNA levels of the target genes were determined relative to the endogenous reference gene β-actin according to the formula 2 to the power of delta cycle threshold (2ΔCt), where ΔCt=Ct, reference gene–Ct, target gene. (II) Densitometry analysis of VEGF Western blot. Densitometry of VEGF western blot revealed a similar pattern as that observed at the mRNA level (Fig. 3II). Graphs indicate mean values with standard deviation. Data were analysed by means of unpaired t-test to test for the effect of rHuKGF and elastase, respectively. ES=Elastase–saline (emphysema group); SS=Saline–saline (healthy group); EK=Elastase–rHuKGF (therapy group). *P<.05 and **P<.01 versus the respective control group.
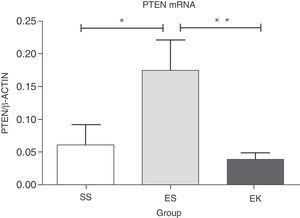
PTEN has been reported as a negative regulator in Akt cell survival pathway. Over-expression of this gene results in deregulation in cell survival signalling. Here, our data shows significantly more up-regulation in mRNA expression of PTEN (P<.04) in emphysematous lungs (ES) than in healthy ones (SS). The beneficial role of rHuKGF in emphysema lungs was further noted when a significant reduction in the mRNA level of PTEN (P<.008) was observed in the ES group, and importantly, was comparable to healthy lungs (Fig. 5).
Relative mRNA expression of Akt pathway antagonist (PTEN) in whole lung tissue. The expression level of PTEN was significantly induced in elastase-challenged lungs in contrast to the therapy group. In the therapy group there was a significant decrease in PTEN expression levels, and these were comparable to control. The mRNA levels of the target genes were determined relative to the endogenous reference gene β-actin according to the formula 2 to the power of delta cycle threshold (2ΔCt), where ΔCt=Ct, reference gene–Ct, target gene. Graphs indicate mean values with standard deviation. Data were analysed by means of unpaired t-test to test for the effect of rHuKGF and elastase, respectively. ES=Elastase–Saline (emphysema group); SS=Saline–Saline (healthy group); EK=Elastase–rHuKGF (therapy group). *P<.05 versus the respective control group.
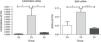
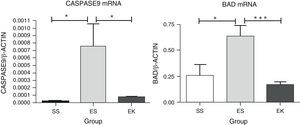
To lose alveolar units, alveolar cell apoptosis would be expected even in porcine pancreatic elastase model of emphysema. To assess apoptosis in our experimental animal models, the mRNA expression of apoptotic markers, i.e., Caspase-9 and Bad, were studied in the Akt pathway. Here, the normalised mRNA levels of Caspase-9 (P<.01) and Bad (P<.01) in emphysematous lung tissue (ES) were significantly more up-regulated than in healthy lungs (SS). However, a promising effect of rHuKGF in emphysema (EK) was observed. In the therapy group (EK), we found more reduced expression levels of Caspase-9 (P<.02) and Bad (P<.0007) than in emphysematous lungs (ES), which indicates that rHuKGF has a tendency to counteract alveolar cell apoptosis (Fig. 6).
Relative mRNA expression of apoptotic markers (Caspase-9 and Bad) in whole lung tissue. The expression level of Caspase-9 and Bad were significantly induced in elastase-challenged lungs in contrast to the therapy group. In the therapy group there was a significant decrease in Caspase-9 and Bad expression levels, and these were comparable to control. The mRNA levels of the target genes were determined relative to the endogenous reference gene β-actin according to the formula 2 to the power of delta cycle threshold (2ΔCt), where ΔCt=Ct, reference gene–Ct, target gene. Graphs indicate mean values with standard deviation. Data were analysed by means of unpaired t-test to test for the effect of rHuKGF and elastase, respectively. ES=Elastase–Saline (emphysema group); SS=Saline–Saline (healthy group); EK=Elastase–rHuKGF (therapy group). *P<.05 versus the respective control group.
The pathogenesis of pulmonary emphysema is not fully understood, although several mechanisms have been proposed, including an imbalance of proteases and antiproteases, chronic inflammation and oxidative stress. In addition to these mechanisms, recent studies suggest another mechanism involved in the development of pulmonary emphysema, which is based on an increase in apoptotic alveolar epithelial and endothelial cells in the lungs.35 However, pulmonary emphysema may also be interpreted as the consequence of a failure of the repair processes of the lung. At present, there are no therapeutic options available that allow the repair of lost alveoli in emphysematous condition. Hence, the induction of alveolar regeneration is still a major challenge in the development of novel therapies for emphysema. Only recently, administration of KGF has proved to be a potent growth factor that possesses both protective as well as curative properties in emphysema.20,36 However, the downstream molecular mechanism governing survival of the alveolar cell has not been explored so far. Hence, in this study, we attempted to demonstrate the potential effect of rHuKGF in the activation of the Akt signalling cascade by the stimulation of VEGF production in emphysematous mice.
Our findings strongly suggested a potential role of rHuKGF in the emphysematous lungs of mice. The prospective role of rHuKGF was well observed in the tissue architecture using the histopathology and morphometry destructive index (DI) analysis. The photomicrographs show the loss of alveolar septa in emphysematous lungs when compared with healthy ones. This loss of alveolar septa was recovered in the therapy group, and was very comparable to healthy groups. Similar findings have also been reported by Fehrenbach et al., where mean intercept length was used to quantify the damage and recovery of alveolar tissue.20 Here, we used destructive index (DI)-based analysis as a tool to quantify both the damage and recovery of alveolar tissue to assess the prospective role of rHuKGF. The average DI value of emphysematous lungs is higher than that of healthy lungs. A similarly high DI value in heavy smokers versus control was also observed by Robbesom et al.33 We believe that the higher DI values may be due to the stringency of our measurement conditions, ruling out possible biases such as suboptimally inflated tissue. Interestingly, the DI values were significantly reduced upon supplementation of rHuKGF in emphysematous lungs. Such reciprocation in DI values may be due to regeneration of alveolar septa walls, which resulted in increased numbers of intact alveolar spaces. After investigating the prospective role of rHuKGF on tissue architecture, we then did the same with rHuKGF in the Akt signalling cascade in emphysematous mice lungs.
As reported by Shiojima and Walsh,37 binding of VEGF to the VEGFR2 activates the Akt signalling cascade, which is important in mediating cell survival, proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis. In addition, KGF has a potential tendency to induce Akt activation, which may be the common underlying mechanism of epithelial cell cytoprotection in different tissues.38,39 In the lung, similar results were obtained by Ray et al., who reported that KGF stimulates the secretion of VEGF, which enhances cytoprotection of endothelial cells by Akt activation.40,41,29 Here, upon supplementation of rHuKGF in emphysematous lungs, the mRNA levels of candidate genes (VEGF, VEGFR2, PI3K and Akt), involved in the Akt signalling cascade were found to be up-regulated to the optimum level observed in healthy condition. In addition, protein expression of VEGF was significantly induced in rHuKGF-received emphysematous lungs. This suggests that rHuKGF has the potential to establish normal lung architecture following loss of alveolar tissues by stimulating VEGF expression in emphysematous lungs. It has been reported earlier that in emphysematous lungs of smokers and patients with COPD, the mRNA and protein expression of VEGF and VEGFR2 was down-regulated.42 This reduction in VEGF/VEGFR expression may lead to endothelial cell apoptosis and emphysematous changes.43–46
In addition, KGF-supplemented emphysematous lungs show an induction in the mRNA levels of PI-3K, which were reduced in emphysematous lungs. Such induction of PI-3K improves the interaction of VEGFR2 with PI-3K for activation of the downstream signalling cascade, thus maintaining cell viability.47 Furthermore, the favourable effect of rHuKGF was also noticed at the mRNA level of Akt. The expression, which was reduced in the emphysema group, was found to be increased after supplementation of rHuKGF in emphysematous lungs. Such induction in the expression of Akt may have multiple beneficial effects on cellular processes, particularly in alveolar cell proliferation and survival. The induction in Akt kinase activity by KGF in a dose- and time-dependent manner has also been discussed by Shenying et al.48 This group concluded that KGF is most effective in maintaining cell viability by stimulating Akt kinase activity before exposure to apoptosis-inducing stimuli.48
We further found that rHuKGF has the potential to minimise over-expression of PTEN and caspase-9 to optimum level in emphysematous lungs. PTEN acts as an antagonist of cell survival by down-regulating the Akt pathway through dephosphorylation,49 and hence inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate [PI (3,4,5) P3]. Over-expression of PTEN in alveolar epithelium has been reported to cause a marked reduction in cell proliferation, a marked increase in apoptosis, and an incomplete functional differentiation, thus negatively regulating the cell survival pathway.50 Similarly, increased expression of caspase-9 has been found to be involved in cell apoptosis and decreased cell survival.51 Here, the mRNA levels of PTEN and caspase-9 in rHuKGF-supplemented emphysematous lungs were down-regulated in contrast to emphysematous lungs. Such favourable changes might be due to suppressed over-expression of PTEN and caspase-948 and induced Akt activation, which favours decreased alveolar cell apoptosis and increased cell survival.
The pro-apoptotic Bad is the primary target of Akt, and Akt phosphorylates Bad, thus rendering it inactive for apoptotic signal.52,53 Datta et al. hypothesised that the PI3K/Akt pathway may lead to Bad phosphorylation and may thereby suppress cell death and promote cell survival.54,55 Particularly in emphysema, Hu et al.56 showed an increased expression of Bad in human airway smooth muscle cells. Here, the expression of Bad was found to be more up-regulated in emphysematous lungs than in healthy ones, which might be due to the failure of Akt-phosphorylating Bad. However, the potential effect of rHuKGF on Bad was further assessed in emphysematous lungs. The expression of Bad was markedly more down-regulated in the therapy group than in emphysematous lungs, and was identical to healthy lungs. These findings again highlight the potential beneficial effects of rHuKGF supplementation in cell survival and maintenance programme.
The data generated from this study strongly suggests that rHuKGF can be a potent molecular medicine, which may induce the endogenous VEGF conferring important survival signals necessary for the maintenance of the normal lung structure.
ConclusionThe findings from this study demonstrate the therapeutic efficacy of rHuKGF to rectify the Akt-dependent cell survival pathway that is deregulated in emphysema. The favourable effects were noticed in the architecture and quantitative analysis of tissue. Furthermore, genes that are associated with the Akt-dependent cell survival pathway regulating alveolar cell survival were constructively expressed in accordance with the exogenous rHuKGF supplementation in emphysematous lungs. Taken collectively, the maintenance of alveolar cell survival in the therapy group due to the amelioration of the Akt-dependent cell survival pathway suggest it could be used to treat emphysema patients. However, more detailed studies are needed.
Authors’ ContributionJai Prakash Muyal participated in the design of the study and performed animal model preparation, statistical analysis, supervised the work and helped draft the manuscript. Dhananjay Kumar carried out RNA isolation from lung tissues, cDNA synthesis and quantitative PCR. Sudhir Kotnala carried out Histopathology, Destructive Index and Western blotting. Vandana Muyal contributed to western blot and manuscript preparation. Amit K Tyagi helped to provide and prepare different animal models.
Conflict of InterestThe authors declare they have no conflict of interest directly or indirectly related to the manuscript contents.
The authors thank Mr. Rashid Ali (Institute of Nuclear Medicine and Allied Sciences, DRDO, New Delhi, India) for helping in handling animals. The authors thank the Department of Science and Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India for financial assistance and express their sincere gratitude to Swedish Orphan Biovitrum (SOBI), Stockholm, Sweden for providing rHuKGF.
Please cite this article as: Prakash Muyal J, Kumar D, Kotnala S, Muyal V, Tyagi AK. El factor de crecimiento queratinocítico humano recombinante induce la progresión de la supervivencia celular mediada por Akt en ratones enfisematosos. Arch Bronconeumol. 2015;51:328–337.