Despite the importance of spirometry, its use and quality are limited in the Primary Care setting. There are few accredited training programs that have demonstrated improvement in the quality of spirometric studies. In this paper, we analyze the short- and long-term effectiveness of a supervised training program for performing and interpreting spirometries.
MethodologyOurs is an intervention study with before and after measurements. The target population included teams of physicians and nursing staff at 26 health-care centers in the area of Vigo (Galicia, Spain). The structured training program involved 2 theoretical and practical training sessions (that were 2months apart), an intermediate period of 30 supervised spirometries performed in the respective centers and weekly e-mail exercises. Effectiveness was evaluated using exercises at the beginning (test 1) and the end (test 2) of the 1st day, 2nd day (test 3) and one year later (test 4), as well as the analysis of spirometries done in month 1, month 2 and one year later. Participants also completed a survey about their satisfaction.
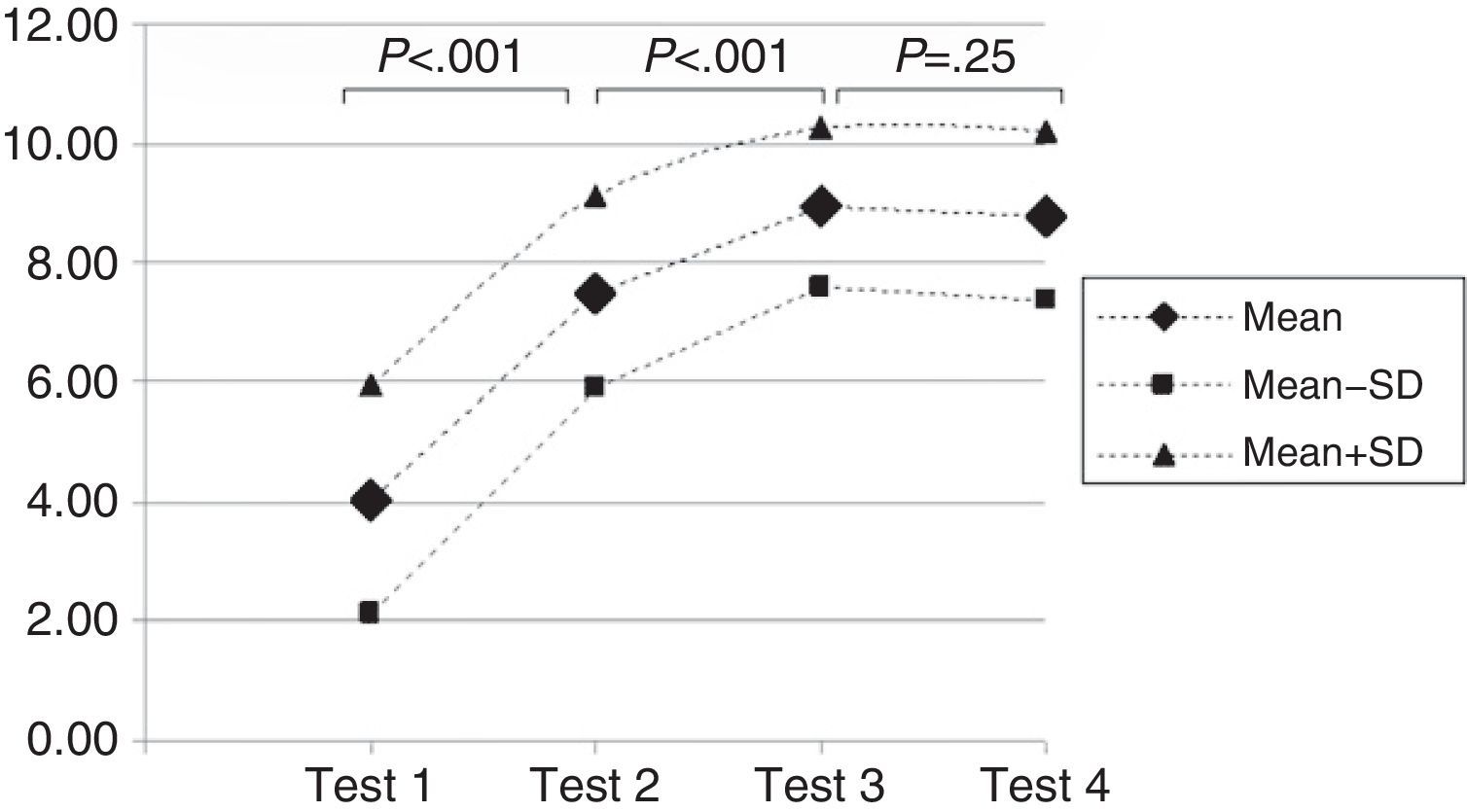
Results74 participants initiated the program; 72 completed the program, but only 45 participated in the one-year evaluation. Mean test scores were: 4.1±1.9 on test 1; 7.5±1.6 on test 2; 8.9±1.3 on test 3, and 8.8±1.4 on test 4. During month 1, the percentage of correctly done/interpreted tests was 71%, in month two it was 91% and after one year it was 83% (P<.05).
ConclusionsA training program based on theoretical and practical workshops and a supervised follow-up of spirometries significantly improved the ability of Primary Care professionals to carry out and interpret spirometric testing, although the quality of the tests diminished over time.
A pesar de la importancia de la espirometría, su utilización y calidad son limitadas en atención primaria. Existen escasos programas formativos acreditados que hayan demostrado una mejora de la calidad de los estudios. En este trabajo analizamos la efectividad a corto y a largo plazo de un programa de formación tutelado sobre la realización e interpretación de espirometrías.
MetodologíaEstudio de intervención, con medición antes-después. Población diana: equipos de médicos/as-enfermeros/as de 26 centros de salud del área de Vigo. Programa formativo estructurado con 2 sesiones teórico-prácticas (separadas 2 meses), un periodo intermedio de tutelado de 30 espirometrías realizadas en sus centros y ejercicios semanales enviados por e-mail. Evaluación de la efectividad mediante ejercicios al inicio (test 1) y al final (test 2) de la primera jornada, en la segunda jornada (test 3) y tras un año (test 4). Análisis de las espirometrías realizadas en el mes 1, en el mes 2 y tras un año. Se realizó también una encuesta de satisfacción.
ResultadosIniciaron 74 alumnos, finalizaron 72, con solo 45 en la evaluación al año. La puntuación media en los test fue: 4,1±1,9 en test 1; 7,5±1,6 en test 2; 8,9±1,3 en test 3, y 8,8±1,4 en test 4. En el mes1 el número de pruebas correctamente realizadas/interpretadas fue del 71%, del 91% en el mes2 y, tras un año, del 83% (p<0,05).
ConclusionesUn programa formativo basado en talleres teórico-prácticos y el seguimiento tutelado de espirometrías hechas en sus centros mejora significativamente la capacidad de los profesionales de atención primaria para la realización e interpretación de esta prueba, aunque la calidad de los estudios decrece con el tiempo.
Spirometry, as a basic element of the lung function examination, should be considered a fundamental technique in the early detection, diagnosis, severity assessment and follow-up of chronic respiratory diseases, especially those with chronic airflow obstruction.1–4 It is an inexpensive, non-invasive technique that requires little time, so is ideally suited for use in primary care (PC). There is a need for it to become more widespread in this setting for the diagnosis of a disease as prevalent as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and indeed it has been recommended by all of the scientific societies.5–7 However, increasing the use of spirometry in this healthcare field remains an unresolved issue, and the reality of care is far from ideal, as published studies indicate limited access to the test, lack of training for its implementation (which translates into poor quality tests) and difficulty in classifying respiratory diseases using the results.2,4,8–12 In order to be able to improve these aspects, it is imperative to have good training and continuing education programs that certify the expertise of PC professionals, thereby ensuring spirometry tests of sufficient quality to enable clinical decisions to be taken using them.2,12 This is one of the objectives of the Spanish health system's National Strategy on COPD.7 Although other options for implementing spirometry in PC have been studied, such as the possibilities offered by information and communication technologies (ICT), with variable results, professional training remains essential.2,13–15 Many training programs have demonstrated an improvement in the quality of studies performed, but the results and characteristics of the activities vary greatly15; in some of these, this improvement is not sufficient to ensure quality studies in a significant percentage of patients, and many have observed that the improvement is not maintained over time.2,13,16–19 Furthermore, there are very few studies published in Spain.14,15,20 The American Thoracic Society (ATS) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) have established well defined quality control criteria for spirometry, both for the equipment and the tests, but they do not include indications on strategies for ensuring sustained quality in fields where spirometry is performed by non-specialized professionals.15 For these reasons, the ERS is presently undertaking a project to harmonize and standardize spirometry training.21,22
The aim of this study was to analyze the short- and long-term effectiveness of a new theoretical-practical course for PC professional teams to improve both theoretical-practical knowledge and the quality of spirometries performed in the participants’ own health centers and their interpretation.
MethodologyThis was an intervention study, with before and after measurements, to improve the quality of spirometric studies. The target population was teams, made up of one member of the medical staff and another member of the nursing staff, from 26 health centers within the healthcare area of Vigo (Galicia, Spain). Participants presented voluntarily after an announcement made by the PC Management, unaware at any time that in addition to the training program, accredited by the Regional Continuing Education Committee of Galicia, its impact on the knowledge acquired and the quality of the studies performed in their clinical practice would be analyzed. The designer of the activity (AFV) and the tutors were pulmonologists from Complejo Hospitalario Universitario de Vigo (CHUVI) (Galicia, Spain). The course took place during 2010.
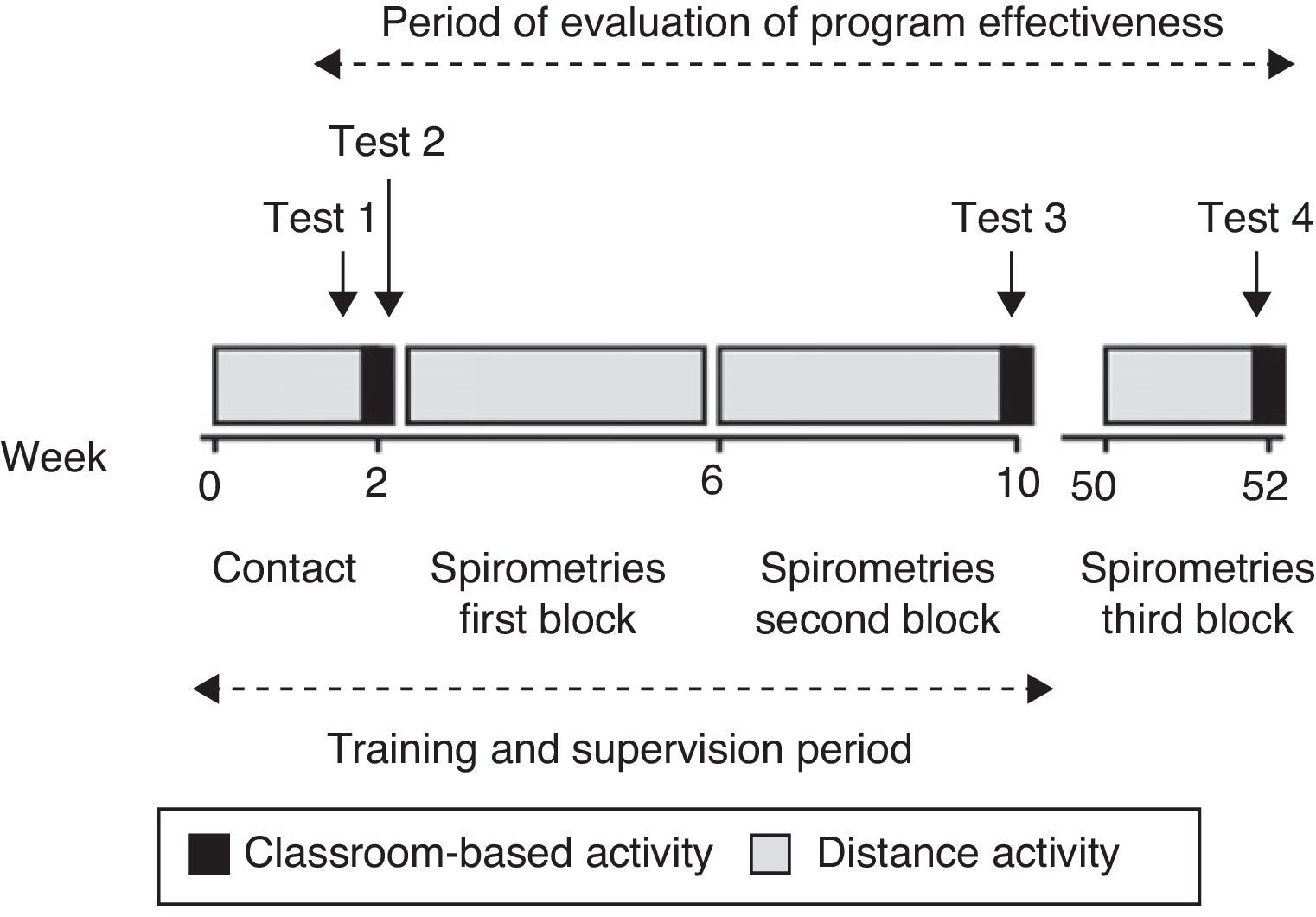
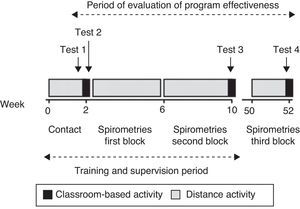
Structure of the Training ProgramThis was a structured program that included 4 well-differentiated stages, represented graphically (as is the analysis of its effectiveness) in Fig. 1.
- I.
Contact with the PC teams (preliminary phase). For 2 weeks, the tutors (or staff selected by them) traveled to the 26 participating health centers to make initial contact with the participants, and to assess the condition of each spirometer with which the practical part was to be carried out. If any defect was detected in the material or working order of the spirometers, it was brought to the attention of the PC Management, so that the problem could be resolved before the course began.
- II.
Initial theoretical-practical training day (first day). A 4h classroom session (2h of theory and 2h of practical exercises) was organized (one day per 13 teams), using scientific society recommendations as guidelines.23
During the first 2h of the session, the topics listed in annex 1 were taught. In the following 2h, the attendees performed 20 real practical exercises relating to validity, reproducibility and interpretation of spirometries of various complexities, and at least one spirometry (role-play) on another of the attendees; all exercises were corrected in situ by the tutors.
The theoretical content and practical exercises performed and corrected were given to the participants for use as reference material during the rest of the course.
- III.
Practical phase in their health centers under the supervision of the teaching team (supervised phase). For 2 months, the participants, organized in teams as mentioned, performed spirometry tests in their own centers (a minimum of 15 spirometries/month for each physician/nurse team, at least 3 with a bronchodilator test). This was a distance activity, during which the students could contact the teachers by e-mail or cell phone, to resolve any queries. The spirometries performed (without identifying the patient to maintain data confidentiality) and their corresponding interpretation, following the guidelines recommended during the theoretical training day, were sent by Galician Health Service (SERGAS) internal mail during the last week of each month to the teaching team (spirometries block 1 and 2). The pulmonologists reviewed all the studies and their interpretation, and issued an individual report with corrections, which was forwarded to each participating team by the same route. In this supervised phase, the participants also had to solve exercises from real cases (4 exercises), sent fortnightly by e-mail, in which they had to evaluate the acceptability and reproducibility of the tests, and interpret the baseline spirometries and cases with a bronchodilator test. The answers also had to be sent by e-mail within 2 weeks.
- IV.
Classroom session for reviewing knowledge, analyzing errors and assessment for passing the course (second theoretical-practical day). At this last 4h classroom session, which took place 2 months after the first session, there was a brief review, the mistakes made most frequently during the supervised phase were discussed and examined and finally the participants performed the theoretical and practical exercises required to be able to proceed to assessment and subsequent accreditation. Examination of the knowledge and abilities acquired included:
- –
A theoretical knowledge test (20 questions).
- –
Resolution of 20 practical cases: 5 to assess the reproducibility, 5 on acceptability, 5 to interpret a baseline spirometry and 5 to interpret a spirometry with a bronchodilator test.
- –
Correct performance of a spirometry test on another participant (role-play), in which the different aspects of the technique, explanation to the patient, correct performance of the maneuver, proper encouragement of the patient both at the start and during the entire maneuver and detection of possible errors committed were evaluated.
- –
The end-of-course evaluation included assessment of the spirometry tests sent during the supervised phase (number, quality), the answers to the fortnightly practical exercises and the score of the various evaluation exercises performed during the second classroom session (theoretical, practical exercises and role-play); a minimum score of 80% was required to pass the course. Depending on the score, each medical and nursing staff team from each health center would be graded as pass or fail.
Analysis of the Effectiveness of the ProgramTo evaluate the effectiveness of the program, all students answered a 10-question test on 5 practical cases with real spirometries, with 2 questions on each spirometry (test 1), in which they had to evaluate the validity of the test and its interpretation. To be able to analyze the improvement, this same exercise was also performed at the end of the first day (test 2) with other cases, in the second classroom session after the 2 months of supervision (test 3) and one year after the first activity (test 4). These tests were from different cases, but of similar complexity, selected randomly from a bank of cases performed by the teaching team itself. Annex 2 shows an example of a spirometry from those included in one of the tests, with its 2 corresponding questions.
Similarly, the validity and interpretation of spirometries performed in month 1, month 2 (both in the supervised phase) and one year after the start of the course were analyzed. To that end, all participants were contacted 10 months after the end of the activity, offering them the possibility of having a new evaluation and they were requested to provide studies carried out in the previous 2 weeks (spirometries block 3).
Finally, all participants also completed a standard satisfaction survey about various aspects of the activity carried out during the second classroom session.
All course participants gave their consent for inclusion in this study.
Statistical AnalysisThe overall results were expressed as percentages and absolute frequencies for the qualitative variables, and as mean and standard deviation (SD) for the numerical variables, except for the satisfaction evaluation, for which only the mean scores are available. Comparison of the discrete variables was performed using the Chi-squared test or Fisher's exact test. Quantitative variables were analyzed using the Students t-test. A P value <.05 was considered statistically significant. The analyses were performed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences, version 15.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA).
ResultsSeventy-four participants began training (37 teams) and 72 completed it (97.2%). The mean age of the participants was 48 (SD 8) years, 32% males, with professional experience of 22 (SD 10) years. Forty percent (40%) had previously attended a spirometry course, with a mean duration of 3 (SD 7) hours. According to the scale described, 90% of the professionals were considered competent, and of these, 22% were considered excellent (score close to 100% with correct answers to all fortnightly exercises sent by email).
At the end of one year after the start of the activity, only 45 of the competent participants (62.5%) could be reevaluated; in the remaining cases, it was not possible to contact them, mostly due to work transfer to other health areas.
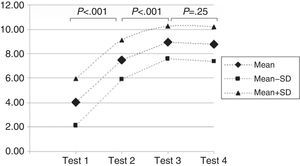
With respect to evaluation of the course effectiveness, the mean scores for each of the tests, out of a possible maximum of 10, were: 4.1±1.9 in test 1; 7.5±1.6 in test 2 (P<.001 between test 1 and 2); 8.9±1.3 in test 3 (P<.001 between test 2 and 3), and 8.8±1.4 in test 4 (P=.25 between test 3 and 4) (Fig. 2).
During the first supervised month, the number of spirometries correctly performed and interpreted was 370 of the 521 received (71%); in the second month, it was 562 of 619 (90.9%) (P<.0001). Of the 255 spirometries performed by participants in the one-year evaluation, 211 (83%) were valid and were well interpreted (P=.0004 compared to the result in month 1 and .007 compared to month 2).
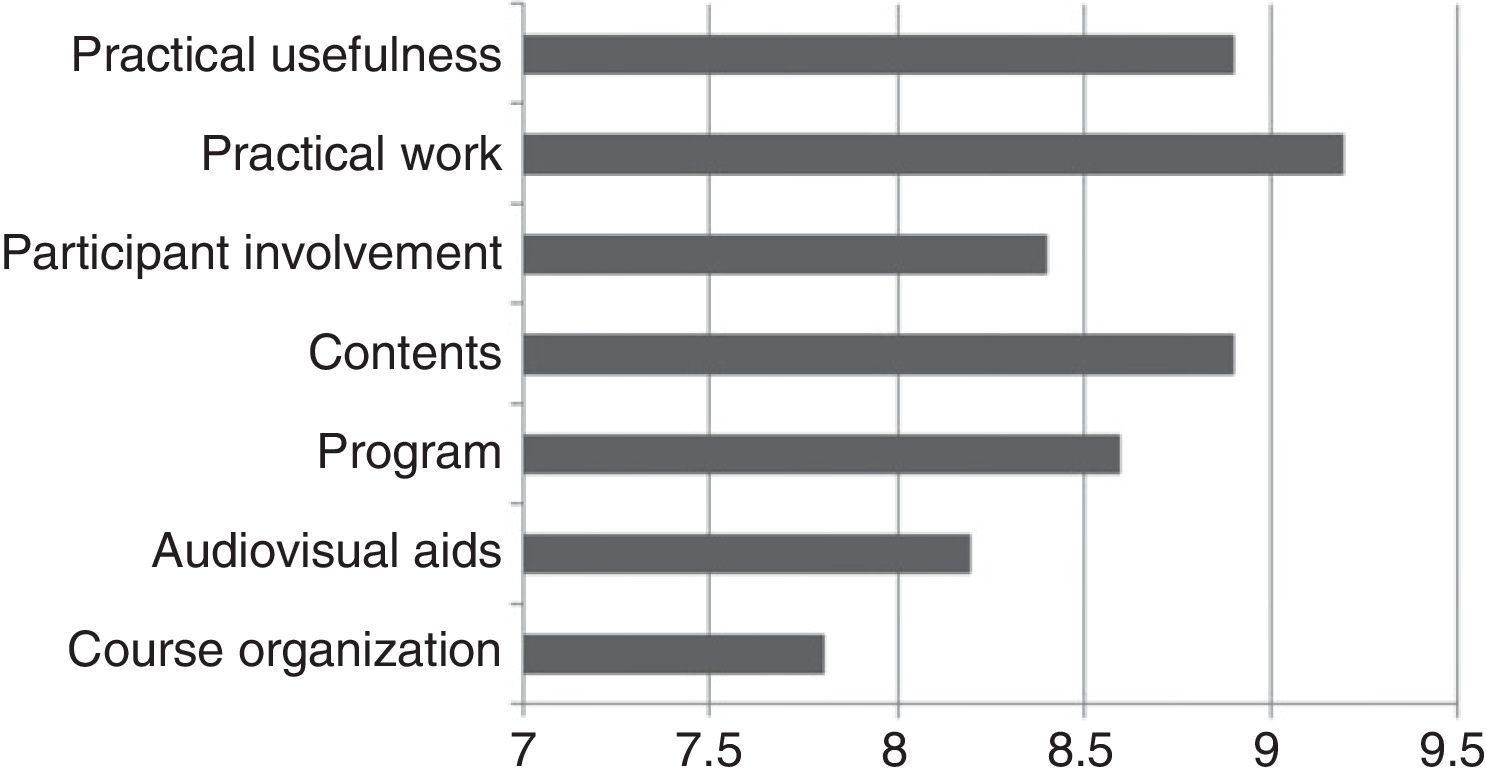
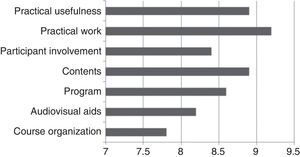
The results of the satisfaction survey completed by the participants are shown in Fig. 3, with an overall mean of 8.6 points out of a maximum score of 10.
DiscussionOver the years, since accepting that spirometry needs to be generally applied as an essential test for the study of respiratory diseases, various programs have been designed to train technicians in how to carry out this test correctly. This has become more important since the introduction of spirometry in PC, where studies must be performed in most professional cases with little previous training in lung function. The most widely used training method is theoretical-practical courses, lasting a few hours and of limited proven efficacy in the mid-long term.2 It has even been documented that a simple educational intervention, by a visit from a specialist to physicians and nursing staff explaining the spirometry technique improves the quality of testing and reduces referrals to specialized care for this reason.24 However, there are really very few training programs in which the results have been analyzed.
Based on these limited previous experiences, the training program designed and implemented by our group is new in that, added to the theoretical-practical classroom-based training days, the participants perform spirometries in their own centers for 2 months, with their own spirometers and under supervision. This allows them to have daily contact if required with the teaching team to resolve queries or problems. The studies they perform are reviewed and discussed to correct possible mistakes. With this training activity, we found that the theoretical knowledge of the participants improved significantly after the first classroom session, with the level of improvement increasing after 2 months of supervision, and remaining one year after the start of the activity. With respect to the number of studies performed by the participants in their own centers that were valid and correctly interpreted, this increased significantly in the second month of supervision with respect to the first, although it decreased after a further 10 months, albeit slightly.
In addition, the program had a high level of acceptance and participation, which is a very important aspect in these types of activities, and was due in part to the direct contact with the tutors during the 2 months of supervision. Only two members of one team who had started the course dropped out, owing to problems with the spirometry equipment in their center. Despite the strict control and evaluation system using multiple practical and theoretical exercises, the course results were satisfactory, with more than two thirds of the professionals passing the course and accredited as capable of performing and interpreting spirometries with sufficient quality for clinical decision making.
A further characteristic to highlight in this course is that the training given was similar for medical and nursing staff, because we believe that both must know how spirometry is performed and interpreted, although in practice the technicians are usually nursing staff and those who interpret the studies are medical staff.
Another possible strength of this type of training activity is that it allows the creation of working teams in each center made up of nursing and medical professionals, who could be a reference for the other center professionals in this technique, as well as acting as a link between the PC professionals and specialized care. Other possible benefits, in addition to improving the quality of the diagnoses of obstructive diseases such as COPD in this care setting, could be a reduction in the number of inappropriate referrals to specialized care, and the possibility of adjusting treatments based on the functional severity.
Training programs are not only intended to have spirometries performed in PC, but also that these studies are of sufficient quality to be able to take clinical decisions based on them. In our case, despite the major improvement and good initial results in the quality of the spirometries, these worsened discretely one year after completion of the activity, although they still remained at acceptable levels and were far superior to other studies.16 Eaton et al.16 also showed in a previous study that even taking part in a 2h theoretical-practical course significantly improved the number of valid recordings and reduced the frequency of errors, although these results diminished over time, improving again following a refresher workshop. However, this study found that the percentage of tests that met the requirements for acceptability and reproducibility according to the ATS was less than 15%, so these spirometries do not have sufficient quality for clinical decision making. Schermer et al.17 published their experience with a course consisting of two 2.5h sessions, one month apart. If visits from lung function technicians to the health centers were added to this, the validity of the spirometric tests in PC was maintained. Furthermore, in their case, the percentage of non-reproducible tests was similar in the spirometries performed in the PC centers by the trained technicians, with respect to those performed in the lung function laboratory, so they concluded that spirometries with adequate quality can be performed in PC.17 Thus, although there are few studies carried out in this respect, and with discordant results, it does seem that repetition in the weeks following the training activity improves results.2
One limitation of our study is that the reproducibility in the spirometries was not initially analyzed, since the participants only sent a printout of one of the maneuvers.
However, in view of the good results of the supervised training program presented here in our healthcare area (SERGAS) under the direction of the authors of this study, the same course was extended to the entire Galician region with minimal modifications, the main one being that it included an evaluation of the reproducibility, so that the participants had to send the best three maneuvers from each study. With the data from the first edition of the SERGAS course in the Vigo area, we analyzed the number of spirometries that were valid and had reproducible maneuvers (data not shown). We found that of the 244 spirometries received the first month, 84% were valid and reproducible; in the second month, of the 260 received, this percentage rose to 91.5%. Thus, we consider that the PC professionals trained in this program managed to perform spirometries that were of sufficient quality to be reliable and used in their clinical practice, at least in the early months after the start of the activity.
Another small limitation is that it was only possible to reevaluate 62.5% of the participants one year later, due in large part to the countless changes in the work place, especially with regard to nursing staff who, once trained, have to leave their post to cover other needs.
Using the data reported in this study, it could be of interest to propose a new project to evaluate whether holding periodic refresher workshops after completion of training could maintain the quality level of the spirometries in the longer term, which is probably the most significant weak point.
The training program presented here is an alternative to try to extend the use of spirometry in PC, and to improve the quality of the studies. Nevertheless, there are other options that may be equally useful and valid for this purpose, such as the use of telemedicine applications15 or performing spirometries online.14 The choice of the best method will depend on the possibilities of its implementation in each healthcare area, depending on different aspects, such as available infrastructures, location and characteristics of the PC centers at which it is aimed.14
In conclusion, we may state that this study shows how a spirometry training program aimed at PC professionals, which in addition to classroom-based theoretical-practical and online sessions includes a supervised phase with personalized correction of spirometries performed in their own health centers, significantly improves the knowledge and ability to perform quality studies. However, although the theoretical-practical knowledge remained over time, the quality of the studies performed or their interpretation worsened significantly, which would justify the need for periodical support workshops to maintain the level of training among these staff.
FundingThe research leading to these results has not received any specific funding, but falls within the European Union Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/REGPOT-2012-2013.1) under grant agreement no. 316265, BIOCAPS.
Conflict of InterestsThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
To Fernando Lago Deibe and Concepción González Paradela, heads of study, Primary Care Management for the Vigo Area, and to all the participating professionals for their work and collaboration in this study. To the SERGAS Directorate-General for Health Care for their support.
Please cite this article as: Represas-Represas C, et al. Efectividad a corto y largo plazo de un programa tutelado de formación en espirometrías para profesionales de atención primaria. Arch Bronconeumol. 2013;49:378–82.