Nitric oxide (NO) levels can be measured at proximal (maximum airway NO flux [J′awNO]) and distal (alveolar NO concentration [CANO]) levels. Four inflammatory patterns have been described in asthmatic individuals, although their relevance has not been well established. The objective was to determine J′awNO and CANO in order to establish four inflammatory categories in asthmatics.
Material and methodsCross-sectional study of a sample consisting of healthy and asthmatic children. Exhaled NO was determined at multiple flows. J′awNO and CANO were obtained according to the two-compartment model. The asthma control questionnaire (ACQ) and spirometry were administered to asthmatic children. Patients were categorized as type I (normal J′awNO and CANO), type II (elevated J′awNO and normal CANO), type III (elevated J′awNO and CANO) and type IV (normal J′awNO and elevated CANO). Correlation between FENO,50, J′awNO and CANO was analyzed using Spearman's R Correlation Test. Analysis of variance and paired comparisons were performed using the Bonferroni correction.
ResultsOne hundred sixty-two children were studied, of whom 49 (32.23%) were healthy controls and 103 (67.76%) asthmatics. In the control subjects, FENO,50 (ppb) (median and range) was 11.5 (1.6–27.3), J′awNO (pl/s) was 516 (98.3–1470) and CANO (ppb) was 2.2 (0.1–4.5). Forty-four (42.7%) of the asthmatic participants were categorized as type I, 41 (39.8%) as type II, 14 (13.5%) as type III and 4 (3.88%) as type IV. Good correlation was observed between J′awNO and FENO,50 (r=0.97). There was no association between J′awNO and CANO. FEV1/FVC decreased significantly in type III (mean 79.8±7.5). Morbidity was significantly higher in types III and IV.
ConclusionsNormal values obtained are similar to those previously reported. Asthmatics with high CANO showed higher morbidity. No correlation was found between proximal and distal inflammation.
El óxido nítrico (NO) puede medirse a nivel proximal (flujo máximo NO en vía aérea [J¿awNO]) y distal (concentración alveolar de NO [CANO]). Se han descrito 4 patrones inflamatorios en asmáticos, aunque su relevancia no ha sido bien establecida. El objetivo ha sido determinar el J¿awNO y la CANO para establecer 4 categorías inflamatorias en asmáticos.
Material y métodosEstudio transversal de una muestra de niños sanos y asmáticos. Determinación de NO exhalado a flujos múltiples. De acuerdo con el modelo bicompartimental se obtuvieron la CANO y el J¿awNO. En asmáticos se realizó cuestionario de control de asma (CAN) y espirometría forzada. Categorización de pacientes en tipo i (J¿awNO y CANO normal), tipo ii (J¿awNO elevado y CANO normal), tipo iii (J¿awNO y CANO elevados) y tipo iv (J¿awNO normal y CANO elevado). Estudio de correlación entre FENO,50, J¿awNO y CANO mediante R de Spearman. Análisis de la varianza y comparaciones pareadas, mediante corrección post hoc de Bonferroni.
ResultadosSe estudiaron 162 niños: 49 (32,23%) controles sanos y 103 (67,76%) asmáticos. Se excluyeron 10 niños, 4 (2.4%) porque las determinaciones fueron incorrectas y 6 (3,7%) porque las determinaciones no siguieron el modelo lineal (valores de CANO negativos). En controles la FENO,50 (ppb) (mediana y rango) fue 11,5 (1,6–27,3), J¿awNO (pl/s) 516 (98,3–1.470) y CANO (ppb) 2,2 (0,1–4,5). De los asmáticos, 44 (42,7%) se categorizaron en tipo i, 41 (39,8%) en tipo ii, 14 (13,5%%) en tipo iii y 4 (3,88%) en tipo iv. Buena correlación entre J¿awNO y FENO,50 (r=0,97). No hubo asociación entre J¿awNO y CANO. Disminución significativa de FEV1/FVC en tipo iii (media 79,8±7,5). La morbilidad fue significativamente superior en tipos iii y iv.
ConclusionesLos valores de normalidad obtenidos son similares a los previamente publicados. Los asmáticos con CANO elevado presentaron mayor morbilidad. No hay correlación entre inflamación proximal y distal.
Asthma is the most common chronic disease of the lower airways in childhood. It presents with bronchial hyperreactivity and variable airflow obstruction, and is characterized by episodes of wheezing, cough and difficulty in breathing.1
International guidelines for the management of asthma1,2 classify the disease according to its severity or level of control, and do not consider the degree of airway inflammation. However they do suggest studies to evaluate whether monitoring inflammation could improve disease management in clinical practice.3,4 In this regard, there is evidence indicating that asthma control is correlated with the degree of inflammation, and that symptoms are more severe when this reaches the most distal lung compartments.5,6
A number of studies have focused on differentiating between the proximal origin of the inflammation (measured indirectly via the fractional exhaled nitric oxide [NO] at a flow of 50ml/s: FENO,50, and maximum airway NO flux: J′awNO) and/or distal inflammation (measured by the alveolar NO concentration: CANO) in children7 and adults with asthma.8 Elevated CANO values have been related with poorly controlled asthma in children7 and adults, persistent nocturnal symptoms,9 poorly controlled severe asthma10 and disease refractory to treatment,11 as well as with the risk of exacerbation.12 However, few studies in adults have attempted to classify patients according to the location and/or spread of the inflammation,13 and even fewer have done so by determining NO in children.14
One such study, conducted by Puckett et al.14 reported distinct clinical patterns of asthma when asthmatics were classified into 4 inflammatory types based on CANO and J′awNO measurements. Children with elevated CANO values had poorer asthma control and higher morbidity, regardless of atopy, inhaled glucocorticoid therapy, and lung function. Nevertheless, the utility of this compartmentalization in routine practice remains to be clarified, and the technique has not yet been standardized.
The primary objective of this study was to define four inflammatory phenotypes in asthmatic children by determining nitric oxide in the proximal (J′awNO) and distal or alveolar (CANO) airways, and to relate these with their clinical manifestations.
Materials and MethodsThis study was approved by the Ethics and Research Committee of the University Hospital where it was conducted. Informed consent was obtained in all cases, and permission to use the data was granted by the parents and/or guardians and the child when required under current legislation due to the child's age.
This was a cross-sectional study with prospective data collection from a consecutive sample of children aged between 6 and 16 years old diagnosed with asthma according to GINA 2012.2 Patients were screened in Pediatric Respiratory Medicine outpatient clinics between January and August 2012. Asthmatic patients with no background treatment and those on inhaled glucocorticoids (IGC) were included. A sample of healthy children of the same age was also recruited during the same period using the same methodology.
Patients with asthma exacerbation or respiratory infection at the time of the visit were excluded. Also excluded were those who declined to participate, those who did not meet the inclusion criteria, those who did not cooperate in performing the required techniques, and those with associated diseases or morbidities.
Asthma severity and level of control were classified according to GINA 2012.2 Allergic rhinitis was defined as signs and symptoms consistent with this diagnosis, allergen-specific immunoglobulin E in blood (class III or higher) and/or skin prick test positive for 1 or more airborne allergens; food allergy as signs and symptoms consistent with this diagnosis and allergen-specific IgE in blood (class III or higher); and atopic dermatitis as signs and symptoms consistent with this diagnosis.2,15
Prior to the forced spirometry, all study patients underwent determination of single-breath and multiple flow (50, 100 and 200ml/s) exhaled NO using an online system and stationary chemiluminescent analyzer (Eco Medics AG-CLD 88 sp- Switzerland) with DENOX 88 flow adaptors, following European Respiratory Society (ERS) and American Thoracic Society (ATS) recommendations published in 2005.16 The tests were performed in triplicate, and the mean value of the three measurements was calculated for each corresponding flow rate with less than 10% variability.
The Tsoukias and George two-compartment model and equation17 was applied to calculate the CANO and J′awNO. Although other more complex models have since been developed, we did not use them for this study.18–20 The flow rate and volume were calibrated daily, and the NO was calibrated monthly.
All study asthmatics underwent forced spirometry (MasterLab. Version 5.3. Viasis®, Wuerzburg, Germany) as per ATS/ERS recommendations.21 Zapletal equations22,23 were used to calculate the percentage of normal.
The patient's medical history was taken and physical examination carried out; parents (of children aged under 9 years) or the patients themselves (children aged over 9 years) were also asked to complete the asthma control questionnaire (CAN).24 The CAN questionnaire consists of nine questions related to symptoms presented in the past 4 weeks, with four possible answers (0–4) each and a final score ranging between 0 (best control) and 36 points (worst control).
The following are considered the cut-off points for normal values according to the literature: ≤25ppb for FENO,5025,26; ≥80% for the relative value of FEV1 (% predicted),1,2 and a score of less than 8 points on the CAN questionnaire.24 In the case of CANO and J′awNO, the cut-off point for normal values was considered to be the upper limit calculated for the group of healthy children included in this study.
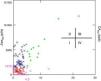
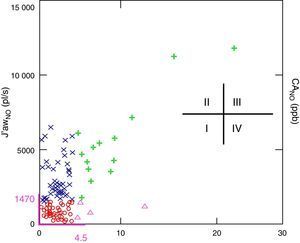
Four inflammatory types were established in the asthmatic group based on CANO and J′awNO: type I (normal J¿awNO and CANO), type II (elevated J¿awNO and normal CANO), type III (elevated J¿awNO and CANO) and type IV (normal J¿awNO and elevated CANO).
The quantitative variables analyzed were age (years), weight (kg), height (cm), determination of NO (ppb) at three expiratory flows (FENO,50, FENO,100, FENO,200), CANO (ppb) and J′awNO (pl/s). The following were also analyzed in the asthmatic group: score obtained in the CAN questionnaire (points), forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1 as a percentage of predicted), forced vital capacity (FVC as a percentage of predicted), FEV1/FVC ratio (as a percentage of predicted) and forced expiratory flow between 25% and 75% of FVC (FEF25–75 as a percentage of predicted).
The following qualitative variables were analyzed: sex, allergic rhinitis, sensitization to respiratory allergens, atopic dermatitis, food allergies, severity and level of asthma control, treatment received and morbidity presented in the past month defined as the occurrence of at least one exacerbation, including those that required oral glucocorticoids, visits to the emergency department and/or hospital admission in the previous 4 weeks.
Correlation between FENO,50, J′awNO and CANO was analyzed using Spearman's R Correlation Test. Since usual treatment with IGC can act as a confounding factor in FENO,50, J¿awNO and CANO values, statistical analysis was adjusted for the IGC variable by multiple regression analysis.
Descriptive analysis of the variables was carried out for each inflammatory type, and clinical characteristics were compared using the χ2 test for qualitative variables: sex, personal atopy, treatment, level of control, FEV1≥80%, CAN<8, and morbidity. The Kruskal–Wallis test was used for the remaining variables. Analysis of variance and paired comparisons between the inflammatory types were performed using the Bonferroni post hoc correction.
The sample size was estimated based on predicted correlation coefficients according to data published in the literature.7,9,14
An alpha level of 5% was established in all cases. Statistical analysis was performed using statistical package SYSTAT 9.0™.
ResultsA cohort made up of 162 children was studied. All measurements were correctly performed in 158 (97.5%) patients: 49 (32.2%) healthy controls, 23 (15.1%) untreated asthmatics and 80 (52.5%) asthmatics on IGC. Four children (2.4%) in whom the NO determinations were not correctly performed were excluded. Of those included, the NO measurements did not follow the linear model (negative CANO values) in six cases (all asthmatics), so they were also excluded. There were no significant differences in age, weight, FENO,50 or forced spirometry with respect to the study groups.
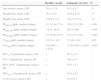
There were no significant differences in age, weight, height or sex between the healthy control group and the asthmatic group (P>.05) (Table 1).
Descriptive Characteristics of Healthy and Asthmatic Study Patients.
| Healthy (n=49) | Asthmatic (n=103) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean±SD | 10.1±1.9 | 10.5±2.7 | .9 |
| Weight (kg), mean±SD | 38±13.9 | 41.6±13.9 | .17 |
| Height (cm), mean±SD | 139.4±13.1 | 144.3±15.4 | .13 |
| FENO,50 (ppb), median (range) | 11.5 (1.6–27.3) | 35.4 (3.5–234) | <.001 |
| FENO,100 (ppb), median (range) | 7.6 (1–18.8) | 20 (3–200) | <.001 |
| FENO,200 (ppb), median (range) | 4.7 (0.96–10.7) | 12.3 (2.7–187) | <.001 |
| CANO (ppb), median (range) | 2.2 (0.1–4.5) | 2.7 (0.1–24) | .022 |
| J′awNO (pl/s), median (range) | 516 (98.3–1.470) | 1.703 (120–11.805) | <.001 |
| FEV1 (% predicted), mean±SD | x | 99.3±13 | – |
| FVC (%predicted), mean±SD | x | 100±9.7 | – |
| FEV1/FVC (%predicted), mean±SD | x | 83.9±7.1 | – |
| FEF25–75 (%predicted), mean±SD | x | 82.3±22 | – |
| CAN (score), mean±SD | x | 6.8±6.5 | – |
CAN: asthma control questionnaire; CANO: alveolar nitric acid concentration; FEF25–75: forced expiratory flow between 25% and 75% of the FVC; FENO,100: fractional exhaled nitric oxide at a flow rate of 100ml/s; FENO,200: fractional exhaled nitric oxide at a flow rate of 200ml/s; FENO,50: fractional exhaled nitric oxide at a flow rate of 50ml/s; FEV1: forced expiratory volume in the first second; FVC: forced vital capacity; J¿awNO: maximum airway nitric oxygen flux; NO: nitric oxide; pl/s: picoliters/second; ppb: parts per billion; SD: standard deviation.
In the healthy control group, FENO,50 (ppb) (median and range) was 11.5 (1.6–27.3), J¿awNO (pl/s) 516 (98.3–1470) and CANO (ppb) 2.2 (0.1–4.5) (Table 1).
In the case of CANO and J′awNO, the normal cut-off point was considered to be the upper limit calculated for the group of healthy children (<4.5ppb for CANO and <1470pl/s for J′awNO).
A close association was observed between J′awNO and FENO,50 (r=0.97; P<.05) and also (although to a lesser extent) between J′awNO and FENO,100 (r=0.62) and J′awNO and FENO,200 (r=0.4). However, no significant association was found between CANO and J′awNO (r=−0.001) or between CANO and FENO,50 (r=−0.002). Statistical analysis was adjusted for usual treatment with IGC by multiple linear regression; no differences were found in the results obtained. Starting from this point, and based on the upper limits for J′awNO and CANO in the group of healthy subjects, asthmatic children (n=103) were classified into the four abovementioned inflammatory types (Figure 1). In the asthmatic group, the most common type was type I (n=44; 42.7%), followed by type II (n=41; 39.8%), while type III and IV inflammatory patterns were much less frequent (n=14; 13.5% and n=4; 3.8%, respectively).
Exhaled nitric oxide categories based on the upper threshold for J′awNO and CANO obtained in the group of healthy children. J′awNO vs CANO scatterplot. Normal J′awNO<1470 (pl/s) and normal CANO<4.5 (ppb) (in purple). Type I (circle): Normal J′awNO and CANO; Type II (x): elevated J′awNO and normal CANO; Type III (cross): elevated J′awNO and CANO; Type IV (triangle): normal J′awNO and elevated CANO.
There were no gender or age differences in the four inflammatory types (Table 2).
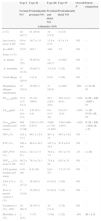
Characteristics of the Four Inflammatory Categories Defined According to the J′awNO and CANO Values Obtained in Healthy Children.
| Type I | Type II | Type III | Type IV | Overall P | Paired comparison | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal NO | Predominantly proximal NO | Proximal and distal NO | Predominantly distal NO | |||
| Asthmatics (103) | ||||||
| n (%) | 44 (42.7) | 41 (39.8) | 14 (13.5) | 4 (3.8) | ||
| Age (years), mean±SD | 9.9±0.41 | 10.7±1.9 | 11.9±0.73 | 9.3±1.4 | NS | – |
| Sex (M/F) | 27/17 | 24/17 | 10/4 | 3/1 | NS | – |
| Atopy, n (%) | ||||||
| A. rhinitis | 33 (75) | 36 (87.8) | 12 (85.7) | 4 (100) | NS | – |
| A. dermatitis | 14 (31.8) | 20 (48.7) | 3 (21.4) | 1 (25) | NS | – |
| Food allergy | 9 (20.4) | 1 (2.4) | 0 (0) | 2 (50) | NS | – |
| Respiratory allergen sensitization | 31 (70.4) | 39 (95.1) | 13 (92.8) | 4 (100) | .009 | I<II, III, IV |
| FENO,50(ppb) | 15.4 (3.5–54.1) | 53 (19–109.6) | 95.7 (28.6–234) | 36.5 (14.5–44.4) | <.001 | II, III>I/III >II/III>IV |
| CANO(ppb) | 1.8 (0.1–4.4) | 2.45 (0.2–4.4) | 6.9 (4.7–24) | 5.6 (4.7–12.9) | <.001 | I<III, IV/II<III, IV |
| J′awNO(pl/s) (median and range) | 684 (120–2.348) | 2.651 (1.515–6.475) | 4.894 (1.770–11.805) | 1.003 (466–1.445) | <.001 | II, III>I/III>II/II, III>IV |
| FEV1(%) | 102±13.1 | 96.1±12.4 | 96.7±14 | 98.5±14.2 | NS | – |
| FVC (%) | 100±9.6 | 98.8±10.2 | 101.5±10.5 | 97.4±6.8 | NS | – |
| FEV1/FVC (%) | 85.8±6.3 | 82.3±7.5 | 79.8±7.5 | 85.3±7.9 | .03 | I>III |
| FEF25–75(%), mean±SD | 88.2±22.3 | 76.3±21.3 | 73.8±24 | 82.5±25 | NS | – |
| CAN (points), median and range | 4 (0–29) | 6 (0–26) | 6 (0–27) | 7.5 (3–17) | NS | – |
| CAN≥8, n (%) | 12 (27.2) | 16 (39.2) | 6 (42.8) | 2 (50) | NS | |
| Poor or partial control, n (%) | 7 (15.9) | 12 (29.2) | 6 (42.8) | 1 (25) | NS | – |
| Treatment, n (%) – IGC | 38 (86.3) | 29 (70.7) | 10 (71.4) | 3 (75) | NS | – |
| Morbidity, n (%) | 2 (4.5) | 7 (17) | 7 (50) | 1 (25) | .001 | III>I, II |
A. dermatitis: atopic dermatitis; A. rhinitis: allergic rhinitis; CAN: asthma control questionnaire; CANO: alveolar nitric acid concentration; FEF25–75: forced expiratory flow between 25% and 75% of vital capacity; FENO,50: fractional exhaled nitric oxide at a flow rate of 50ml/s; FEV1: forced expiratory volume in the first second; FVC: forced vital capacity; IGC: inhaled glucocorticoids; J¿awNO: maximum airway nitric oxygen flux; M/F: male/female; Morbidity: presence of at least one exacerbation including those requiring oral corticosteroids, visits to the Emergency Department or admission, in the past 4 weeks; NO: nitric oxide; pl/s: picoliters/second; ppb: parts per billion;. SD: standard deviation.
With respect to atopy, significantly lower sensitization (positive skin prick test) to the respiratory allergens studied was found (P=.01) in the group of asthmatics included in phenotype I (70.4%) compared to the rest (95.1%, 92.8% and 100% for phenotypes II, III and IV, respectively).
There were no differences in terms of background treatment with IGC in the four groups (86.3%, 70.7%, 71% and 75% for types I, II, III and IV, respectively).
The differences amongst the 4 inflammatory phenotypes with respect to J′awNO, CANO and FENO,50 are shown in Table 2.
The asthmatic group was, overall, a group of children with mild, well-controlled asthma (median CAN score=5; range 0–29) and normal baseline spirometry (mean FEV1=99.7%; mean FEV1/FVC=85%). With respect to lung function (baseline forced spirometry), the FEV1/FVC ratio was significantly lower in phenotype III (mean 79.8±7.5) compared to type I (mean 85.8±6.3). No significant differences in FEV1/FVC ratio were found in the rest of the phenotypes. Other spirometric variables studied did not differ in the 4 groups (Table 2). Taking into account the number of participants included in type IV (only 4), a new analysis was carried out, combining groups III and IV as a group with high CANO; no differences were found in the results obtained.
The percentage of patients with FEV1<80% (indicative of poor control)2 was 4.5%, 7.3%, 7.1% and 25% for types I, II, III and IV respectively. Although fewer patients in the low CANO group (phenotypes I and II) had an FEV1<80 compared to those in the elevated CANO group (phenotypes III and IV) (6.2% vs 11.1%), the differences were not significant (P=.42).
Similarly, no differences were found (P=.5) in the CAN questionnaire score in the 4 categories studied (4, 6, 6 and 7.5 for phenotypes I, II, III, and IV, respectively). No significant differences were found on combining the low CANO (phenotypes I and II) and high CANO (phenotypes III and IV) groups. The percentage of patients with CAN≥8, indicative of poor control,21 was 27.2%, 39.2%, 42.8% and 50% for types I, II, III and IV, respectively. There were no differences (P=.35) between patients included in the low CANO (phenotypes I and II) and elevated CANO (phenotypes III and IV) groups (33% vs 44.4%).
The percentage of patients with partially or poorly controlled asthma2 was 15.9%, 29.2%, 42.8% and 25% for phenotypes I, II, III and IV, respectively. The differences were not significant (P=.15). There were no differences either (P=.35) in the degree of control when low CANO groups (phenotypes I and II) were compared to elevated CANO groups (phenotypes III and IV) (22.3% vs 38.8%).
Significant differences (P=.001) were found in morbidity in the past month amongst the inflammatory phenotypes. The percentage of patients with at least 1 exacerbation, including having to visit the emergency department and/or admission for asthma in the past month, was 4.5%, 7%, 50% and 25% for phenotypes I, II, III and iv respectively. This difference was significant between phenotype III and phenotypes I (P<.001) and II (P=.017) (Table 2). As previously shown, combining the elevated CANO (phenotypes III and IV) and low CANO (phenotypes I and II) groups, the morbidity recorded was significantly higher in patients with elevated CANO values.
DiscussionIn line with the findings of other authors,7,14,27 our cohort showed no association between proximal (J′awNO) and distal (CANO) NO; however, J′awNO and FENO,50 were strongly associated. With respect to lung function, the FEV1/FVC ratio was significantly lower in phenotype III (mean 79.8±7.5) than in phenotype I (mean 85.8±6.3), which is consistent with published studies.14 The morbidity presented in the past month was higher in phenotype III compared to phenotypes I (P<.001) and II (P=.017). Finally, the normal values found for J′awNO and CANO were similar to those published in the literature.
Our failure to find an association between J′awNO and CANO indicates that these two measurements provide independent information. Moreover, the strong association found between J′awNO and FENO,50 indicates that a flow rate of 50ml/s is adequate for determining the proximal NO. J′awNO did not appear to provide any additional information, so the determination of FENO,50 could be sufficient to characterize proximal inflammation. Proximal inflammation was not consistently associated with the level of control or with the risk of exacerbation in children.28,29 One possible explanation for these findings is the confounding influence of factors such as IGC treatment or atopy, which affect proximal NO. In our sample, asthmatic patients were included consecutively regardless of the treatment they received. Statistical analysis was therefore adjusted for IGC treatment by multiple regression analysis; no differences were found in the results. Most asthmatics (80/103) received daily treatment with low or medium doses of IGC (fluticasone 100 or 200μg/day); there were no differences in the use of IGC in the 4 inflammatory types.
On the basis of these findings, 4 inflammatory types were established: type I (normal NO), type II (predominantly proximal NO), type III (proximal and distal NO) and type IV (predominantly distal NO) (Table 2). In our study, as in other published series,14 the phenotypes without distal inflammation (phenotypes I and II) were the most common (82.5%).
In forced spirometry, the FEV1/FVC ratio was significantly lower in phenotype III compared to phenotype I. Although the percentage of patients with FEV1<80% (indicative of poor control)2 in the low CANO group (phenotypes I and II) was lower than those in the elevated CANO group (phenotypes III and IV) (6.2% vs 11.1%), no differences were found. There were no differences amongst the 4 groups for the other spirometric variables studied (Table 2).
The percentage of patients with at least 1 exacerbation, including the need for oral glucocorticoids, visits to the emergency department and/or admission in the last month, was significantly higher in phenotype III compared with phenotypes I (P<.001) and II (P=.017) (Table 2). As mentioned above, the recorded morbidity was higher in patients with elevated CANO when groups III and IV (elevated CANO) and groups I and II (low CANO) were combined. These findings, which are consistent with the literature,6,14 support the appearance of distinct inflammatory types based on the location and spread of NO, and suggest that measuring distal inflammation could be complementary to spirometry and/or the determination of proximal NO for assessing disease control. This association between elevated CANO and higher morbidity in the past month could be due to inflammation in the more distal territory, which could contribute to airflow limitation.30 However, some authors31,32 did not find any association between CANO, level of control and disease severity in children and adults with stable asthma, although other studies have found abnormal FENO,50 and normal CANO during exacerbations. In this respect, Mahut et al.33 have stated that the usefulness of alveolar NO in asthma has yet to be determined.
No differences were found between patients in the low CANO and elevated CANO phenotypes as regards CAN questionnaire score≥8 (indicative of poor control),24 in contrast to the findings of other authors14 and the Asthma control test.34 We chose the CAN questionnaire for our study, as it is currently the only questionnaire validated in the Spanish pediatric population.24 Likewise, although the proportion of well-controlled asthmatics was higher in phenotypes I and II, and the proportion of poorly or partially controlled asthmatics was higher in phenotypes III and IV, no differences were found in the level of control when low CANO types were compared with elevated CANO types. The fact that differences were found on analyzing the qualitative variable “morbidity” and not on analyzing the CAN could be due to the absence of an item regarding use of oral glucocorticoids during exacerbations in the questionnaire. Moreover, completing the questionnaire could have underestimated the symptomatology presented in the last month if we compare it with the objective measure of the number of admissions, number of visits to the emergency department (collected from medical reports) or use of oral glucocorticoids (data collected through prescription use).
We should point out, however, that our study cohort of asthmatics was generally a group with mild, well-controlled asthma and normal baseline spirometry. The inclusion of more severe asthmatics could perhaps have modified our results.
Like other authors,14 we found differences in atopy amongst phenotypes. The group of asthmatics included in phenotype I (70.4%) were found to have lower sensitization (positive skin prick test) to the respiratory allergens studied, compared with the others (types II, III and IV) (P=.01).
Unlike other published series,14 no differences were found as regards IGC treatment. According to some studies,11,35 IGC therapy does not appear to affect CANO or improve control in asthmatics with elevated CANO values. CANO and asthma control did, however, respond to systemic corticosteroids and to leukotriene antagonists. Although well-designed longitudinal studies are needed to determine the best therapy for asthmatics with elevated CANO, these findings suggest that confirming the presence of distal inflammation could help in choosing treatment in these patients.
Since significant differences have been described in CANO measurements according to the methodology used,36 CANO and J′awNO were determined in healthy controls using the methodology described above.17 The results obtained for CANO (median 2.2ppb; range 0.1–4.5) and J′awNO (median 516pl/s; range 98.33–1470pl/s) were similar to those described by other authors.7,14,27,37 In contrast, Mahut et al.6 found more elevated CANO levels (mean 4.2±2ppb) and lower J′awNO levels (mean 320±130pl/s). These differences could be explained by the different populations and/or methodology used.36
One of the major limitations of this study was the lack of a standardized technique for determination of CANO and J′awNO. The two-compartment model17 has some limitations: the compartments proposed may not be completely airtight, and the measurements obtained may vary according to the flow rate selected. The selection of flows used depends on the patients’ lung capacity and extent of cooperation.27
ConclusionsThe main outcome of this study was that inflammatory types with elevated alveolar NO values (types III and IV) have greater morbidity. These findings support the appearance of distinct inflammatory types based on the location and/or spread of NO, and suggest that measuring distal inflammation by CANO could complement spirometry and/or determination of proximal NO by J′awNO or FENO,50 in the assessment of disease control.
Finally, the normal values found for both J′awNO and CANO were similar to those published previously in the literature.
Conflict of InterestsThe authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in drafting this manuscript.
We thank all the patients who participated and their families, as well as all the staff of the Pediatric Respiratory Medicine Section for their cooperation and dedication in conducting this study.
Please cite this article as: Corcuera-Elosegui P, Sardón-Prado O, Aldasoro-Ruiz A, Korta-Murua J, Mintegui-Aramburu J, Emparanza-Knorr JI, et al. Patrones inflamatorios en niños asmáticos basados en la determinación de óxido nítrico alveolar. Arch Bronconeumol. 2015;51:279-284.