Introduction
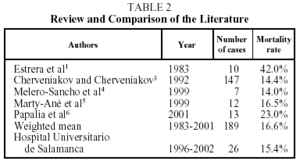
Mediastinitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of the connective tissues of the mediastinum. The acute process is generally due to gram-positive cocci infections which produce purulent secretions that collect in the mediastinum. Acute mediastinitis is a rare, aggressive disease with a high mortality rate. A clear, complete description of diagnostic criteria for mediastinitis is provided by Estrera et al1, and in Archivos de Bronconeumología, González-Aragoneses et al2 reported 2 cases of descending necrotizing mediastinitis originating in the oropharynx, recommending posterolateral thoracotomy for all mediastinitis cases. The literature describes mortality rates ranging from 14% to 42%.1-6 High mortality correlates with delayed diagnosis or treatment7 whereas early treatment seems to reduce mortality.8 The present study is a retrospective review of patients who were initially diagnosed and treated for acute mediastinitis in the department of thoracic surgery of the Hospital Universitario de Salamanca, Spain, from January 1994 to March 2002.
Clinical Observation
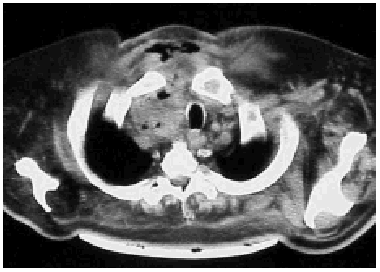
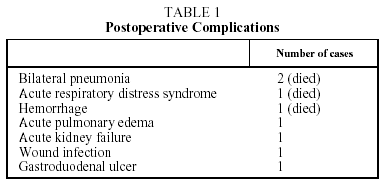
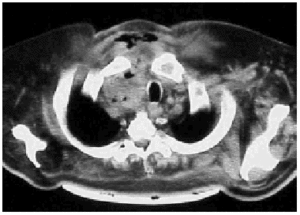
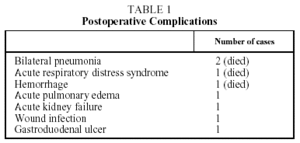
During the study period we treated 26 cases (20 men and 6 women) for acute mediastinitis. The mean age of the patients was 55 years (range 2685 years). In 17 cases (64%) mediastinitis originated in the esophagus: 8 (30%) occurred after resection of esophageal carcinoma and 9 (34%) were secondary to esophageal perforation. Four of the perforations were due to spontaneous rupture (Boerhaave syndrome), 4 were iatrogenic, and 1 was caused by ingestion of a foreign body (a lamb bone). In 6 cases (23%), the cause was oropharyngeal infection due to dental or peritonsillar abscess (Figure), and 3 cases (12%) were secondary to median sternotomy wound infection. Mediastinitis was associated with pleural empyema in 20 cases (76.9%) and with peritonitis in 1 case (3.5%). All diagnoses were confirmed by computed axial tomography. In the cases with infection originating in the esophagus, contrast-enhanced images were obtained to locate the perforation site. Diagnosis was reached within 12 hours in 15 cases (56.7%) and within 24 hours in 8 (30.8%). Diagnosis and, therefore, treatment were delayed for the remaining three patients (12.5%). All the patients underwent thoracotomy except one who was treated by means of chest tube drainage. In addition to mediastinal debridement and drainage, 10 patients underwent esophagectomies or resection of the esophago-gastric reconstruction (deferring a new reconstruction), 5 received primary sutures of the esophagus covered with an intercostal muscle or pericardial fat flap, 1 was reconstructed with a greater pectoral muscle flap, and 1 underwent sternectomy plus intrathoracic omental transposition. The patients required a mean 3.33 (range 25) surgical procedures in separate operations not counting deferred reconstructions. Four patients (15.4%) died: 2 in relation to esophageal disease and 2 with descending necrotizing mediastinitis. Postoperative complications are summarized in Table 1.
Figure. Mediastinitis due to oropharyngeal infection. Cervical subcutaneous emphysema and purulent secretions in the right paratracheal region.
Discussion
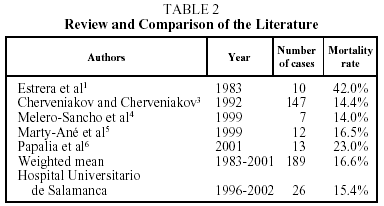
Most authors have described an increase in the incidence of acute mediastinitis in recent years.9-13 Such an increase, if real, might be the result of a rising number of procedures on the esophagus or a greater interest on the part of authors in the diagnosis and treatment of the problem. Some have reported a relation between early diagnosis and treatment and lower mortality10,13 and have also indicated that certain nonspecific problems, such as an initial diagnosis of pneumothorax, pneumoperitonea, sepsis, or shock, could cause delay in reaching a full diagnosis and treatment.10 Diagnosing acute mediastinitis through conventional x-rays alone may delay treatment, and if mediastinitis is suspected based on clinical signs, computed axial tomography should be performed. Once diagnosis is confirmed, aggressive treatment is recommended.14 Aggressive treatment is defined as complete mediastinal debridement with excision of necrotic tissue, and, if necessary, insertion of multiple mediastinal, pleural, and cervical drains. Posterolateral thoracotomy is the approach of choice15,16 because it allows good exposure of the mediastinal compartments. Median sternotomy is inappropriate as it exposes the patient to the additional risk of sternal osteomyelitis. Sternectomy plus omental muscle flap surgery should be reserved for cases of severe sternal osteomyelitis.17 When mediastinitis originates in the oropharynx, trans-cervical drainage is insufficient. Drainage guided by computed tomography may be useful, but only in initial stages and in some cases of post-sternotomy mediastinitis, according to El Oakley and Wright19 and Berg et al.20 For patients with spontaneous rupture or iatrogenic perforation of the esophagus, the esophagus may be sutured directly if diagnosis is early and no serious underlying esophageal disease is present.3 In the remaining cases with infection originating in the esophagus, esophagectomy with gastrostomy and jejunostomy are indicated. In cases of mediastinitis secondary to gastroplasty or coloplasty, the reconstruction should be removed in order to proceed with a second reconstruction at a later time. The literature describes an overall mortality rate ranging from 14% to 42%, from which we have calculated a weighted mean of 16.6%, which is similar to the mortality rate of 15.4% in our series (Table 2). In conclusion, we strongly advise a high degree of suspicion, early diagnosis, and initiation of aggressive treatment.
Correspondence: Dr. P. Macrí.
Sección de Cirugía Torácica. Hospital Universitario de Salamanca.
P.º San Vicente, 58. 37007 Salamanca. Spain.
E-mail: paolomacri@katamail.com
Manuscript received February 18, 2003.
Accepted for publication April 18, 2003.