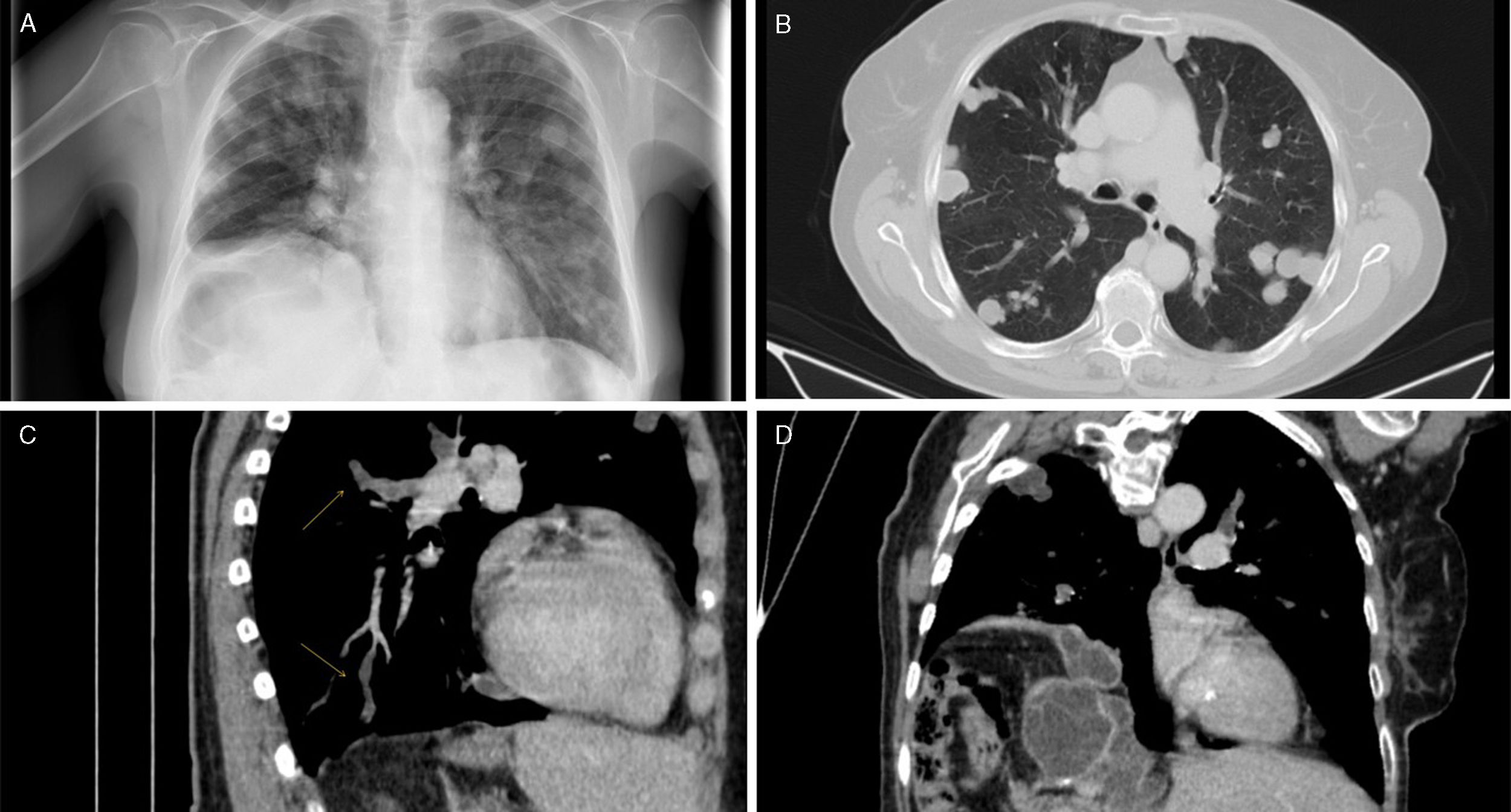
We report the case of a 76-year-old woman, non-smoker, operated for hepatic hydatid cysts 8 years previously. She consulted with a 4-day history of cough, purulent expectoration without fever, and dyspnea. Examination was significant for painless hepatomegaly. Chest radiograph (Fig. 1A) showed multiple nodules of various sizes in both lung fields and elevation of the right hemidiaphragm. Differential diagnosis was performed, taking into account metastasis, lung cancer, and hydatidosis. Chest CT showed nodular images of fluid density (Fig. 1B), some of which were located inside the arterial branches (Fig. 1C). The right diaphragmatic dome showed another hepatothoracic transitional cyst (Fig. 1D). Anti-Echinococcus granulosus IgG antibody titers (ELISA) were positive. Treatment began with albendazole.
Hydatidosis is a zoonosis caused by tapeworm larvae of the Echinococcus genus. Its main reservoir is dogs, with humans acting an accidental host by contact with dogs and consumption of contaminated food. Latency is long, with slowly growing cysts located mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, the lungs or other organs of the body.1 Diagnosis is clinical, radiological and serological. Clinical symptoms are usually due to rupture, superinfection, or anaphylaxis. This disease can recur after surgery of the primary cyst, dissemination of cyst contents – as in the present case–, or after rupture.2 However, Echinococcus granulosus can penetrate the filter of the vena cava, without requiring the presence of liver cysts or a history of surgical intervention. So, although multiple pulmonary nodules are most often metastatic tumors, multiple pulmonary hydatidosis should be taken into account in the differential diagnosis.
Please cite this article as: Martín Asenjo M, Martín Guerra JM, Álvarez Álvarez PL. Nódulos pulmonares a estudio. Arch Bronconeumol. 2019;55:379.