Introduction
Sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome (SAHS) constitutes a recognized public health problem both because of its high prevalence in the general population and the morbidity and mortality it causes.1 If we consider an apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) over 10 together with the presence of excessive daytime sleepiness to indicate a diagnosis of SAHS, then the prevalence of SAHS among the middle-aged in Spain is estimated to be approximately 3% to 3.5%.2
SAHS should be diagnosed by polysomnography (PSG), although a valid diagnosis can be established by respiratory polygraphy that has been properly validated for populations with high or low probability of the diagnosis.3,4 Nevertheless, diagnosis is usually delayed significantly because the few sleep laboratories that are available are working at capacity.5 Considering the demonstrated relation between SAHS and a 2- to 7-fold greater likelihood of a patient having a traffic accident,6,7 an increased risk of cardiovascular disease or related death,8-11 and the great efficacy of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) treatment on the main symptoms,12,13 the search for alternative diagnostic approaches would seem to be a priority, particularly in the effort to identify the most severe forms of the disease and initiate early treatment until a sleep study can confirm the diagnosis.
Therefore, various suggestions--from subjective clinical assessment14 to the application of clinical,15-21 functional,22 or anthropometric23 parameters--have been put forth for identifying a priori the likelihood that a patient has SAHS or a certain AHI. Among the range of options, the ones most often studied have been clinical parameters. Several studies have evaluated their role as diagnostic tools through the creation of predictive models using multivariate analysis.14,15,18-21 Results have varied, although the models generally have high sensitivity (between 78% and 95%) and low specificity (between 41% and 63%) for AHI cut points between 5 and 20 and different prevalences of SAHS in the studied population.24
For Spain, the Spanish Society of Pulmonology and Thoracic Surgery (SEPAR) has issued a series of recommendations for treating SAHS patients, establishing an arbitrary AHI threshold of 30 to distinguish patients who, depending on their symptoms and cardiovascular history, will be most likely to respond to CPAP treatment.12 Accordingly, we believe that predicting which patients are likely to have an AHI ≥30 would have useful therapeutic application and allow CPAP treatment to reach the most severe cases early in the disease (provided clinical criteria and medical history are sufficient to warrant prescription), while waiting for tests to confirm the diagnosis. At least such an approach would allow such patients to have priority when scheduling tests. We have not found any studies in the Spanish literature on the diagnostic value of clinical parameters for predicting an AHI ≥30 in patients referred for specialist consultation. Therefore, the present study was designed to analyze the predictive value of such parameters relative to an AHI cut point of ≥30.
Material and Methods
All patients referred to our service with a suspected diagnosis of SAHS from January 2001 through August 2002 were studied. Our respiratory medicine department is part of a first-referral regional hospital that provides specialist care to a population of 60 000. SAHS was suspected if 1 of 3 cardinal symptoms was reported: chronic snoring, excessive daytime sleepiness, or observed apneas. Patients with daytime respiratory insufficiency or congestive heart failure were excluded. All patients were given a polygraph test using the AutoSet® (AS) Portable Plus II (ResMed Corp, Sydney, Australia). When the AS auto-CPAP device is set in diagnostic mode, various respiratory variables and heart rate can be recorded. Nasal airflow is measured by a cannula with a pressure transducer and oxygen saturation by a digital pulse oximeter, apneas are counted according to the patient's position by a body position sensor and thoracoabdominal movements are recorded by way of signals from an elastic band with a piezoelectric sensor. Automatically, using appropriate software (Autoview 98, version 2.0), the AS calculates the AHI as well as the apnea index and the hypopnea index by subtraction of each of the previous 2 variables. Although the AS does not permit the total apnea index to be changed, each apnea can be classified manually as obstructive, mixed, or central with information from recordings of respiratory effort provided by the thoracoabdominal band. A respiratory event was defined as apnea when nasal airflow fell more than 75% and as hypopnea when it fell between 50% and 75%, for longer than 10 seconds in each case. The AHI was defined as the number of respiratory events (apneas or hypopneas) per recording hour. All data were calculated in function of total recording time. All tests were performed in dedicated hospital rooms prepared by trained personnel. Patient characteristics (age and sex), anthropometric data (body mass index [BMI] in kg/m² and neck circumference in centimeters), medical history (mainly cardiorespiratory signs such as hypertension, cardiac or cerebrovascular events, bronchial asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), signs and symptoms (daytime sleepiness by a validated Spanish language version of the Epworth test,25 the existence of observed apneas and their frequency, and the occurrence of asphyxia), and the referring caregiver's subjective feeling (dichotomized) as to each patient's probability of having an AHI ≥ 30. A diagnosis of hypertension was established according to the recommendations of the World Health Organization.26 The morning after the polygraph test, the patient filled in a form about his or her subjective feeling about the amount (in hours) and quality (goodaveragebad) of sleep. Tests were considered valid if the patient reported having had at least 3 hours with a minimum sleep quality estimated as average. Tests were considered invalid if there was a technical failure or if the patient had disconnected the device and recording had not lasted at least 3 hours. In both cases, the polygraph was repeated. SAHS was diagnosed if the AHI was ≥ 10.
Statistical Analysis
The commercial statistics software packet SPSS 9.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois, USA) was used. Quantitative variables were reported as means (SD) and qualitative variables as absolute values followed by percentages between parentheses. Normal distribution was checked using a Kolgomorov-Smirnov test. The sample was divided into 2 groups: group 1 consisted of patients with an AHI ≥ 30 and group 2 consisted of those with an AHI <30. To select the appropriate variables for a logistic regression model to calculate the likelihood of an individual's belonging to each of the 2 groups, a bivariate analysis was first performed for all variables studied using a Student t test or a χ² test for quantitative or qualitative variables, respectively. A P value less than .20 was established as significant for between-group comparisons for selecting terms that were initially candidates for the model. Once the initial variables were identified, quantitative terms were converted to qualitative ones to facilitate the clinical application of the model. Conversion was performed by constructing curves of diagnostic yield (a receiver operating characteristic curve) to determine the optimal cutoff points for each variable to maximize diagnostic yield. The statistical program was designed to eliminate terms entered into the model that presented colinearity such that they gave redundant information, selecting the best models with a P value of .05 for entering a variable and a P value of .10 for eliminating it by forward selection (Wald statistic). Once the definitive model was obtained, the P value (individual probability of belonging to group 1 or 2) that would establish the largest percentage of correct diagnoses was calculated. With these data, we calculated sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), posttest probability, negative predictive value (NPV), diagnostic accuracy, pretest probability or prevalence, along with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI), and the diagnostic and predictive capacity of the chosen model. Finally the model was validated prospectively using the same terms for diagnostic yield.
Results
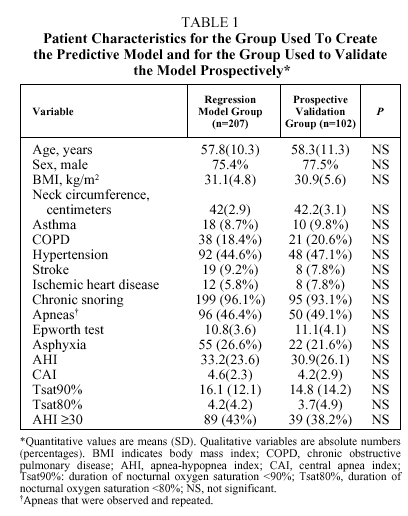
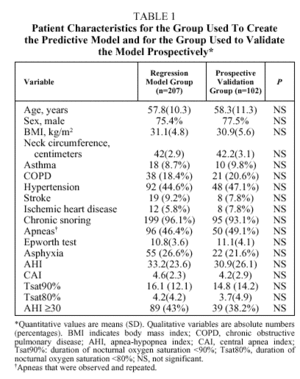
The number of patients initially enrolled was 329. Patients were excluded if they had daytime respiratory insufficiency (n=10), congestive heart failure (n=3), declined to participate (n=5), or died before the study took place (n=2). Therefore, 309 patients (76.4% men) entered into analysis. Their mean (SD) age was 58(13.45) years (range 24-83 years). Seventy-three percent were referred from primary care, 15% came from an otorhinolaryngologist, and 12% from a variety of internal medicine specialists. Data from 207 patients were analyzed retrospectively to construct a logistic regression model and the resulting equation was validated prospectively with data from the remaining 102 patients. No significant differences were found between the patient characteristics for the two groups, as shown in Table 1.
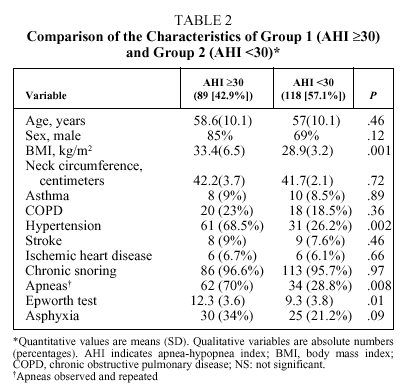
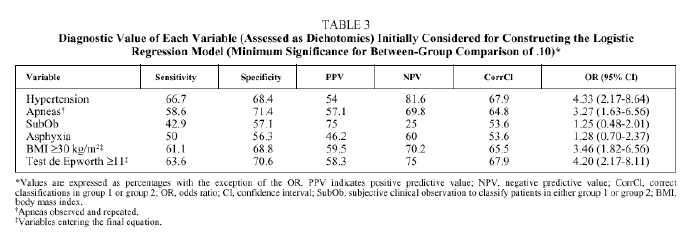
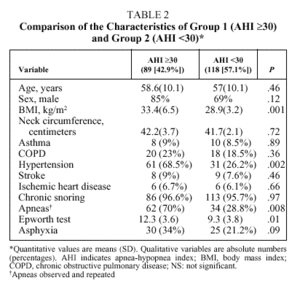
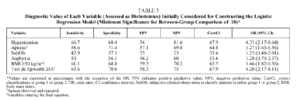
Bivariate analysis identified variables that were candidates for inclusion in the model from data available for the set of 207 patients initially analyzed (Table 2). BMI, the presence of observed and repeated apneas, the presence of hypertension, subjective clinical suspicion, Epworth test score, and the occurrence of asphyxia were significantly more frequent or higher in group 1 patients (AHI ≥ 30). To convert quantitative to qualitative variables, the cut points that best distinguished between groups 1 and 2 were a BMI ≥ 30 and an Epworth test score ≥ 11. The diagnostic values of individual variables entered into the model are shown in Table 3.
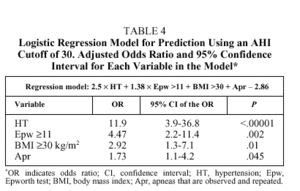
The best regression equation (n=207) was as follows:
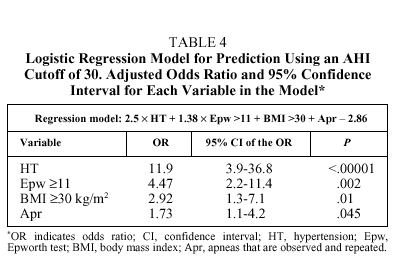
logit P = 2.5 HT + 1.5 Epw + BMI + 0.6 Apr2.1
where logit P is loge(1-p)/p, HT is the presence (1) or absence (0) of hypertension, Epw, is an Epworth test score ≥11 (1) or <11 (0); Apr is the presence (1) or absence (0) of observed and repeated apneas, and BMI is ≥30 (1) or <30 (0). The levels of significance and the odds ratios (OR) and their corresponding 95% confidence intervals are shown in Table 4. The best cutoff point (best P value) for classifying individuals as belonging to group 1 or group 2 was .5. With these data the overall diagnostic capacity of the model was as follows: sensitivity 80.2% (95% CI, 75%-86%), specificity 93.4% (95% CI, 89%-95%), PPV 89.6% (95% CI, 84%93%), and NPV 86.9% (95% CI, 81%-90%). The percentage of correctly classified patients was 87.9%, meaning there were 11 false positives and 14 false negatives. The false positives had significantly higher Epworth scores than the rest of the patients [15(3) vs 8(3), P<.001], whereas there were significantly more hypertensive patients among the false negatives (79% vs 44.6%; P<.008). Therefore, if the pretest probability of correctly classifying an individual (prevalence of patients with an AHI ≥30 on the polysomnographic study) was 43%, the posttest probability (after applying the logistic regression model) was 89.6%, indicating a 46.6% gain in correctly classified patients (P>.0001).
The following results were obtained when the model was applied prospectively (n=102): sensitivity 83.1% (95% CI 79%-91%), specificity 91.1% (95% CI 85%-96%), PPV 87.1% (95% CI 84%-95%), NPV 84.5% (95% CI 76%-91%), percentage correctly classified 87.3%, pretest probability 38.2%, posttest probability 87.1%, and gain in correctly classified patients 48.9% (P>.0001). There were no significant differences observed in the results for the group from whose data the logistic regression model was derived and those for the group used to validate the model.
Discussion
Clinical parameters for patients referred to the respiratory medicine specialists with suspected diagnoses of SAHS had high predictive value for identifying those with an AHI ≥30. This finding may be useful for making early treatment decisions while waiting for PSG to confirm the diagnosis or at least for assigning priority to such patients when scheduling tests.
Several studies have sought to find a diagnostic procedure for identifying patients with SAHS or for predicting various AHIs before PSG, as part of an effort to avoid more expensive and less readily available diagnostic tests as well as to initiate early CPAP treatment under the assumption that patients usually face fairly long waiting lists.14-23
Among such studies have been those using unusual lung function parameters,22 measures of upper airway structures,23 or calculations performed with complex neural network computer programs.19 All have been shown to have considerable diagnostic value for identifying SAHS patients but little practical clinical utility given their complexity or lack of availability.
The most often studied parameters have been the clinical signs and symptoms that are easiest to see and measure. Studied individually, such clinical variables have not had acceptable predictive value for diagnosing SAHS.18 Only neck circumference has demonstrated a certain degree of predictive value in some studies,27 although some authors conclude that that measurement may combine linearly with other variables such as age, sex, or BMI and, therefore, would provide redundant information.1518 We found no significant differences, however, between neck circumference in group 1 (AHI ≥30) and group 2 (AHI <30) patients. The reported predictive value of this variable may only appear when lower cutoff points are used (<20) and may lose its power to discriminate when disease is more severe. Other clinical variables such as the presence of hypertension, observed apneas, BMI or excessive daytime sleepiness have been reported to have modest diagnostic value when studied individually using an AHI cutoff between 5 and 20, usually because those variables have low NPVs.18 Deegan et al,15 however, found that although clinical variables studied individually have low NPVs and sensitivities, but very high PPVs and specificities, at low AHI cutoffs (≥10), NPV and sensitivity increase considerably while PPV and specificity decrease only moderately as higher cutoffs are chosen (≥20), with a consequent increase in overall diagnostic value. Our results suggest that the aforementioned variables have better-than-average value for distinguishing patients with an AHI ≥30, with correct diagnoses exceeding 65% in most cases. Nevertheless, because this improvement in diagnostic capability for high AHI cut points is still modest, the clinical application for individual variables is still scarce. Finally, the clinician's subjective guess about the diagnosis did not have predictive value; in other studies, as in our stu dy, the percentage of correct diagnosis generally fails to exceed 50% to 60%.14 As a result, various combinations of clinical variables have been used in regression models to try to predict the presence of SAHS for different AHI cut points (usually between 5 and 20) in pati ents referred to sleep clinics.14,15,18,19,21 Results have varied depending mainly on the probability of having SAHS based on symptoms and on the AHI cut point used for diagnosis, although sensitivity has usually been high (>85%) and specificity low (<55%) for AHI cutoffs between 5 and 20.20 With such results, these equations may have value for ruling out the diagnosis but not for confirming it or for supporting early treatment.
The logistic regression model from our study showed excellent ability to predict which patients would have an AHI ≥30. The equation includes 4 variables typical of predictive models published to date: the presence of hypertension, the presence of observed and repeated apneas, the Epworth test score, and BMI. All of them are dichotomized, and the last two are relevant to cutoffs of 11 and 30, respectively. The OR for each variable seems to indicate that using higher than usual AHI cutoffs leads to a significant change in the relative weight of each variable's predictive value, the greatest changes occurring for hypertension (OR=11.9) and a high Epworth test score (OR=4.47) as opposed to age, sex, presence of apneas, or anthropometric variables (neck circumference or BMI), although there is no change in which variables finally enter the model. It is important to point out that the presence of apneas only had predictive value when the sleeping partner indicated that they were repeated. It seems logical to think that most snorers experience apneic events normally and even that a few are pathological. The sleeping partner becomes aware of such events and reports them faithfully, even when apneas are not repeated often enough to define a high AHI. This situation can lead to overestimating the existence of isolated nighttime apneas. Our study would therefore not apply to subjects without companions who can become aware of the existence of such apneic events, for example to individuals who live or sleep alone (12% in our patient series).
Of the 25 patients (12.1%) who were not correctly classified by the model, 11 were false positives and 14 were false negatives. A careful look at these patients indicates that the false positives were different from the other patients in having very high Epworth test scores (over 15). All had been referred for PSG because of excessive daytime sleepiness in spite of having a negative AS because of the "relatively" low NPV of the AS (78%) in comparison with that of PSG in patients similar to those in our series. Three had increased upper airway resistance syndrome and were finally treated with CPAP, 4 had SAHS (with AHI findings of 19, 22, 33, and 29), and the remaining 4 had negative PSG findings and are undergoing tests to investigate the reason for pathological daytime hypersomnia. The false negatives were mostly hypertensive individuals. Hypertension in our study was not actively investigated but was recognized in the medical history.
The AS polygraphic study used instead of PSG assessment is logically of limited diagnostic value according to our study. However, it is important to point out that this device is widely validated in the literature for different cutoff points and prevalences of SAHS.28-30
The reasons for our model's high diagnostic and predictive ability are complex. The explanation for the higher overall value of the model may lie in 2 features of our study: the high AHI selected as the cut point and the high pretest probability. For none of the variables in the final model was the sensitivity low; rather they all had moderate sensitivites, between 50% and 67%. If each variable is considered an individual diagnostic test, the use of several alongside one another to classify patients (as occurs in the use of predictive equations) would increase sensitivity and NPV considerably. The parallel decrease in specificity and PPV that would correspond to the increase in sensitivity might be compensated for, in the case of specificity, by the high cut point chosen to classify the patients and, in the case of PPV, by the high pretest probability for that cut point in our series. Finally, the high specificity values and PPV for the individual variables in the equation may influence the behavior of the model. Therefore, the diagnostic value of our model may change if it is applied to different patient populations.
In conclusion, we think that clinical parameters may have considerable predictive value for distinguishing patients with an AHI ≥30 among those referred to a respiratory medicine specialist, allowing the eventual mention of such parameters in SEPAR recommendations12 for the early treatment of SAHS. Such inclusion may save considerable time in initiating CPAP treatment for the patients who are most ill or may serve to give priority to severely ill patients when scheduling diagnostic tests.
Correspondence: Dr. M.A. Martínez García.
Unidad de Neumología. Servicio de Medicina Interna.
Hospital General de Requena.
Paraje Casa Blanca, s/n. 46340 Requena. Valencia. España.
E-mail: med013413@nacom.es
Manuscript received January 13, 2003.
Accepted for publication April 29, 2003.