Various clinical trials have been published on the optimal clinical management of patients with pleural exudates, particularly those caused by malignant tumors, while little information is available on the diagnosis and treatment of pleural transudates.
The etiology of pleural transudates is wide and heterogeneous, and they can be caused by rare diseases, sometimes constituting a diagnostic challenge. Analysis of the pleural fluid can be a useful procedure for establishing diagnosis. Treatment should target not only the underlying disease, but also management of the pleural effusion itself.
In cases refractory to medical treatment, invasive procedures will be necessary, for example therapeutic thoracentesis, pleurodesis with talc, or insertion of an indwelling pleural catheter. Little evidence is currently available and no firm recommendations have been made to establish when to perform an invasive procedure, or to determine the safest, most efficient approach in each case.
This article aims to describe the spectrum of diseases that cause pleural transudate, to review the diagnostic contribution of pleural fluid analysis, and to highlight the lack of evidence on the efficacy of invasive procedures in the management and control of pleural effusion in these patients.
El diagnóstico y tratamiento de los trasudados pleurales ha sido poco estudiado, sobre todo si se compara con el de los exudados, especialmente los malignos, en que diversos ensayos clínicos informan con relativa frecuencia sobre cuál es el manejo óptimo de estos pacientes en la práctica clínica.
La etiología de los trasudados pleurales es amplia, heterogénea, a veces corresponde a enfermedades raras y, en ocasiones, constituye un auténtico reto diagnóstico. El análisis del líquido pleural puede ser una herramienta básica para poder establecer el diagnóstico. El tratamiento debe dirigirse no solamente a la enfermedad subyacente, sino también al propio derrame pleural.
En los casos refractarios al tratamiento médico, habrá que recurrir a procedimientos invasivos como la toracocentesis terapéutica, la pleurodesis con talco, o la inserción de un catéter pleural tunelizado. Sin embargo, en la actualidad, hay muy poca evidencia al respecto y no existen recomendaciones firmes que establezcan en qué situaciones hay que utilizar alguna de estas técnicas invasivas y cuál sería la más eficaz y con menos efectos secundarios para cada una de las enfermedades responsables.
El propósito de este artículo es describir el espectro de enfermedades que causan un trasudado pleural, revisar la aportación diagnóstica del análisis del líquido pleural y poner de manifiesto la escasa evidencia que existe sobre la eficacia de los procedimientos invasivos en el manejo y control del derrame pleural en estos pacientes.
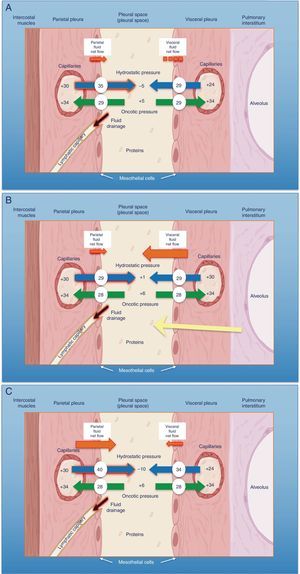
The pleural space normally contains a small amount of fluid that separates the two pleural layers, allowing one membrane to slip over the other. As in other interstitial spaces of the body, differences in hydrostatic and oncotic pressures between the capillaries of both pleural layers and the pleural space causes fluid to pass through the systemic vessels into the pleural space, where it is absorbed by lymphatic capillaries located in the lower regions of the parietal pleura1 (Fig. 1A). The volume and characteristics of the pleural fluid (PF) are determined by a combination of dynamic phenomena that affect systemic and pulmonary circulation, lymphatic drainage, and the movements of the rib cage and the heart.2 Normal PF production is approximately 0.01ml×kg×h, so an individual weighing 60kg would have an entry rate of 15ml/day,3 while pleural lymphatic capillaries can absorb 0.28ml×kg×h, almost 30 times the entry rate.4
Schematic representation of the movement of fluid in the pleural space in normal conditions (A), in heart failure (B) and in trapped lung (C). In normal lung and pleura (A), the balance of hydrostatic and oncotic pressures promotes the formation of pleural fluid. Pressure gradients show a net flow of fluid from the parietal pleura and that balance is maintained in the visceral pleura (pressures in cmH2O). In heart failure (B), fluid in the pulmonary interstitium increases due to increased pulmonary capillary pressures. Fluid that enters the pleural space exceeds the drainage capacity of the pleural lymphatic capillaries. In trapped lung (C), a previous inflammatory process has produced a thick, fibrous visceral pleura. The inability of the lung to expand leads to a negative hydrostatic pleural pressure and this alteration of the Starling's forces leads to the formation of pleural transudate. Pleural effusion may be verging on exudate, depending on how recent the active inflammation was.
Any imbalance between the hydrostatic and oncotic pressures, whether in the pleural space or the blood capillaries, can lead to the accumulation of fluid in the pleural space. In this situation, the fluid is called transudate and the pleura is not diseased. The diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic implications of a transudate, then, differ completely from exudative pleural effusion (PE).
From a clinical point of view, transudate can be distinguished from exudate by measuring various biochemical parameters in the PF and in blood, most often by applying Light's criteria: ratio of total protein in PF/serum (PF/S)>0.5; lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) PF/S>0.6 and LDH in PF>2/3 the normal upper value in blood.5 PF is a transudate if none of the above conditions are met. Other parameters, such as cholesterol, have also been used for differentiating transudate from exudate, but none has demonstrated superiority over the others.6
A transudate can have numerous origins; some are very common, but others are rare, and sometimes unfamiliar. No firm recommendations have been made on the diagnosis and management of these effusions. In many of these patients, PE is the manifestation of disease in another organ and comorbidities are common, so the burden of managing PE is regularly borne by other specialists. Cooperation and agreement with these professionals will be necessary for designing protocols for the coordinated and optimized treatment of PE. This article aims to describe the spectrum of diseases that cause pleural transudate, review how PF analysis contributes to diagnosis, and update management strategies.
Pleural TransudatesHeart FailureEighty-seven percent of patients hospitalized for decompensated heart failure (HF) who require diuretics show PE on their computed tomography (CT).7 HF is the most common cause of transudate8,9 and is responsible for all the PE identified in some series. Prevalence can be as high as 45%.10 The resulting pulmonary edema in these patients increases hydrostatic pressure in the capillaries of the visceral pleura, causing fluid to pass into the pleural space (Fig. 1B).
Cardiac PE tends to present as a lymphocyte-predominant transudate. However, as Light's criteria are designed for the diagnosis of exudates, 25% of cases may be incorrectly classified as exudates, particularly in patients receiving diuretics.11,12 If these drugs correct venous hypertension, PF is not only drained by the lymphatic capillaries, but can also be reabsorbed by the pleural capillaries, which would increase protein and LDH concentrations in the PF to the extent that it meets the biochemical characteristics of an exudate. In these cases, a serum albumin-PF gradient (or gap)>1.2g/dl seems to indicate that the PE corresponds to a transudate, regardless of whether it meets Light's criteria or not.13 However, other factors, such as the presence of a second cause of PE14 or a large number of red blood cells (>10000cells/mm3), can act on LDH levels15 and, in biochemical terms, change a transudate to an exudate.
In this setting, PF or blood determinations of natriuretic peptides, molecules secreted by the ventricles of the heart in response to acute distention, may be useful in the diagnosis of a PE caused by HF. In a recent meta-analysis, the diagnostic yield of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) in PF was: sensitivity 94%, specificity 91%, positive likelihood ratio 10.9, negative likelihood ratio 0.07, and odds ratio 157, with slightly inferior results when the determination was made in blood.16
The diagnosis of cardiac PE is usually established by consistent clinical symptoms and cardiomegaly and bilateral PE on chest radiograph, generally observed in 80% of cases. In these conditions, thoracentesis is not necessary.17 However, in certain circumstances, it is more difficult to establish a diagnosis. This may be due to clinical symptoms (chest pain and fever) associated with unusual radiological findings (no cardiomegaly or a marked asymmetry in the size of the PE) that would justify a diagnostic thoracentesis and determination of natriuretic peptides. Rabin and Blackman found in a series of 78 patients with bilateral PE and no cardiomegaly that only 3 (3.8%) had PE due to HF.18 Single-sided PE, however, does not rule out HF. In a review of 6 series that included 783 patients with PE due to HF, 125 (16%) had right PE and 55 (7%) had left PE.19
A prospective study of 60 patients with PE secondary to HF showed that in 89% of cases, PE resolved after 2 weeks of treatment with diuretics.7 In general, most patients will improve with optimized HF treatment, including diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, β-blockers, or procedures such as pacemaker placement or surgery, if the patient has serious valvular dysfunction.
Talc pleurodesis is a safe and effective technique in the treatment of malignant PE. However, evidence to support its use in benign PE is limited to a few cases in which the etiology of the PE was not even specified20–22 (Table 1). Nor is sufficient evidence available to support the use of the tunneled pleural catheter (TPC), and no cost-effectiveness studies have been performed. In a study conducted in 5 British hospitals, TPC was placed in 9 patients with HF and spontaneous pleurodesis was achieved in 4 (44%).23 In another series, 43 TPCs were placed in 36 patients with refractory HF and PE. In the group treated with talc poudrage by thoracoscopy followed by TPC, pleurodesis was achieved in 80% of cases, while in those patients who received only TPC, pleurodesis occurred in 25%.24 A recent meta-analysis assessed the benefit of TPC in patients with refractory benign PE. Of the 162 (49.8%) with PE due to HF, pleurodesis was achieved in 42.1% (range 0%–92.3%) (Table 1), with a complication rate similar to that of malignant PEs. The authors concluded that TPC is an effective and viable option in the management of patients with refractory benign PE.25 However, randomized clinical trials are needed to determine more accurately the usefulness of these catheters.
Series of Patients With Different Types of Pleural Transudates Treated With Talc Pleurodesis or Tunneled Pleural Catheter.
| Talc Pleurodesis | Tunneled Pleural Catheter | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart Failure | Hepatic Hydrothorax | Heart Failure | Hepatic Hydrothorax | Chronic Renal Disease | ||||||
| Patients | Success n (%) | Patients | Success n (%) | Patients | Success n (%) | Patients | Success n (%) | Patients | Success n (%) | |
| Glazer et al.21 | 6 | 5 (83.3) | 4 | 3 (75) | ||||||
| Bhatnagar et al.23 | 9 | 4 (44) | 19 | 2 (11) | ||||||
| Majid et al.24 | 15* | 12 (80) | ||||||||
| 28 | 7 (25) | |||||||||
| Patil et al.25 | 162 | 68 (42) | ||||||||
| Porcel26¶ | 189 | 142 (75) | ||||||||
| Chen et al.27 | 24 | 8 (33) | ||||||||
| Potechin et al.28 | 8 | 3 (37.5) | ||||||||
Trapped lung is a sequela of inflammation of the pleural space that leads to the formation of a fibrous membrane over the visceral pleura, preventing the lung from expanding29 and increasing negative pressure in the pleural space. Differences in hydrostatic pressure between the systemic capillaries of the parietal pleura and the pleural space can be very high, so the net flow of fluid into the pleural space will increase in order to decrease the pressure difference (Fig. 1C).
PF generally meets the criteria for transudate,29 since PE is generated by differences in existing hydrostatic pressures. However, the characteristics of the PF will depend on the time at which the thoracentesis is performed. If this is done at an early stage, when the disease is still active, the protein level, and less frequently the LDH level, of the PE will often be in the range of that of exudate.30
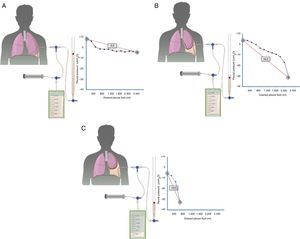
Diagnosis is based on four findings: (1) post-thoracentesis hydropneumothorax or PE that cannot be drained due to onset of chest pain; (2) transudative PF; (3) initially negative pleural pressure that falls even further as PF is removed, causing pleural elastance >14.5cmH2O/l (Fig. 2A–C), and (4) an air-contrast chest CT (that is, after diagnostic pneumothorax is performed during pleural manometry) demonstrating thickening of the visceral pleura.29
Curves obtained by manometry, with their elastance value, in normal lung (A), in a lung becoming trapped (B) and a trapped lung (C). With pleural effusion in a normal lung (A), initial pleural pressure will be slightly positive. As fluid is aspirated, the pleural pressure will drop slowly and the lung will be expanded gradually. Once all the effusion is removed, the lung will come into contact with the chest wall and the elastance obtained will be normal. In the lung in the process of becoming trapped (B), visceral pleura will become slightly thickened, and initial pleural pressure will be slightly positive, as in normal lung. When the fluid is removed, in principle, the diaphragm will expand progressively and pleural pressure will drop slowly. At some point the lung is trapped and unable to expand more and the pressure will drop quickly giving rise to a high elastance, with a bimodal pressure/volume curve. In the trapped lung, the visceral pleura has a thicker layer of fibrin which prevents the lung from expanding, so the initial pressure will be negative (C). The removal of fluid, on the one hand, and the rigidity of the lung, on the other hand, cause a rapid decline in pleural pressure and will lead to high elastance.
Trapped lung does not usually require any treatment if symptoms are mild or absent. Evacuating thoracentesis should not be repeated, since a similar amount of PF will accumulate again in an attempt to “normalize” the negative pleural pressure. In cases in which dyspnea is debilitating, TPC would be an option, since in addition to evacuating the liquid, pleurodesis can be achieved in some cases. However, there is still insufficient evidence outside its use in malignant PE. As a final alternative, if all other causes for the dyspnea are excluded, pleural decortication may be proposed.
Hepatic HydrothoraxHepatic hydrothorax is defined as PE in a patient with liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension with no associated heart, lung or pleural disease.31 Prevalence varies between 5% and 10% of patients with cirrhosis,26 of whom 80% have concomitant ascites.26 Two factors influence the accumulation of fluid in the pleural space: firstly, a pressure gradient between the peritoneal and pleural spaces (due to negative pressure), favoring the one-way passage of ascitic fluid to the thorax; and secondly, diaphragmatic defects that are often seen in the tendinous portion of the right diaphragm. This, in addition to the piston effect of the liver, means that most of these PEs are right-sided (80%).32–37 In patients without ascites, the mechanisms by which PF forms are the same.38 Hepatic hydrothorax is generally associated with a poor prognosis, with a 1-year survival of 43%.39
PE is usually a transudate40 with a relatively high pH,41 but 18% of cases might have the biochemical characteristics of exudate.42 A thoracentesis should always be performed and the PF should be analyzed to exclude associated heart, lung or pleural disease, and also to detect the main complication of hepatic hydrothorax, spontaneous bacterial empyema (bacterial infection of a previous hydrothorax in which pneumonia has been ruled out), which occurs in 13% of patients with cirrhosis and PE. According to existing studies, suspicion cannot be established from analysis of the ascitic fluid, instead, the PF must be analyzed.32 The PF of patients with liver cirrhosis may sometimes be a chylothorax.43 This may be due to the fact that these patients have a high liver capillary pressure, with a commensurate increase in lymphatic flow in the liver and the thoracic duct,44 which could lead to the formation of chylous ascites.
The most common treatments include salt restriction, diuretics, and therapeutic thoracentesis. In the case of ascites or refractory hydrothorax, the definitive treatment is liver transplantation.45 If this is contraindicated, an alternative is to implant a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt46 and, as a last resort, surgical repair of the diaphragm may be considered.47 Talc pleurodesis appears to be a highly risky procedure, with a periprocedural mortality of 45%.41 In a review of 11 series that included 189 patients with hepatic hydrothorax treated with thoracoscopic pleurodesis, mostly by talc insufflation, pleural symphysis was achieved in 142 cases.26 In a review of the clinical practice of British hospitals, the TPC was used in 19 patients with hepatic hydrothorax. Spontaneous pleurodesis was achieved in only 2 (11%) and, moreover, various complications developed.23 Finally, in a recent study, Chen et al. achieved spontaneous pleurodesis in 8 (33%) of 24 patients treated with a TPC. The mean time until pleurodesis was 132 days; after withdrawal of the catheter, PE did not recur in any case, and adverse effects (PF infection) were observed in only 4 patients (16.7%)27 (Table 1).
Peritoneal DialysisThe incidence of PE among patients receiving peritoneal dialysis is 1.6%, and it can develop between 1 day and 8 years after beginning the procedure.48 The size of the PE can be such as to force dialysis to be suspended. Intra-abdominal pressure that is slightly positive in normal conditions increases linearly in proportion to the volume of dialysis solution instilled.49 Intra-abdominal pressure and volume can increase the pressure of the abdominal wall and, consequently, of the abdominal support structures, causing the dialysis solution to leak from the peritoneal cavity, possibly through diaphragmatic defects, into the pleural space. PE is generally small and right-sided, although on occasions it is bilateral. Massive PEs have been described in women, always in the right side.50
In PE due to peritoneal dialysis, PF is a transudate with very high glucose levels (range 200–2000mg/dl).51 Diagnosis is precisely established by the presence of a transudate with very low protein levels (<1g/dl) and a glucose PF/S ratio of >2.
In a retrospective study of 257 patients receiving hemodialysis for renal failure, 52 (20%) developed PE.52 In 9 of the 14 patients (64.3%) who underwent thoracentesis, the PF was a transudate. The cause of the PE was associated with fluid overload in 6 of these 9 patients (66.7%), and with HF in 2 cases (22.2%). Among the patients with transudates, PE was predominantly bilateral (85.7%).
The recommended treatment for PE caused by peritoneal dialysis is to apply conservative measures such as a temporary switch to hemodialysis or the use of smaller-volume exchanges. Recently, Potechin et al. placed a TPC in 8 patients with a PE associated with end-stage renal disease, achieving spontaneous pleurodesis in 3 (37.5%), with no major complications28 (Table 1).
Metastatic Pleural EffusionUp to 10% of malignant PEs behave biochemically as transudates.53 Several mechanisms may be involved: (1) in an initial phase, PF is accumulated more as a result of obstruction of the lymphatic drainage than tumor infiltrating the pleura. As physiological PF is an ultrafiltrate with low protein levels, in these circumstances it would take several weeks for the accumulated protein concentration to become greater than 50% of the serum concentration54; (2) the pleural transudate is caused by another concomitant disease, since a tumor that affects the pleura does not necessarily produce PE. In some cases, this second disease could be identified55; (3) both the tumor and another disease capable of producing a pleural transudate contribute to the development of the PE.
In the case of transudate pleural effusion, the difficulty lies in knowing when to request PF cytology to rule out malignancy. A recent study suggested that cytology to rule out malignancy should be requested if the PE is left-sided, if nodules/lung masses, pulmonary atelectasis or mediastinal lymphadenopathies are observed on the chest X-ray or CT, if the patient does not have dyspnea, if the PF is of serous bloody appearance, or if PF carcinoembryonic antigen levels are high.53
Other CausesOther less common diseases can cause transudates, such as nephrotic syndrome9,56–58 (excessive loss of proteins via the glomerulus), urinothorax59,60 (accumulation of urine in the pleural space as a result of injury or obstruction of the urinary tract), duropleural fistula61–64 (cerebrospinal fluid passing into the pleural space as a result of a penetrating injury during a laminectomy), extravascular migration of a central venous catheter65–68 (catheters of insufficient length habitually placed in the left subclavian vein erode or pierce the superior vena cava in the azygos recess), glycinothorax69,70 (perforation of the urinary bladder wall during transurethral prostatectomy with the subsequent administration of a solution of glycine to irrigate the bladder), ventriculoperitoneal and ventriculopleural shunting71–76 (complication of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt in which cerebrospinal fluid passes into the pleural space), and pulmonary veno-occlusive disease77–79 (obstruction of the pulmonary veins and venules due to intimal fibrosis). The etiopathogenic mechanisms by which these PEs are produced are described in Table 2, along with the radiological characteristics, peculiarities and the treatment of each one.
Characteristics of Pleural Transudates With Unusual Etiology.
| Entity | Chest X-ray | Etiopathogenesis | Diagnosis | Other Characteristics | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nephrotic syndrome | Bilateral and small56 | Renal protein loss | Long-standing transudate Hypoalbuminemia Proteinuria | Rule out existence of associated PTE58 | Loop diuretics Low-sodium diet Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors Statins Antiplatelets |
| Urinothorax | One-sided. In the same side as the obstructive urinary disease59 | Obstructive urinary disease with passage of urine from the retroperitoneal or abdominal cavity into the pleural space due to pressure gradient | Creatinine PF/S>159 | Transudate (sometimes exudate as defined by high LDH levels)59 pH and glucose levels may be low59 Fluid of similar appearance and odor to urine59 | Direct treatment of the underlying urinary disease, with or without drainage of the PE |
| Duropleural shunt | One-sided. Variable size | Duropleural shunt. CSF flows through a pressure gradient61,62 | Demonstration of ß2-transferrin in PF63 | Transudate. Clear appearance (like water) with TP<1g/dl61,62 | Surgical ligation or chest drain |
| EMCVC | Uni or bilateral Small/massive Ipsi/contralateral | SCV erosion caused by a catheter too short in length | PE on chest Rx Abnormal catheter location Transudate65 | If glucose is administered, glucose PF/S>1 If parenteral nutrition is administered, milky PF (triglycerides>110mg/dl) TP<1g/dl in all cases. | Catheter withdrawal If PE is small, observation. Otherwise, therapeutic thoracentesis or chest tube |
| Glycinothorax | Right | Passage of glycine solution into the abdominal cavity and then into the pleural space | Previous bladder surgery Elevated glycine PF/S69,70 | PF is sometimes bloody | Discontinue bladder irrigation Therapeutic thoracentesis if needed |
| Ventriculoperitoneal and ventriculopleural shunts | Single-sided of variable size | Obstruction of fistula by fibrous tissue or accumulation of detritus | PF is CSF72 | Sometimes eosinophilic PE Sometimes empyema | Add acetazolamide |
| Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease | Usually bilateral On occasions, Kerley B lines77,78 | Increase of fluid in the pulmonary interstitium as a result of obstruction of the pulmonary veins | High probability based on clinical suspicion, physical examination, bronchoscopy and radiologic results79 Lung biopsy | PF is probably transudate | Oxygen, high-dose diuretics, slow, progressive increase of epoprostenol dosing, and lung transplant |
CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; EMCVC: extravascular migration of a central venous catheter; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; PE: pleural effusion; PF: pleural fluid; PF/S: pleural fluid/serum ratio; PTE: pulmonary thromboembolism; Rx: chest X-ray; SVC, superior vena cava; TP: total protein.
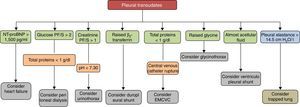
Pleural transudates are caused by a wide spectrum of diseases, ranging from HF to very rare entities. Diagnosis is based on clinical data and PF analysis, which can contribute decisively to diagnosis (Fig. 3). Although medical treatment for each causative disease is usually well established, at least among the more common ones, some cases are refractory, and in these, various possibilities has been opened up with the introduction of new interventional procedures, not yet sufficiently validated, that make management more complex. Studies and clinical trials that provide quality data and more evidence are required if the treatment of these patients is to be optimized.
AuthorshipLucía Ferreiro. Author and editor. Concept and design. Final approval of the manuscript.
José Manuel Porcel. Co-author. Review and final approval of the manuscript.
Luis Valdés. Author and editor. Concept and design. Final approval of the manuscript.
Conflict of InterestsThe authors state that they have no conflict of interests.
We thank Fernando Vázquez Vázquez for designing the figures.
Please cite this article as: Ferreiro L, Porcel JM, Valdés L. Diagnóstico y manejo de los trasudados pleurales. Arch Broncopneumol. 2017;53:629–636.