Pulmonary hypertension is a hemodynamic disorder defined by abnormally high pulmonary artery pressure that can occur in numerous diseases and clinical situations. The causes of pulmonary hypertension are classified into 5 major groups: arterial, due to left heart disease, due to lung disease and/or hypoxemia, chronic thromboembolic, with unclear and/or multifactorial mechanisms. This is a brief summary of the Guidelines on the Diagnostic and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the Spanish Society of Pulmonology and Thoracic Surgery. These guidelines describe the current recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of the different pulmonary hypertension groups.
La hipertensión pulmonar es un trastorno hemodinámico definido por el aumento anómalo de la presión arterial pulmonar, que puede presentarse en numerosas enfermedades y situaciones clínicas. Las causas de hipertensión pulmonar se clasifican en 5 grandes grupos: arterial, debida a cardiopatía izquierda, debida a enfermedad pulmonar y/o hipoxemia, tromboembólica crónica y de mecanismo no establecido y/o multifactorial. El presente documento expone de forma resumida las recomendaciones de la Guía de Diagnóstico y Tratamiento de la Hipertensión Pulmonar de la Sociedad Española de Neumología y Cirugía Torácica. En dicha guía se presentan las pautas actuales de diagnóstico y tratamiento de los distintos grupos de hipertensión pulmonar.
This document is a summary of the recommendations of the Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension prepared by the Spanish Society of Pulmonology and Thoracic Surgery,1 that was drawn from the clinical practice guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Respiratory Society.2 For more details, please refer to the original guidelines,1 (https://issuu.com/separ/docs/normativa_70?e=3049452/44188557). The levels of evidence and class of recommendation used are set out in Table 1.
Levels of Evidence and Class of Recommendation Used in the Guidelines.
| Levels of evidence | |
| A | Data derived from multiple randomized clinical trials or meta-analysis |
| B | Data derived from a single randomized or large non-randomized studies |
| C | Consensus of expert opinion, small or retrospective studies, or patient registries |
| Classes of recommendation | |
| I | Evidence and/or general agreement that a particular treatment or procedure is beneficial, useful, or effective |
| II | Conflicting evidence and/or diverging opinions about the usefulness/effectiveness of a given treatment or procedure |
| IIa | Evidence/opinion tends toward usefulness/effectiveness |
| IIb | Usefulness/effectiveness is less supported by evidence/opinion |
| III | Evidence or general agreement that a particular treatment or procedure is not useful/effective and, in some cases, may be harmful |
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a hemodynamic, pathophysiological disorder defined by elevated mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP) ≥25mmHg, measured by right heart catheterization (RHC).2 PH can occur in various clinical processes, that can be classified into 5 groups (Table 2).
Classification of Pulmonary Hypertension (European Society of Cardiology/European Respiratory Society, 2015).
| 1. Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) |
| 1.1. Idiopathic |
| 1.2. Hereditary |
| 1.2.1. BMPR2 mutation |
| 1.2.2. Other mutations |
| 1.3. Induced by drugs and toxins |
| 1.4. Associated with: |
| 1.4.1. Connective tissue disease |
| 1.4.2. HIV infection |
| 1.4.3. Portal hypertension |
| 1.4.4. Congenital heart disease |
| 1.4.5. Schistosomiasis |
| 1′. Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease and/or pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis |
| 1′.1. Idiopathic |
| 1′.2. Hereditary |
| 1′.2.1. EIF2AK4 mutation |
| 1′.2.2. Other mutations |
| 1′.3. Induced by drugs, toxins, and radiation |
| 1′.4. Associated with: |
| 1′.4.1. Connective tissue disease |
| 1′.4.2. HIV infection |
| 1″. Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn |
| 2. Pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease |
| 2.1. Left ventricular systolic dysfunction |
| 2.2. Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction |
| 2.3. Valvular disease |
| 2.4. Congenital/acquired obstruction of the left ventricular inflow/outflow tract and congenital cardiomyopathy |
| 2.5. Congenital or acquired pulmonary vein stenosis |
| 3. Pulmonary hypertension due to respiratory disease and/or hypoxemia |
| 3.1. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| 3.2. Diffuse interstitial lung disease |
| 3.3. Other lung diseases with mixed restrictive and obstructive pattern |
| 3.4. Sleep disordered breathing |
| 3.5. Alveolar hypoventilation |
| 3.6. Chronic exposure to high altitudes |
| 3.7. Lung development disorders |
| 4. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension and other pulmonary artery obstructions |
| 4.1. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension |
| 4.2. Other pulmonary artery obstructions |
| 4.2.1. Angiosarcoma |
| 4.2.2. Other intravascular tumors |
| 4.2.3. Arteritis |
| 4.2.4. Congenital pulmonary artery stenosis |
| 4.2.5. Parasitosis (hydatid disease) |
| 5. Pulmonary hypertension with unclear and/or multifactorial mechanisms |
| 5.1. Hematologic diseases: hemolytic anemia, myeloproliferative disorders, splenectomy |
| 5.2. Systemic diseases: sarcoidosis, pulmonary histiocytosis, lymphangioleiomyomatosis, neurofibromatosis |
| 5.3. Metabolic disorders: glycogen storage disease, Gaucher's disease, thyroid disorders |
| 5.4. Other: pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy, fibrosing mediastinitis, chronic renal failure (with/without dialysis), segmental pulmonary hypertension |
Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) is the main tool for the early detection and screening of PH. The probability of PH according to TTE findings is shown in Table 3.
Probability of Pulmonary Hypertension Based on Transthoracic Echocardiography Results.
| Low | TRV ≤2.8m/s or not measurable |
| Intermediate | TRV 2.9–3.4m/s; or VRT ≤2.8m/s or not measurable, in the presence of other ultrasonographic signs of pulmonary hypertension |
| High | TRV >3.4m/s; or TRV 2.9–3.4m/s, in the presence of other ultrasonographic signs of pulmonary hypertension |
| * Other echocardiographic signs that indicate pulmonary hypertension: |
| Ventricles |
| Basal RV/LV ratio >1.0 |
| Flattening of interventricular septum (LV eccentricity index >1.1 in systole or diastole) |
| Pulmonary artery |
| Doppler acceleration time of the RV outflow tract <105ms and/or mesosystolic notch |
| Pulmonary regurgitation velocity in protodiastole >2.2m/s |
| PA diameter >25mm |
| Inferior vena cava and right atrium |
| Inferior vena cava diameter >21mm with decreased inspiratory collapse (<50% in deep inspiration or <20% in normal inspiration) |
| Right atrium area (end systolic) >18cm2 |
PA: pulmonary artery; RV, right ventricle; LV, left ventricle; TRV: tricuspid regurgitation velocity.
TTE screening for PH is recommended in asymptomatic subjects in the following risk groups:
- –
Patients with systemic sclerosis [I, B].
- –
First-degree relatives of patients with a diagnosis of hereditary pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) [I, C].
- –
Patients with portal hypertension who are candidates for liver transplantation [I, B].
In other cases, TTE will be performed on the basis of clinical suspicion.
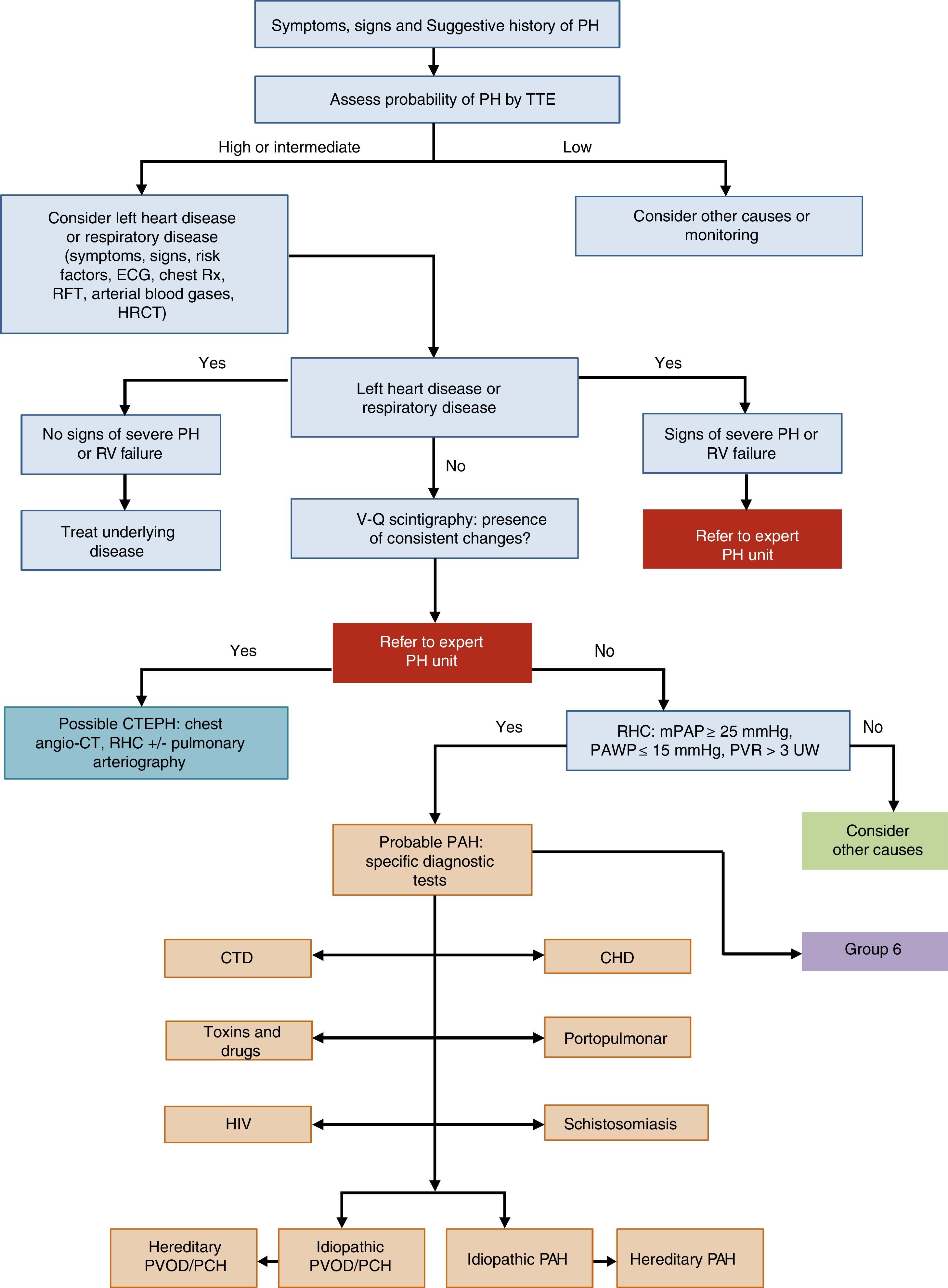
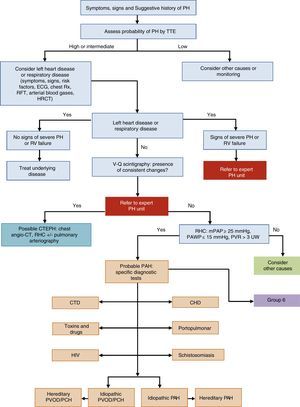
General Approach to DiagnosisThe diagnostic algorithm of PH is shown in Fig. 1. TTE will be performed if PH is suspected. If the probability of PH is intermediate or high, left heart disease (PH group 2) and chronic respiratory disease (PH group 3) will be ruled out. Patients in these PH groups or those with severe right ventricular dysfunction will be referred to an expert in PH2 [IIa, C]. When PH has been ruled out in groups 2 and 3, ventilation–perfusion lung scintigraphy will be used to rule out thromboembolic disease. If perfusion defects are observed on the ventilation–perfusion scintigraphy, a study for probable chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension will be performed. Hemodynamic diagnosis with RHC will be carried out in an expert PH unit [I, C]. If PAH is confirmed, the subtype should be identified.
Diagnostic algorithm for pulmonary hypertension.
CHD: congenital heart disease; CT: computed tomography; CTD: connective tissue disease; CTEPH: chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension; ECG, electrocardiogram; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; HRCT: high-resolution computed tomography; mPAP: mean pulmonary arterial pressure; PAH: pulmonary arterial hypertension; PAWP: pulmonary arterial wedge pressure; PCH: pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis; PH: pulmonary hypertension; PVOD: pulmonary veno-occlusive disease; PVR: pulmonary vascular resistance; RFT: respiratory function tests; RHC: right heart catheterization; RV: right ventricle; Rx: chest X-ray; TTE: transthoracic echocardiography; V-Q: ventilation–perfusion; WU: Wood units.
In patients with idiopathic, hereditary, or drug-related PAH, a vasodilator test with inhaled nitric oxide or iv epoprostenol will be performed during the RHC diagnostic procedure [I, C]. The test is positive if mPAP drops ≥10mmHg to reach a value ≤40mmHg, with no reduction in cardiac output [I, C]. The subtype will be identified by contrast echocardiography, autoimmunity testing, hepatotropic virus serology, and HIV serology (Fig. 1). If there is a family history of PH, or if it is suspected, a study to identify BMPR2 gene mutations is advisable.3–5
The diagnosis of pulmonary veno-occlusive disease (PVOD) or pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis (PCH) is based on clinical data, very low carbon dioxide diffusing capacity, severe hypoxemia, and consistent findings on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT).6 It can also be diagnosed from the presence of EIF2AK4 gene mutations.6
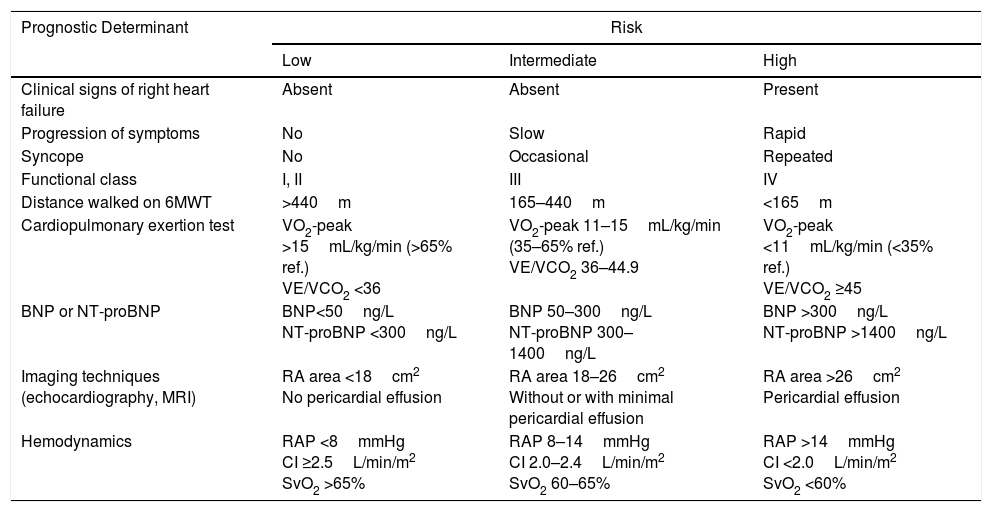
A set of variables associated with survival are used for evaluating prognosis2 (Table 4). For monitoring, clinical parameters and more easily performed tests (functional class [FC], 6-minute walk test, ECG, clinical laboratory tests) should be evaluated every 3–6 months, while the more complex procedures should be performed every 6–12 months,7 or in case of clinical deterioration [I, C].
Prognostic Evaluation in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.
| Prognostic Determinant | Risk | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Intermediate | High | |
| Clinical signs of right heart failure | Absent | Absent | Present |
| Progression of symptoms | No | Slow | Rapid |
| Syncope | No | Occasional | Repeated |
| Functional class | I, II | III | IV |
| Distance walked on 6MWT | >440m | 165–440m | <165m |
| Cardiopulmonary exertion test | VO2-peak >15mL/kg/min (>65% ref.) VE/VCO2 <36 | VO2-peak 11–15mL/kg/min (35–65% ref.) VE/VCO2 36–44.9 | VO2-peak <11mL/kg/min (<35% ref.) VE/VCO2 ≥45 |
| BNP or NT-proBNP | BNP<50ng/L NT-proBNP <300ng/L | BNP 50–300ng/L NT-proBNP 300–1400ng/L | BNP >300ng/L NT-proBNP >1400ng/L |
| Imaging techniques (echocardiography, MRI) | RA area <18cm2 No pericardial effusion | RA area 18–26cm2 Without or with minimal pericardial effusion | RA area >26cm2 Pericardial effusion |
| Hemodynamics | RAP <8mmHg CI ≥2.5L/min/m2 SvO2 >65% | RAP 8–14mmHg CI 2.0–2.4L/min/m2 SvO2 60–65% | RAP >14mmHg CI <2.0L/min/m2 SvO2 <60% |
6MWT: 6-minute walk test; BNP: brain natriuretic peptide; CI: cardiac index; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; NT-proBNP: N-terminal prohormone brain natriuretic peptide; RA: right atrium; RAP: right atrial pressure; SvO2: oxygen saturation of mixed venous blood; VE/VCO2: ratio between minute ventilation and CO2 production; VO2-peak: peak oxygen uptake.
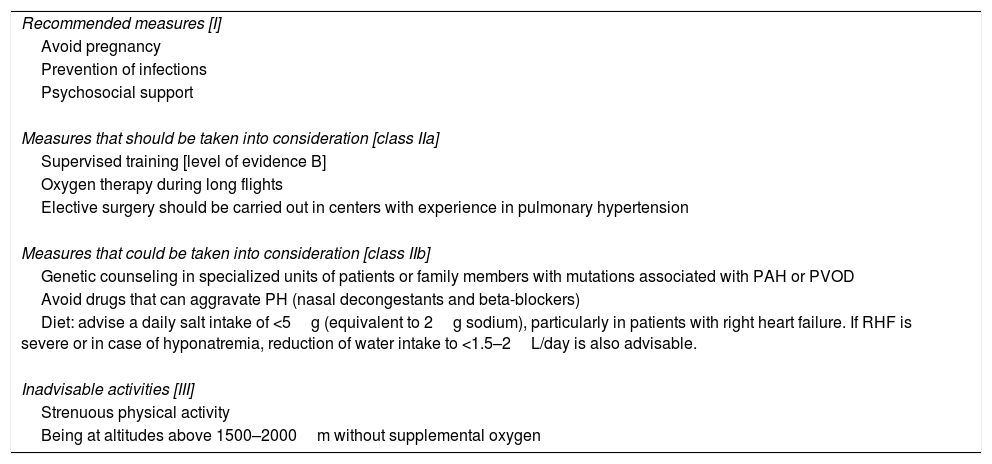
General therapeutic measures for PAH are listed in Table 5. Diuretics are indicated in patients with right ventricular failure and water retention [I, C]. Loop diuretics or aldosterone antagonists should be used.2 Anticoagulation with vitamin K antagonists is recommended in idiopathic and hereditary PAH, and PAH caused by anorectics [IIb, C]. Oxygen therapy is recommended if PaO2 is <60mmHg [I, C]. It may also be considered as an option for correcting desaturation during exercise.2 Regular monitoring of iron levels is recommended, and supplements should be administered if necessary.
General Therapeutic Measures in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.
| Recommended measures [I] |
| Avoid pregnancy |
| Prevention of infections |
| Psychosocial support |
| Measures that should be taken into consideration [class IIa] |
| Supervised training [level of evidence B] |
| Oxygen therapy during long flights |
| Elective surgery should be carried out in centers with experience in pulmonary hypertension |
| Measures that could be taken into consideration [class IIb] |
| Genetic counseling in specialized units of patients or family members with mutations associated with PAH or PVOD |
| Avoid drugs that can aggravate PH (nasal decongestants and beta-blockers) |
| Diet: advise a daily salt intake of <5g (equivalent to 2g sodium), particularly in patients with right heart failure. If RHF is severe or in case of hyponatremia, reduction of water intake to <1.5–2L/day is also advisable. |
| Inadvisable activities [III] |
| Strenuous physical activity |
| Being at altitudes above 1500–2000m without supplemental oxygen |
PVOD: pulmonary veno-occlusive disease; PAH: pulmonary arterial hypertension.
All recommendations have a level of evidence C unless otherwise indicated.
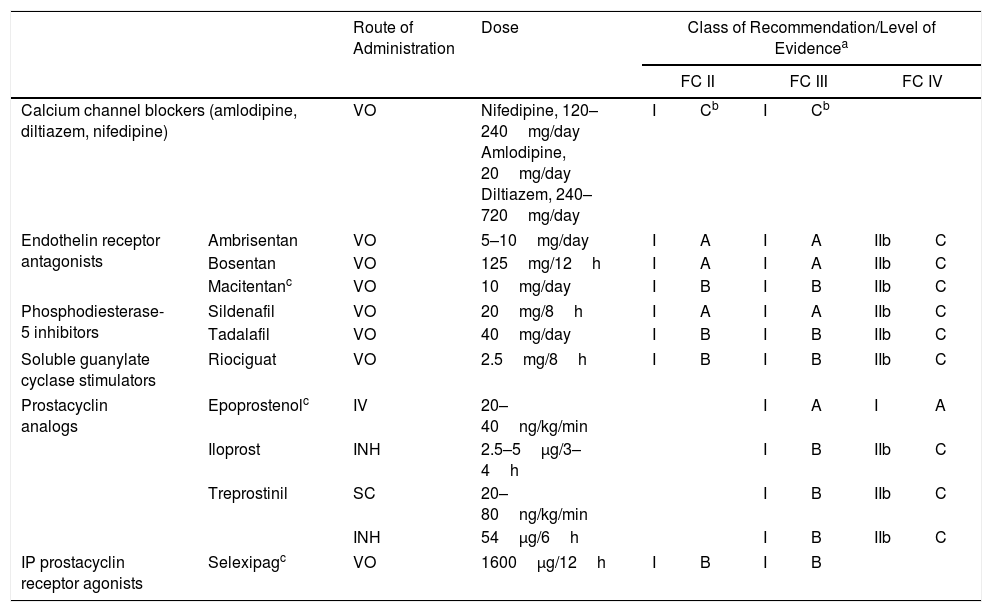
Specific drugs for the treatment of PAH include (Table 6):
- –
Calcium channel blockers: indicated for use in patients with idiopathic PAH and positive vasodilator test [I, C]. High-dose nifedipine, diltiazem and amlodipine are recommended.8
- –
Endothelin receptor antagonists, including ambrisentan, bosentan, and macitentan. Ambrisentan and bosentan can cause liver toxicity, so monthly monitoring of liver enzymes is required. Macitentan carries a risk of anemia, and regular monitoring of hemoglobin levels is recommended.
- –
Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors and soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) stimulators: available PDE5 inhibitors are sildenafil and tadalafil, and the only available sGC stimulator is riociguat. The concomitant administration of PDE5 inhibitors and sGC stimulators is contraindicated.
- –
Prostacyclin analogs and prostacyclin receptor agonists: available prostacyclin analogs include epoprostenol, administered via continuous iv infusion; iloprost, administered by inhalation; and treprostinil, administered in a continuous subcutaneous microinfusion pump. Inhaled treprostinil has also been shown to be beneficial9 (Table 4). Selexipag is a prostacyclin receptor agonist that is administered orally.10
General Recommendations for Single-agent Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.
| Route of Administration | Dose | Class of Recommendation/Level of Evidencea | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC II | FC III | FC IV | |||||||
| Calcium channel blockers (amlodipine, diltiazem, nifedipine) | VO | Nifedipine, 120–240mg/day Amlodipine, 20mg/day Diltiazem, 240–720mg/day | I | Cb | I | Cb | |||
| Endothelin receptor antagonists | Ambrisentan | VO | 5–10mg/day | I | A | I | A | IIb | C |
| Bosentan | VO | 125mg/12h | I | A | I | A | IIb | C | |
| Macitentanc | VO | 10mg/day | I | B | I | B | IIb | C | |
| Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors | Sildenafil | VO | 20mg/8h | I | A | I | A | IIb | C |
| Tadalafil | VO | 40mg/day | I | B | I | B | IIb | C | |
| Soluble guanylate cyclase stimulators | Riociguat | VO | 2.5mg/8h | I | B | I | B | IIb | C |
| Prostacyclin analogs | Epoprostenolc | IV | 20–40ng/kg/min | I | A | I | A | ||
| Iloprost | INH | 2.5–5μg/3–4h | I | B | IIb | C | |||
| Treprostinil | SC | 20–80ng/kg/min | I | B | IIb | C | |||
| INH | 54μg/6h | I | B | IIb | C | ||||
| IP prostacyclin receptor agonists | Selexipagc | VO | 1600μg/12h | I | B | I | B | ||
INH: inhaled; IV: intravenous; SC: subcutaneous; VO: oral.
- –
Atrial septostomy: indicated in patients with FC IV, with right ventricular failure,11 or as a bridge treatment in patients waitlisted for transplantation [IIb, C]. This procedure can be performed in hospitals with experience. It should be avoided in patients with right atrial pressure >20mmHg or SaO2 <85% breathing room air.
- –
Lung transplantation: the most common procedure is double lung transplantation. This is indicated in young patients without associated comorbidity who do not respond fully to medical treatment2 [I, C]. This is the treatment of choice in PVOD and PCH.
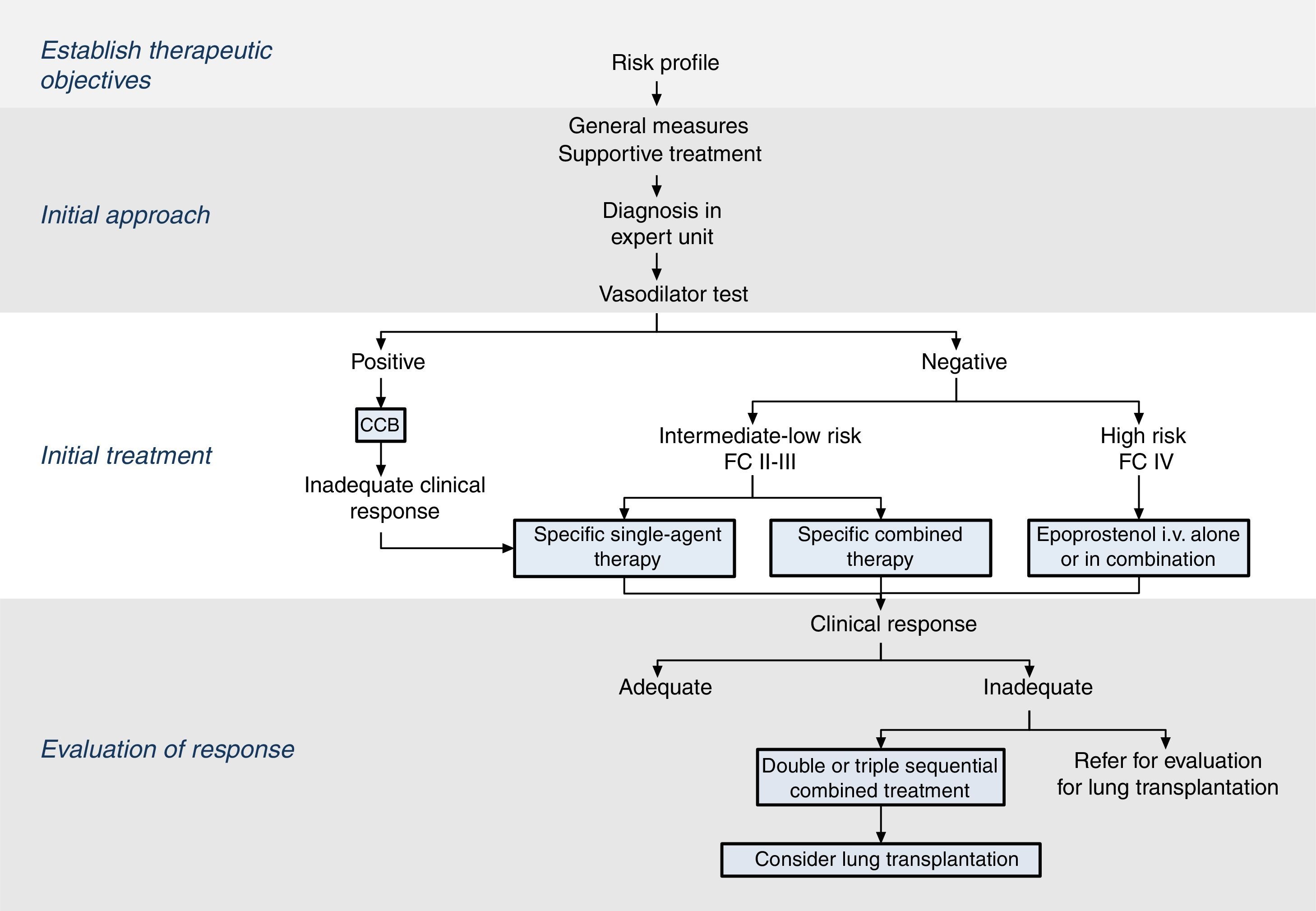
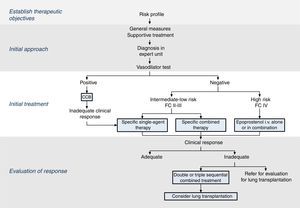
The therapeutic strategy in PAH is based on 4 components (Fig. 2):
Establish therapeutic objectives: the main aim is to ensure that the patient's risk of death is low (Table 4) [I, C]. Characteristics of a low-risk profile include good tolerance to exertion, quality of life, and right ventricular function. The risk will be defined at the beginning, before starting treatment, and in the periodic monitoring visits [I, C].
Initial approach: this includes general measures (Table 5) and supportive therapy. Hemodynamic diagnosis with vasodilator test should be performed in an expert PH unit [I, B], since the result will help define the risk profile and establish the course of treatment.
Initial treatment: in patients with positive vasodilator response, treatment will begin with high-dose calcium channel blockers. If clinical response at 3 months is inadequate, other specific drugs will be used.
Patients with a low or intermediate risk with a negative vasodilator response will begin treatment with specific drugs in monotherapy or combination (Fig. 2). Endothelin receptor antagonists, PDE5 inhibitors and sGC stimulators in monotherapy have been effective in patients with FC II and III. Prostanoids have been evaluated in patients with FC III. The choice of drug is based on the route of administration, safety profile, possible interactions with other drugs, comorbidities, the amount and quality of the available evidence, patient preferences, experience of the physician, and cost.
If combined treatment is selected from the outset, the only combination that has shown superiority to single-agent therapy is ambrisentan plus tadalafil12 [I, B].
In patients with a high-risk profile or FC IV, the treatment of choice is intravenous epoprostenol13 [I, A]. Evidence shows that combined initial treatment with epoprostenol plus 1 or 2 drugs is effective14 [IIa, C].
Response assessment: response to treatment at 3–4 months will be evaluated [I, C]. If response is unsatisfactory, a second or third drug will be added, and possible referral of the patient for lung transplant evaluation will be considered.2 All patients should be followed periodically in an expert PH unit. Visit intervals will be established on the basis of disease severity, but should never be longer than 6 months, even in patients with satisfactory clinical response.2
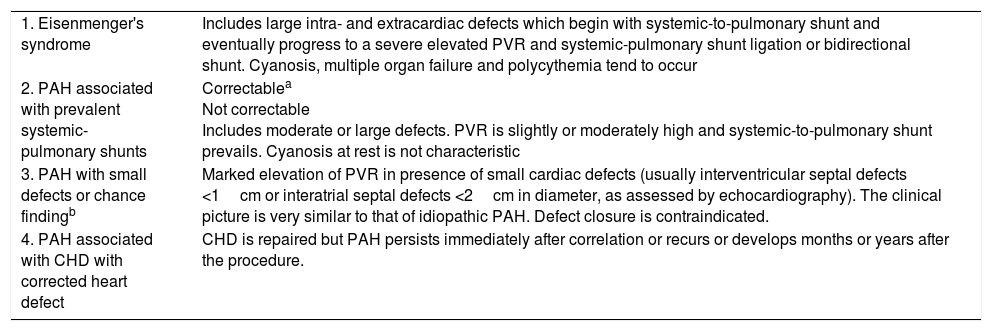
Subtype ConsiderationsCongenital Heart DiseaseCongenital heart diseases are included in PH groups 1, 2, 3, and 5, depending on the underlying mechanism. Table 7 lists the PAH classifications associated with congenital heart disease and Table 8 summarizes recommendations for pharmacological treatment. The following limits are proposed for systemic-pulmonary shunt ligation [IIa, C]: it is indicated if pulmonary vascular resistance is <4Woodunits·m2 and contraindicated for >8Woodunits·m2. Intermediate situations will be assessed individually.15
Clinical Classification of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Associated With Congenital Heart Disease.
| 1. Eisenmenger's syndrome | Includes large intra- and extracardiac defects which begin with systemic-to-pulmonary shunt and eventually progress to a severe elevated PVR and systemic-pulmonary shunt ligation or bidirectional shunt. Cyanosis, multiple organ failure and polycythemia tend to occur |
| 2. PAH associated with prevalent systemic-pulmonary shunts | Correctablea Not correctable Includes moderate or large defects. PVR is slightly or moderately high and systemic-to-pulmonary shunt prevails. Cyanosis at rest is not characteristic |
| 3. PAH with small defects or chance findingb | Marked elevation of PVR in presence of small cardiac defects (usually interventricular septal defects <1cm or interatrial septal defects <2cm in diameter, as assessed by echocardiography). The clinical picture is very similar to that of idiopathic PAH. Defect closure is contraindicated. |
| 4. PAH associated with CHD with corrected heart defect | CHD is repaired but PAH persists immediately after correlation or recurs or develops months or years after the procedure. |
CHD: congenital heart disease; PAH: pulmonary arterial hypertension; PVR: pulmonary vascular resistance.
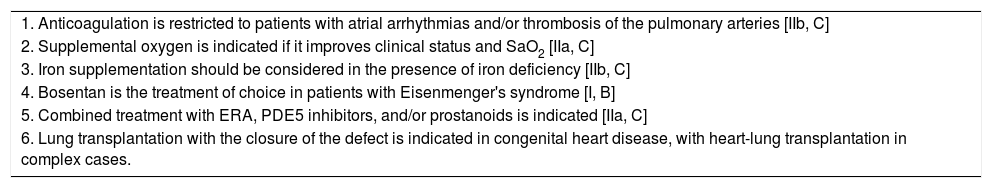
Pharmacological Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Associated With Congenital Heart Disease.
| 1. Anticoagulation is restricted to patients with atrial arrhythmias and/or thrombosis of the pulmonary arteries [IIb, C] |
| 2. Supplemental oxygen is indicated if it improves clinical status and SaO2 [IIa, C] |
| 3. Iron supplementation should be considered in the presence of iron deficiency [IIb, C] |
| 4. Bosentan is the treatment of choice in patients with Eisenmenger's syndrome [I, B] |
| 5. Combined treatment with ERA, PDE5 inhibitors, and/or prostanoids is indicated [IIa, C] |
| 6. Lung transplantation with the closure of the defect is indicated in congenital heart disease, with heart-lung transplantation in complex cases. |
ERA: endothelin receptor antagonists; PDE5 inhibitors: phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors; SaO2: oxygen saturation in arterial blood.
[Class of recommendation, level of evidence].
PAH associated with systemic sclerosis is the most common presentation.16 Annual screening with TTE and carbon dioxide diffusing capacity is recommended in patients with systemic sclerosis17 [I, C]. In other connective tissue diseases, TTE is recommended in symptomatic individuals. Chest HRCT is useful for evaluating the presence of interstitial lung disease and PVOD.18 RHC is recommended whenever PAH is suspected [I, C]. Patients with scleroderma and mPAP 21–24mmHg should be monitored due to their high risk of developing PAH.19
Patients with connective tissue diseases and PAH should be treated according to the general PAH algorithm [I, C]. Oral anticoagulation is associated with a worse prognosis,20 so it should only be used in patients prone to thrombophilia (antiphospholipid antibodies)21 [IIb, C]. Immunosuppressive therapy may benefit patients with PAH associated with systemic lupus erythematosus or mixed connective tissue disease.22
Portopulmonary HypertensionPortopulmonary hypertension is defined as combined portal and pulmonary hypertension. Patients with portopulmonary hypertension have higher mortality than patients with idiopathic PAH,23,24 so referral to expert centers is recommended [I, C]. The use of anticoagulants [III, C] and beta-blockers is not recommended.25 Portopulmonary hypertension is a major risk factor in liver transplantation,26 so it must be ruled out by TTE in all transplant candidates [I, B] and these results must be confirmed with a hemodynamic study. If mPAP is <35mmHg, transplantation can be considered26 [IIb, C]. If mPAP is ≥35mmHg, specific therapy with reevaluation at 3 months is recommended. If PAP remains high despite treatment, liver transplantation is contraindicated [III, C].
HIV InfectionTTE to detect PAH should be performed in cases of unexplained dyspnea [III, C]. Anticoagulation is not recommended because of the risk of bleeding and possible drug interactions [III, C]. Account should be taken of interactions between PDE5 inhibitors and some antiretroviral drugs.
Pulmonary Veno-occlusive Disease and Pulmonary Capillary HemangiomatosisPVOD and PCH share clinical, pathological, and genetic characteristics, and treatment is the same.27 PVOD may be associated with systemic sclerosis, HIV infection, or drugs. The familial form is caused by mutations in the biallelic EIF2AK4 gene.28
Diagnosis is established by clinical criteria, physical examination, bronchoscopy, and radiological tests [I, C], or identification of the EIF2AK4 gene mutation [I, B].
Vasodilators can cause pulmonary edema in PVOD/PCH. Lung transplantation is the treatment of choice, so patients should be referred to a lung transplantation unit after diagnosis [I, C].
Special SituationsPregnancy and birth control: due to the high risk of mortality, patients with PAH should avoid pregnancy [I, C]. The combined use of 2 contraceptive methods is advisable. Progestins are preferable to estrogens. If pregnancy occurs, patients should be informed of the risk and termination should be proposed. Patients who decide to take the risk and continue the pregnancy should be monitored closely in a center with expertise in PH and high-risk pregnancies.
Surgery: surgery confers a high risk of morbidity and mortality, especially if it is unscheduled,29 and should be performed in PH reference centers. Epidural anesthesia is preferable to general anesthesia.29
Right heart failure: diuretics provide symptomatic benefits. In situations requiring ICU admission, the patient's water balance must be optimized with intravenous diuretics, right ventricular overload must be minimized (generally with intravenous prostanoids), cardiac output must be optimized (preferably with dobutamine). Intubation, which frequently produces hemodynamic collapse, should be avoided. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) and other devices should be considered in selected patients.30
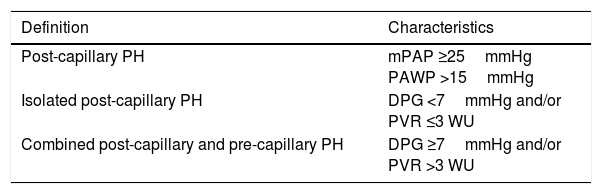
Pulmonary Hypertension due to Left Heart DiseasePH associated with left heart disease is classified as post-capillary. Two types have been identified: Isolated post-capillary PH and combined pre-capillary and post-capillary PH, depending on diastolic pressure gradient values and pulmonary vascular resistance (Table 9).
Hemodynamic Classification of Post-capillary Pulmonary Hypertension.
| Definition | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Post-capillary PH | mPAP ≥25mmHg PAWP >15mmHg |
| Isolated post-capillary PH | DPG <7mmHg and/or PVR ≤3 WU |
| Combined post-capillary and pre-capillary PH | DPG ≥7mmHg and/or PVR >3 WU |
DPG: diastolic pressure gradient (diastolic PAP−PAWP); mPAP: mean pulmonary arterial hypertension; PAWP: pulmonary artery wedge pressure; PH: pulmonary hypertension; PVR: pulmonary vascular resistance; WU: Wood units (mmHg/L/min).
Differential diagnosis between PAH and group 2 PH can be complex, particularly in patients with PH and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Attention will be given to the characteristics indicated in Table 10.31
Data Indicative of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.
| Age >65 years |
| Cardiovascular risk factors: diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, or systemic hypertension |
| Coronary disease |
| Atrial fibrillation |
| Echocardiography: left atrium more dilated than right, left ventricular hypertrophy, interatrial septum bulging into the right atrium, diastolic dysfunction in mitral flow Doppler |
| ECG: presence of left ventricular hypertrophy and Q waves |
The approach focuses on optimizing heart failure treatment [I, B]. Patients with severe combined post-capillary and pre-capillary PH should be referred to expert centers for inclusion in clinical trials and/or individualized treatment [IIa, C]. The use of drugs indicated for PAH is not recommended [III, C].
Pulmonary Hypertension due to Respiratory DiseaseRespiratory diseases most commonly associated with PH are COPD, interstitial lung diseases, and the combination of pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Table 11 shows the hemodynamic classification of PH in this group. PH is usually mild or moderate.32 Severe PH is most often seen in the combination of pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema (CPFE) and is often associated with a disproportionately reduced carbon dioxide diffusing capacity and low PaCO2.33
Hemodynamic Classification of Pulmonary Hypertension Associated With Respiratory Diseases.
| Terminology | Hemodynamic characteristics |
|---|---|
| COPD/IPF/CPFE without PH | mPAP <25mmHg |
| COPD/IPF/CPFE with PH | mPAP ≥25mmHg |
| COPD/IPF/CPFE with severe PH | mPAP >35mmHg or mPAP ≥25mmHg in the presence of low cardiac output (CI <2.5L/min, not explained by other causes) |
CPFE: combination of pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema; CI: cardiac index; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; IPF: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; mPAP: mean pulmonary arterial pressure; PH: pulmonary hypertension.
TTE is the examination of choice for the detection of PH [I, C], although its accuracy in patients with advanced respiratory disease is low. This procedure is indicated if significant PH is suspected or to rule out left heart disease.
The definitive diagnosis of PH is established with RHC. Indications include: 1) correct diagnosis or exclusion of PH in candidates for surgery (transplantation, lung volume reduction); 2) suspected concomitant PAH or chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH); 3) repeated episodes of right heart failure, and 4) inconclusive TTE in cases with high suspicion of PH.34
The treatment of choice in patients with COPD and hypoxemic PH is continuous home oxygen therapy [I, C]. The role of oxygen therapy is less clear in interstitial disease.
Conventional vasodilators or specific PAH drugs are not recommended in COPD patients with mild-moderate PH [III, C].2,35 The use of ambrisentan and riociguat is contraindicated in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [III, A]. Patients with respiratory disease and severe PH should be referred for individualized treatment in a hospital specializing in both conditions [I, C].
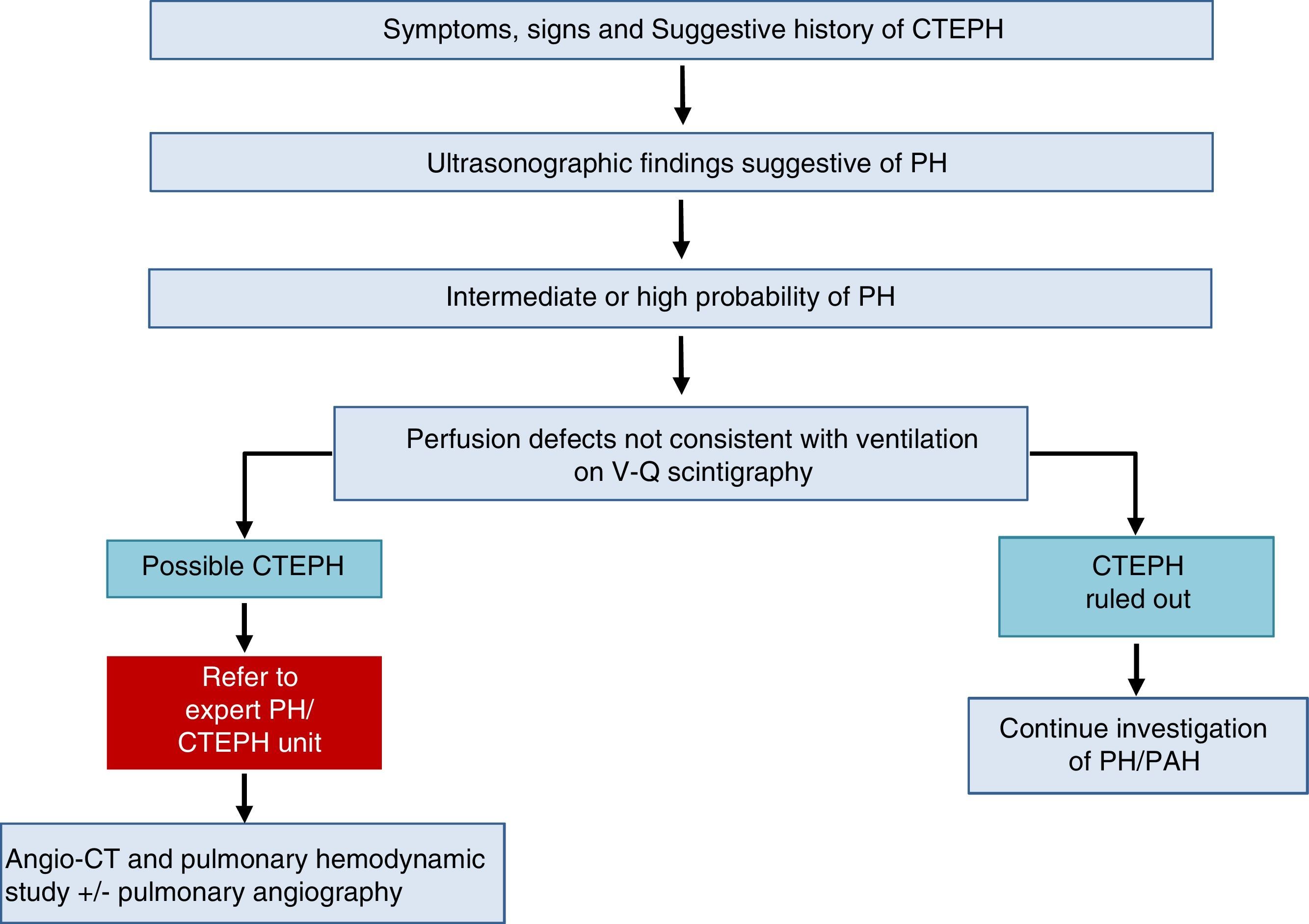
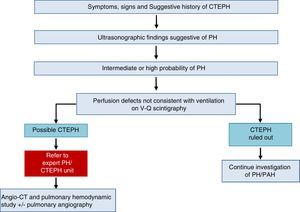
Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary HypertensionA diagnosis of CTEPH is established by the presence of pulmonary thrombosis and pre-capillary PH, after more than 3 months of appropriate anticoagulation.
The diagnostic algorithm for CTEPH (Fig. 3) has 2 components: hemodynamic diagnosis by RHC and localization of thrombotic lesions using imaging techniques (angio-CT and selective pulmonary digital subtraction angiography).
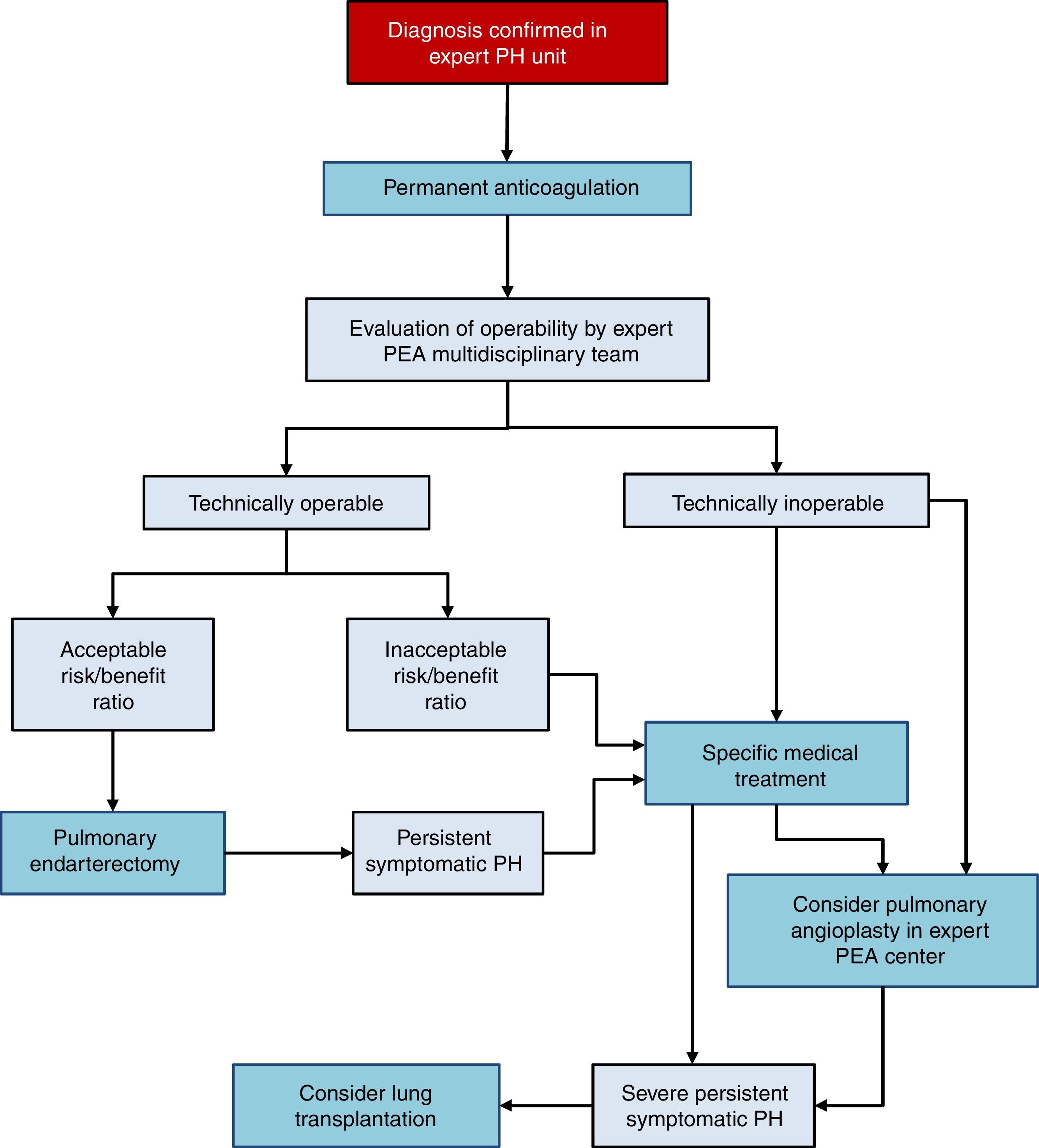
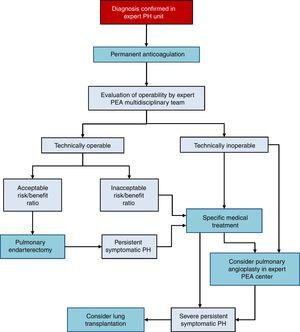
There are 3 treatment options in CTEPH (Fig. 4):
- 1.
Surgery
Pulmonary endarterectomy (PEA) is the treatment of choice [I, C]. This intervention can achieve cure of CTEPH and is appropriate in more than 60% of cases. All patients diagnosed with CTEPH should be evaluated for possible PEA by a multidisciplinary team that includes a specialized surgeon in a hospital with experience in this type of surgery [I, C]. There are 2 accredited centers in Spain.36–38
- 2.
Medical intervention
Patients with CTEPH should receive chronic anticoagulation, even after PEA [I, C]. Vitamin K antagonists are recommended, since there is no evidence to support the use of the new oral anticoagulants. Currently, the only drug specifically indicated for CTEPH is riociguat39 [I, B]. Beneficial effects have been demonstrated with macitentan,40 and to some extent with bosentan.41 Pharmacological treatment is indicated in patients in whom surgery has been ruled out by an expert multidisciplinary committee in PEA and if PH persists after PEA [I, B].
- 3.
Pulmonary angioplasty
Pulmonary balloon angioplasty is a new procedure that has provided good outcomes in patients with obstructive lesions that cannot be accessed with PEA,42–44 although the available evidence is still scant.45 This procedure should only be performed in hospitals with extensive experience in CTEPH, after PEA has been ruled out.2
Pulmonary Hypertension With Unclear or Multifactorial MechanismsThis group includes various etiological processes: hematologic diseases, systemic diseases, metabolic disorders, and a miscellaneous group of disorders (Table 2). Diagnosis is difficult, so management in hospitals with experience in PH is advisable. Currently there is no specific treatment for this group.
Healthcare OrganizationPrimary forms of PH (groups 1, 4, and 5) (Table 2) are rare serious diseases that require complex procedures for diagnosis and treatment. The broad consensus is that patients with diseases of these characteristics should be seen in specialized referral units with experience in the disease.2,46 In 2008, the Spanish Society of Pulmonology and Thoracic Surgery and the Spanish Society of Cardiology prepared a consensus document in which they proposed a healthcare organization for the care of PH patients in Spain based on expert PH units that interact in a network with hospitals at a local level.46 The criteria that expert PH units must meet, as established in the clinical guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology-European Respiratory Society,2 are shown in Table 12. Three CSURs (centers, services or units of reference) for complex PH cases, appointed by the Ministry of Health, have been operating in Spain since 2015.
Recommendations for Expert Pulmonary Hypertension Units.
| Multidisciplinary team of professionals [I, C] |
| Monitoring >50 patients with PAH and CTEPH (ideally >200) [IIa, C] |
| Receive >24 new cases per year with a diagnosis of PAH and CTEPH [IIa, C] |
| Perform >20 right heart catheterizations with vasodilator test every year [IIa, C] |
CTEPH: chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension; PAH: pulmonary arterial hypertension.
[Class of recommendation, level of evidence].
Given the organizational structure of the Spanish healthcare system, care in the area of PH must be set up a network of networks, with expert PH units on an autonomous community level, which interact with associated sites within the autonomous community itself. CSURs, which can deliver PEA programs and care in more complex patients and situations, must operate on a national level.
Expert PH units must set up protocols for consultation circuits and referral for specific diseases and clinical situations: CTEPH (PEA, pulmonary angioplasty), lung transplantation, portopulmonary hypertension, congenital heart disease, connective tissue diseases, genetic studies, elective surgery and care of the pregnant patient.
Conflict of InterestsDr. Barberà has received fees from Actelion, Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pfizer, and has received funding from Actelion, Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline and Pfizer, not related with this publication. Dr. Blanco has received fees from Merck Sharp & Dohme, not related with this publication. Dr. Otero Candelera has received fees from Actelion, Bayer, Rovi, Leo Pharma, and Merck Sharp & Dohme, and has received funding from Bayer and Leo Pharma, not related with this publication. Dr. Lopez-Reyes has received fees from Actelion, and funding from GlaxoSmithKline, Ferrer, and Actelion, not related with this publication. Dr. Otero has received fees from Actelion, Bayer, Glaxo-SmithKline, and Ferrer, not related with this publication. Dr. Pérez-Peñate has received fees from Actelion, Bayer, and Merck Sharp & Dohme, not related with this publication. Dr. Sala declares no conflict of interests. Dr. Escribiano has received fees from Actelion, Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, and Merck Sharp & Dohme, and has received funding from Actelion, Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline and Ferrer, not related with this publication.
The members of the working group are grateful for the revision of the manuscript and the comments made by A. Ballaz, J. de Miguel, J. Guerra, and G. Juan.
Please cite this article as: Barberà JA, Román A, Gómez-Sánchez MÁ, Blanco I, Otero R, López-Reyes R, et al. Guía de diagnóstico y tratamiento de la hipertensión pulmonar: resumen de recomendaciones. Arch Bronconeumol. 2018;54:205–215.