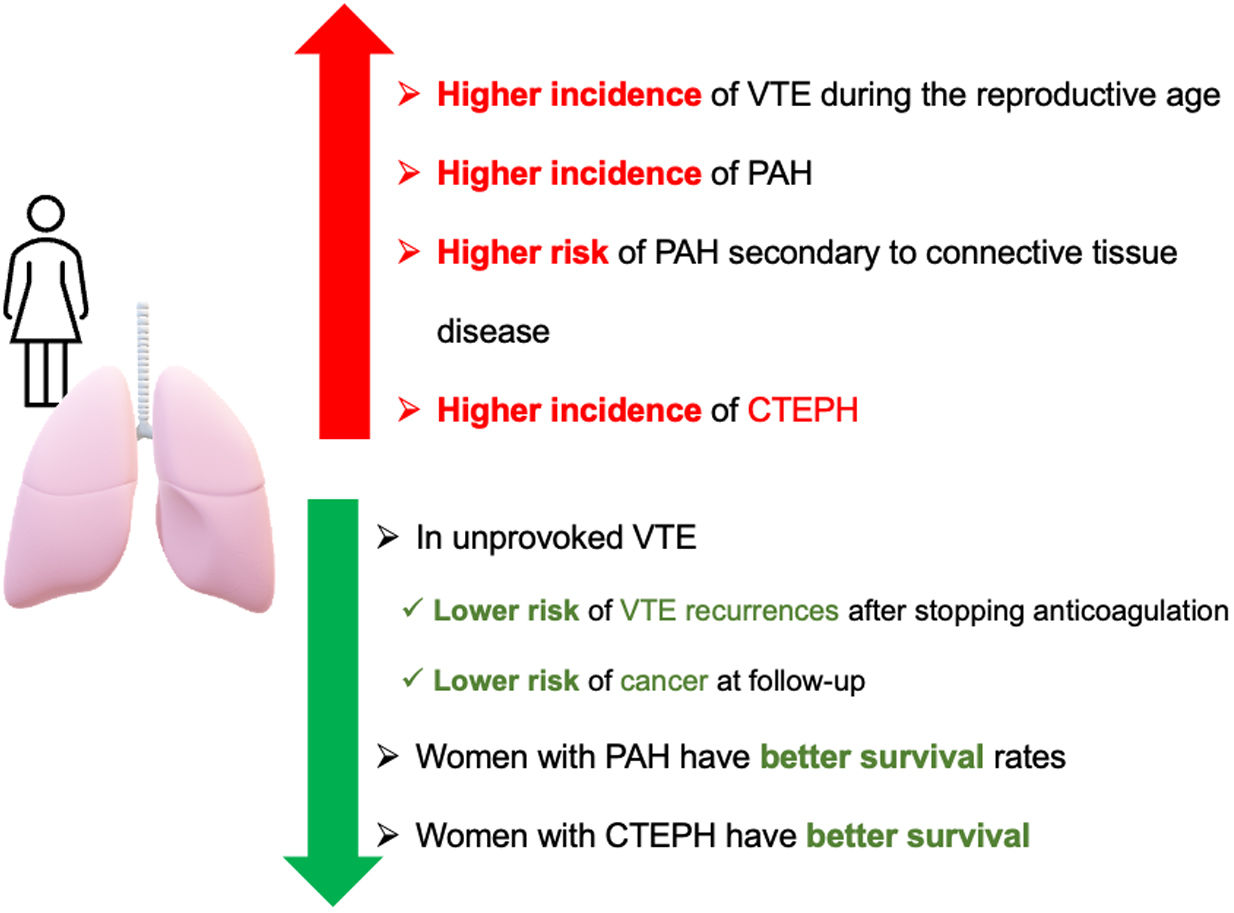
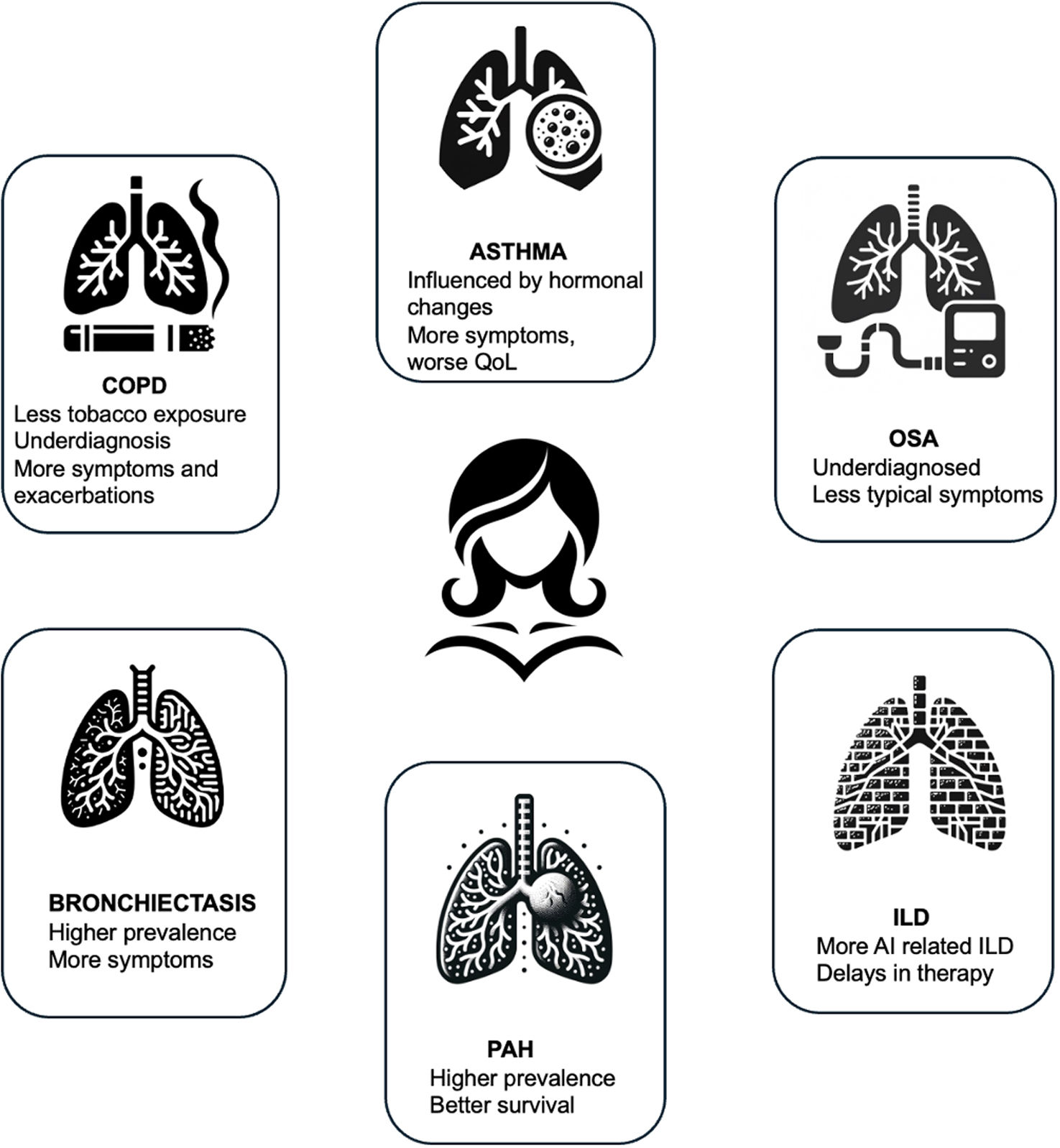
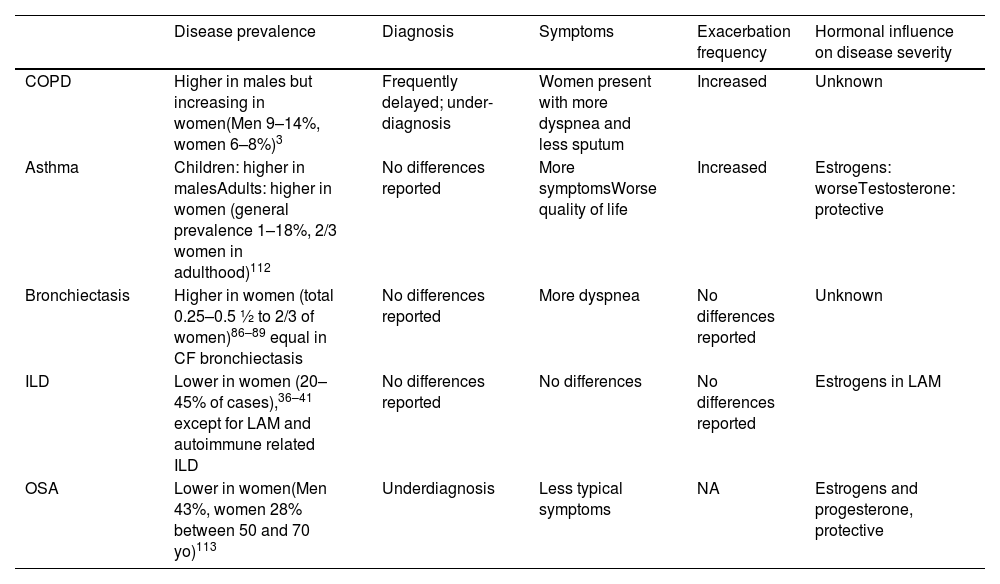
Respiratory diseases exhibit diverse patterns in prevalence, clinical presentations, and outcomes between men and women. Historically, certain conditions were more prevalent in men, but trends have shifted, highlighting the need to understand sex disparities in respiratory health. Social, environmental, and healthcare changes have reshaped the landscape of respiratory diseases, complicating diagnosis and treatment. Moreover, the underrepresentation of women in clinical trials has limited our understanding of their specific needs. In this review, we explore the sex differences in the prevalence, clinical characteristics, and presentation of respiratory diseases, emphasizing the importance of tailored approaches to diagnosis and management. By recognizing and addressing these disparities, we can advance toward more equitable and effective respiratory healthcare for all individuals.
The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more