People with Down syndrome (DS) have high respiratory morbidity, evaluating their respiratory health with standardized, objective tests is desirable. Thus, the objective of this study was to evaluate the technical quality of Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs) to determine which ones are most suitable for this population.
MethodsParticipants included children, teenagers and adults with DS, 5 years of age or older (n=302). The technical quality of the impulse oscillometry system (IOS), forced spirometry, lung-diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO), and 6-min walk test (6MWT) were analyzed by age group. Capnography and pulse oximetry were included in the study. Technical quality was determined on the basis of current international PFTs standards.
ResultsFifty-one percent of participants were males. A total of 184 participants (71%) who completed the IOS fulfilled the quality criteria, while 210 (70%) completed the 6MWT. Performance on forced spirometry and DLCO was poor. All pulse oximetries and 96% percent heart rates obtained had good quality, but exhaled carbon dioxide (PetCO2) and respiratory rate (RR) showed deficient repeatability.
ConclusionsIOS appears to be the most reliable instrument for evaluating lung mechanics in individuals with DS.
Las personas con síndrome de Down (SD) tienen una elevada morbilidad respiratoria, por lo que se recomienda evaluar su salud respiratoria con test objetivos estandarizados. El objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar la calidad técnica de los test de función pulmonar (TFP) para determinar cuáles son los más adecuados para este tipo de población.
MétodosEntre los participantes se incluyeron niños, adolescentes y adultos con SD y edad ≥5 años (n=302). Se analizaron por grupos de edad la calidad técnica de la oscilometría de impulso (IOS), la oscilometría forzada, la capacidad pulmonar de difusión del monóxido de carbono (DLCO) y de la prueba de la marcha de 6 minutos (6MWT). Se incluyeron en el análisis la capnografía y la oximetría de pulso. La calidad técnica se determinó de acuerdo con los estándares internaciones actuales para los TFP.
ResultadosEl 51% de los pacientes eran varones. Un total de 184 participantes (71%) cumplieron los criterios de calidad de la IOS, mientras que 201 (70%) completaron la prueba 6MWT. El desempeño de la espirometría forzada y de la DLCO fue reducido. Todas las oximetrías de pulso que se obtuvieron, así como el 96% de las frecuencias de pulso presentaron buena calidad. Sin embargo, tanto el dióxido de carbono exhalado (PetCO2) como la frecuencia respiratoria (FR) presentaron una reproducibilidad deficiente.
ConclusionesLa IOS parece ser la herramienta más fiable para la evaluación de la mecánica pulmonar en individuos con SD.
Down syndrome (DS) is a genetic alteration characterized by trisomy of chromosome 21.1 People with DS have high respiratory morbidity associated with structural, functional and immunological alterations that have substantial impacts in the medium term.2–4 Thus, evaluating the respiratory health of people with chronic respiratory symptoms using standardized, objective tests is desirable. Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs) require different degrees of cooperation by patients to achieve proper performance and guarantee the reliability of the results for making decisions regarding diagnosis, prognosis and treatment monitoring in cases of respiratory disease. To our knowledge, no studies have yet evaluated and reported quality criteria for these tests in people with DS. Therefore, this study was designed to evaluate the performance and quality of the impulse oscillometry system (IOS), forced spirometry, lung-diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO), and the 6-minute walk test (6MWT), all of which are routinely used to evaluate lung function. Pulse oximetry and capnography were developed and its quality was assessed as well.
The objective of this study was to conduct these PFTs, evaluate the quality of the results obtained, and then determine which one is most useful for assessing lung function in children, teenagers and adults with DS.
2Methods2.1ParticipantsThe protocol and consent for this cross-sectional study were approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee. The study period was from October 7, 2014, to January 15, 2018. The institutions approached to recruit participants included 57 private and 37 public schools that attend to DS populations and care for disabled people (Multiple Care or Integral Development of the Family Centers, DIF-Mexico). The parents and guardians of the children, teenagers and adult participants were also invited to participate, regardless of the level of disability, comorbidities or genetic mechanisms (mosaicism, translocation or trisomy 21) involved in the DS cases. Recruitment involved visiting the aforementioned centers and speaking with institutional authorities, parents and guardians. A total of 302 participants aged 5–55 years, all residing at 2240m above sea level were included. The participants’ parents or guardians signed their informed consent. All PFTs were performed at a third-level referral hospital that attends exclusively respiratory diseases and uninsured patients.
Two trained nutritionists applied a questionnaire, took anthropometric measurements and performed nutritional assessments. All PFTs were supervised by the same experienced technician, who had trained for 6 months in a Respiratory Physiology Laboratory that has ISO-9001-2015 certification (International Organization for Standardization).
2.2Tests performed- 1)
Anthropometrics: we measured height, weight and the body mass index (BMI) using an electronic scale with a body composition monitor (model HBF-500INT; OMRON, USA) and a portable stadiometer (model 213; SECA, USA).
- 2)
Oxygen saturation (SpO2) and heart rate (HR) were estimated by a pulsioximeter, which also provided data on exhaled carbon dioxide (PetCO2) and respiratory rate (RR) (capnograph and LifeSense model LS1-9R oximeter, Nonin Medical). The pulsioximeter was placed on the right index finger to obtain six readings in 1min (i.e., every 10s). Averages are reported. Acceptable measurements for PetCO2 and RR were considered when the participant performed stable breathing at tidal volume. In this case, as well, the average of six measurements is reported.
- 3)
IOS was performed by all participants (MSIOS; Erich Jaeger, CareFusion, San Diego, CA, USA), following recommendations published by several authors.5 Volume at three different flows (<2, 4–6, and >8L/s) and pressure calibrations of the equipment were verified daily using a certified 3-L syringe (maximum variability 3%) at a pressure of 0.2kPa (±0.01kPa).
In addition, linearity at three different flows (<2, 4–6, and >8L/s) was corroborated on a weekly basis. Briefly, with the subject in a sitting position and wearing a nose clip, the procedure was explained in plain language and she/he was allowed to become accustomed to the equipment. IOS measurements were taken during quiet tidal breathing with the subject's cheeks supported by a research assistant. All trials lasted 20s and were performed at 1-min intervals. To evaluate the acceptability of these tests, we focused on resistance at 5Hz (Rrs5) and applied the criteria described by Beydon et al.6 to classify them as acceptable or not. Good repeatability was considered if the intra-test coefficient of variation (CV) was <10%.
Spirometry and DLCO were performed according to American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society (ATS/ERS) 2005 standards.7
- 4)
Forced spirometry was performed using the same equipment as IOS, with a maximum of eight forced expiratory maneuvers, of which three acceptable ones were selected, aiming for a difference ≤0.15L between the two highest forced expiratory volumes in 1s (FEV1) and forced vital capacities (FVC).
- 5)
For the DLCO test (NDD EasyOne PRO), a minimum of two acceptable maneuvers that differed by ≤3mL/min/mmHg were required. The participants selected to perform this test were those who were able to inhale deeply up to total lung capacity and then exhale completely to residual volume.
- 6)
The 6MWT was performed on a hard, flat surface in an interior corridor 40 meters long, following international standards.8 Only one walk was performed because of the long time required to run all the tests. The explanation and instructions for this test were visual and brief so that participants could understand them clearly. During this test, pulse oximetry and blood pressure were measured (standing baumanometer with movable base; Riester, Germany). Individuals were excluded if their SpO2 <90%, if they had uncontrolled heart disease or difficulty in walking, or if they did not understand the instructions, or refused to participate.
In order to evaluate variability among the different PFTs, the CV was calculated for each test. Medians (25th, 75th percentiles) were used to describe the data. Mann–Whitney and Wilcoxon tests were applied to compare medians. STATA ver.12 statistical software (Stata Corp., College Station, TX, USA) was used for all analyses.
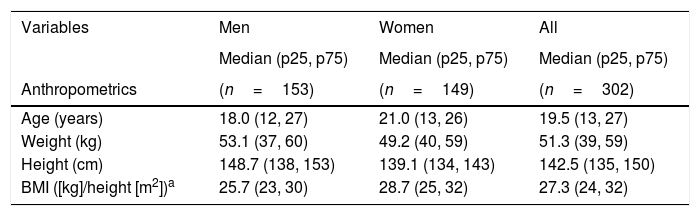
3Results3.1General characteristicsA total of 302 children, teenagers and adults with DS were recruited; 51% were males. Median age was 18 years (12, 27) for males and 21 years (13, 26) for females. Table 1 presents the anthropometric measurements of all participants. Greater overweightness was found for females (BMI=28.7).
Anthropometrics and capnography by gender.
| Variables | Men | Women | All |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median (p25, p75) | Median (p25, p75) | Median (p25, p75) | |
| Anthropometrics | (n=153) | (n=149) | (n=302) |
| Age (years) | 18.0 (12, 27) | 21.0 (13, 26) | 19.5 (13, 27) |
| Weight (kg) | 53.1 (37, 60) | 49.2 (40, 59) | 51.3 (39, 59) |
| Height (cm) | 148.7 (138, 153) | 139.1 (134, 143) | 142.5 (135, 150) |
| BMI ([kg]/height [m2])a | 25.7 (23, 30) | 28.7 (25, 32) | 27.3 (24, 32) |
| Capnography | (n=146) | (n=143) | (n=289) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen saturation (%) | 93 (91, 95) | 94 (92, 95) | 93 (92, 95) |
| Heart rate (bpm) | 78 (65, 86) | 72 (65, 83) | 75 (65, 85) |
| Exhaled carbon dioxide (mmHg) | 36 (32, 39) | 35 (31, 38) | 36 (31, 39) |
| Respiratory rate (breaths per minute) | 20 (16, 23) | 19 (14, 21) | 19 (15, 22) |
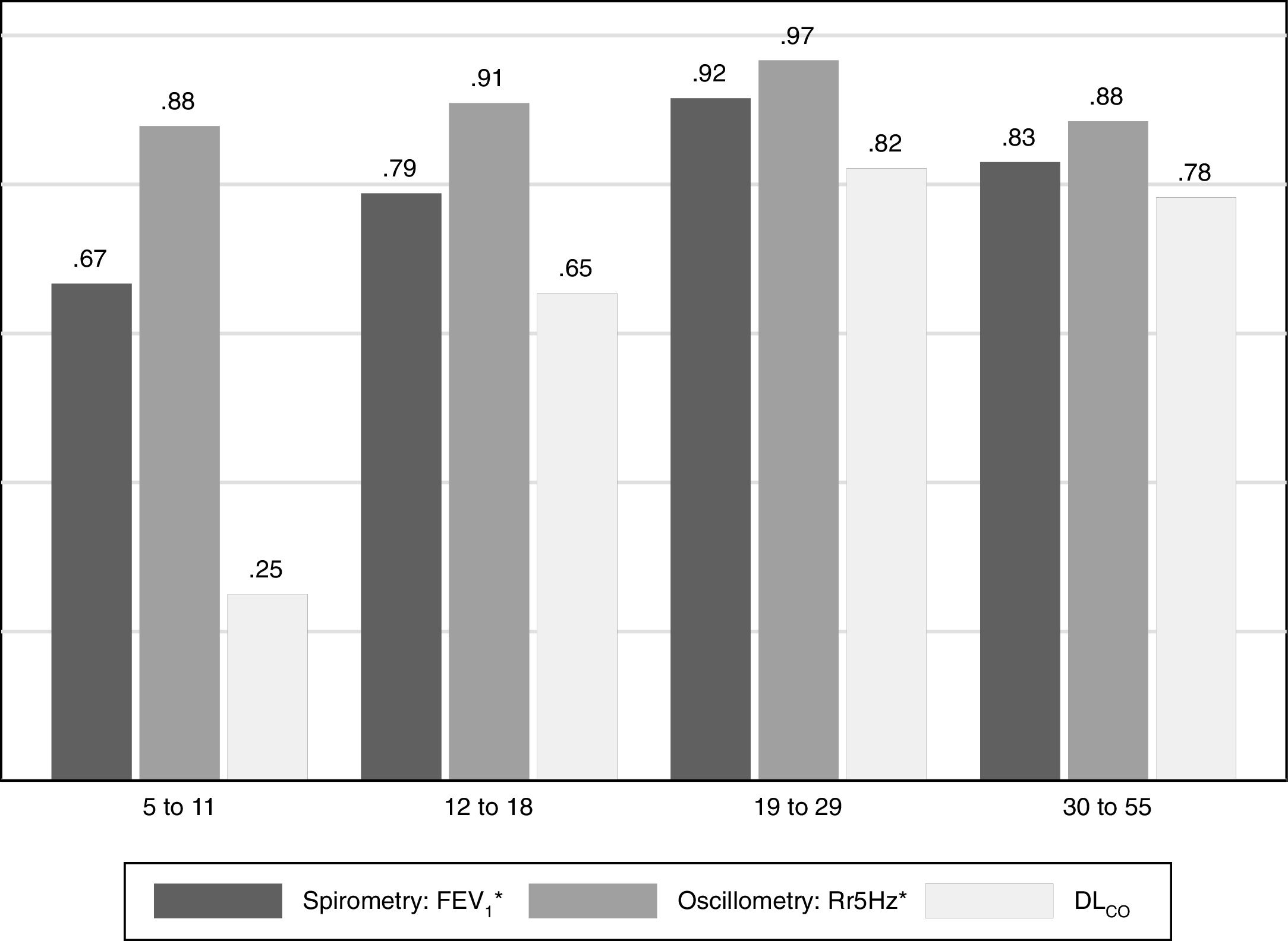
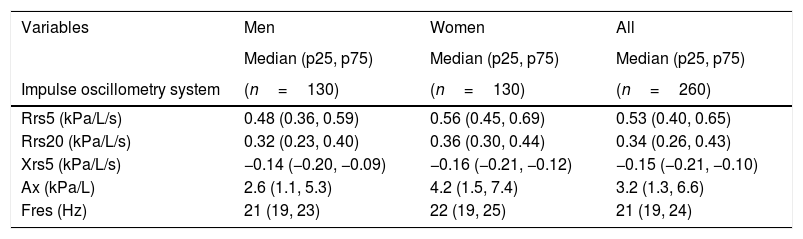
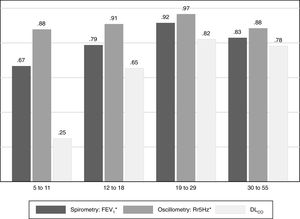
Table 2 shows the median of the main variables of each PFT by gender. Results show that 98% of participants were able to perform at least three IOS maneuvers without artifacts, and that 71% of all tests had adequate acceptability and repeatability (i.e., variability between measurements <10%) with resistance at 5Hz. Over 50% of participants in each age group reached the repeatability criteria. The 19–29 age group achieved the highest proportion of repeatable tests (79%, Table 3). Resistance at 5Hz had the highest percentage of repeatable tests (CV<10%) in the 19–29 age group (97%, Fig. 1).
PFTs results by gender.
| Variables | Men | Women | All |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median (p25, p75) | Median (p25, p75) | Median (p25, p75) | |
| Impulse oscillometry system | (n=130) | (n=130) | (n=260) |
| Rrs5 (kPa/L/s) | 0.48 (0.36, 0.59) | 0.56 (0.45, 0.69) | 0.53 (0.40, 0.65) |
| Rrs20 (kPa/L/s) | 0.32 (0.23, 0.40) | 0.36 (0.30, 0.44) | 0.34 (0.26, 0.43) |
| Xrs5 (kPa/L/s) | −0.14 (−0.20, −0.09) | −0.16 (−0.21, −0.12) | −0.15 (−0.21, −0.10) |
| Ax (kPa/L) | 2.6 (1.1, 5.3) | 4.2 (1.5, 7.4) | 3.2 (1.3, 6.6) |
| Fres (Hz) | 21 (19, 23) | 22 (19, 25) | 21 (19, 24) |
| Forced spirometry | (n=118) | (n=128) | (n=246) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FVC (L) | 2.6 (1.8, 3.2) | 1.9 (1.5, 2.3) | 2.1 (1.6, 2.8) |
| FEV1 (L) | 2.3 (1.8, 2.8) | 1.7 (1.4, 2.1) | 1.9 (1.5, 2.5) |
| FEV1/FVC (%) | 0.92 (0.85, 0.96) | 0.91 (0.84, 0.97) | 0.92 (0.84, 0.97) |
| Diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide | (n=60) | (n=68) | (n=128) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DLCO (mL/min/mmHg) | 27.3 (22, 32) | 17.9 (13, 22) | 21.5 (15, 27) |
| DLCO (% predicted value) | 106 (96, 125) | 88 (70, 100) | 97 (82, 111) |
| DLCO adjusted for altitude (% predicted value)a,† | 93.7 (85, 110) | 77 (61, 88) | 85 (72, 97) |
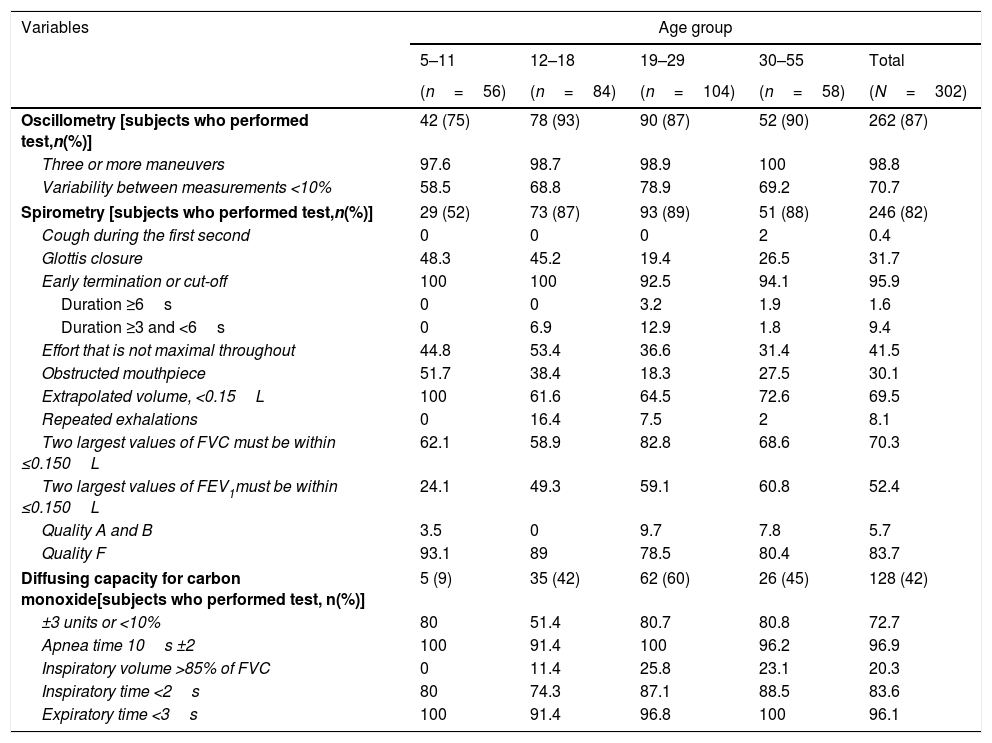
Percentages of subjects who met the quality criteria, by age group and test performed.a
| Variables | Age group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5–11 | 12–18 | 19–29 | 30–55 | Total | |
| (n=56) | (n=84) | (n=104) | (n=58) | (N=302) | |
| Oscillometry [subjects who performed test,n(%)] | 42 (75) | 78 (93) | 90 (87) | 52 (90) | 262 (87) |
| Three or more maneuvers | 97.6 | 98.7 | 98.9 | 100 | 98.8 |
| Variability between measurements <10% | 58.5 | 68.8 | 78.9 | 69.2 | 70.7 |
| Spirometry [subjects who performed test,n(%)] | 29 (52) | 73 (87) | 93 (89) | 51 (88) | 246 (82) |
| Cough during the first second | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.4 |
| Glottis closure | 48.3 | 45.2 | 19.4 | 26.5 | 31.7 |
| Early termination or cut-off | 100 | 100 | 92.5 | 94.1 | 95.9 |
| Duration ≥6s | 0 | 0 | 3.2 | 1.9 | 1.6 |
| Duration ≥3 and <6s | 0 | 6.9 | 12.9 | 1.8 | 9.4 |
| Effort that is not maximal throughout | 44.8 | 53.4 | 36.6 | 31.4 | 41.5 |
| Obstructed mouthpiece | 51.7 | 38.4 | 18.3 | 27.5 | 30.1 |
| Extrapolated volume, <0.15L | 100 | 61.6 | 64.5 | 72.6 | 69.5 |
| Repeated exhalations | 0 | 16.4 | 7.5 | 2 | 8.1 |
| Two largest values of FVC must be within ≤0.150L | 62.1 | 58.9 | 82.8 | 68.6 | 70.3 |
| Two largest values of FEV1must be within ≤0.150L | 24.1 | 49.3 | 59.1 | 60.8 | 52.4 |
| Quality A and B | 3.5 | 0 | 9.7 | 7.8 | 5.7 |
| Quality F | 93.1 | 89 | 78.5 | 80.4 | 83.7 |
| Diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide[subjects who performed test, n(%)] | 5 (9) | 35 (42) | 62 (60) | 26 (45) | 128 (42) |
| ±3 units or <10% | 80 | 51.4 | 80.7 | 80.8 | 72.7 |
| Apnea time 10s ±2 | 100 | 91.4 | 100 | 96.2 | 96.9 |
| Inspiratory volume >85% of FVC | 0 | 11.4 | 25.8 | 23.1 | 20.3 |
| Inspiratory time <2s | 80 | 74.3 | 87.1 | 88.5 | 83.6 |
| Expiratory time <3s | 100 | 91.4 | 96.8 | 100 | 96.1 |
Forced spirometry was performed by 82% of participants, but most results (84%) were of poor quality (grade F with unacceptable maneuvers). In fact, the 19–29 age group achieved only 10% grade A or B quality (to fulfill the ATS quality criteria), mainly due to early termination or expiration cut-off, but also as a result of an obstructed mouthpiece, glottic closure or sub-maximal effort (Table 3). The 5–11 and 12–18 age groups had the highest proportions of poor quality tests (grade F).
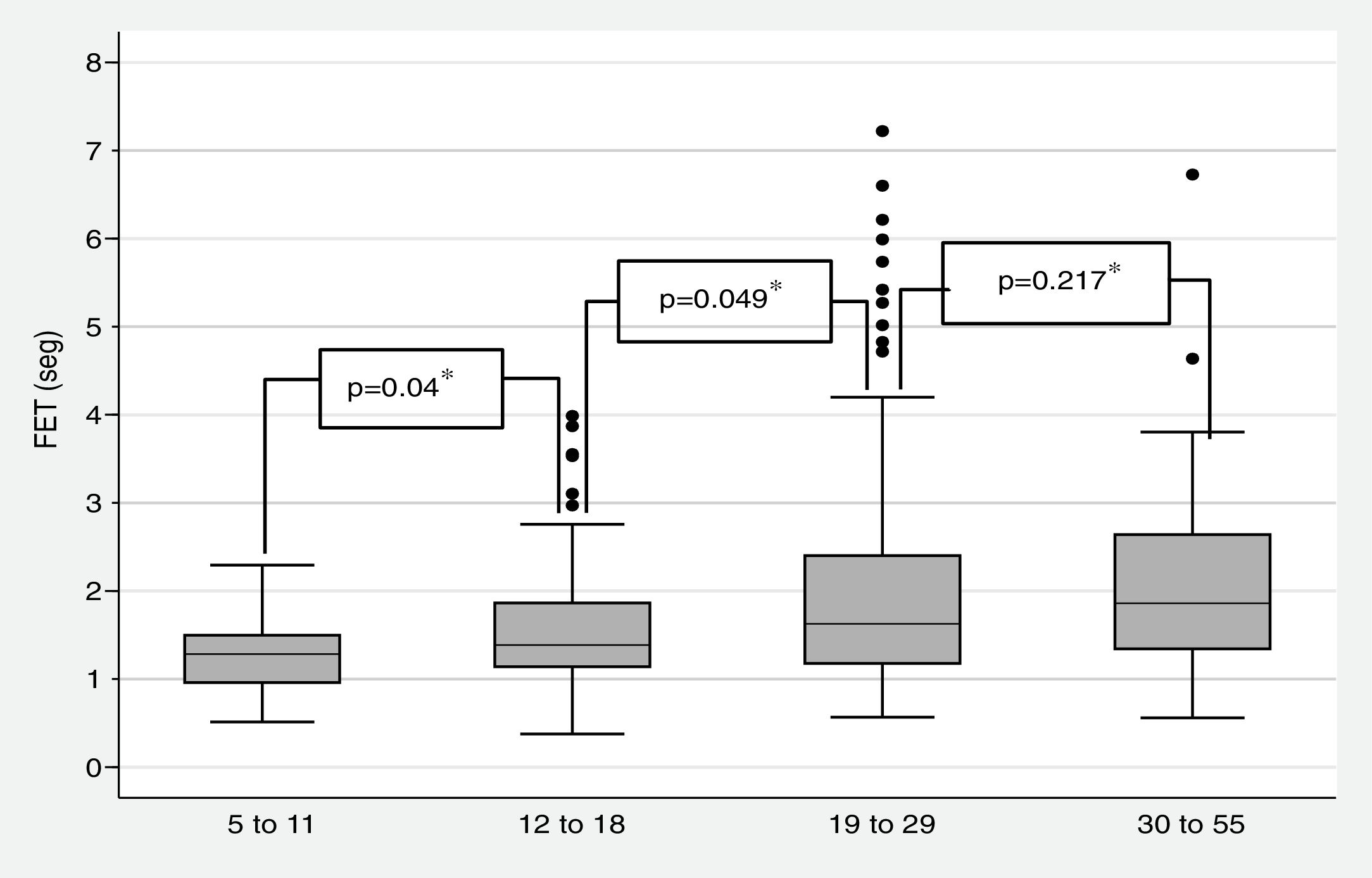
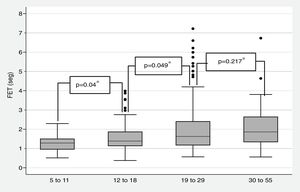
Fig. 2 shows the median forced expiratory time (FET) by age group. In all cases, this measurement was less than 2s, though it tended to increase with age, only 1.6% of participants managed to blow ≥6s [median 1.5s (1.17, 2.13) (Table 3).
Despite these findings, we went on to evaluate the repeatability (<0.150L of the two largest values) of FEV1 and FVC, which were performed by 83% of the 19–29-year-olds for FVC, and 61% of the 30–55-year-olds for FEV1 (Table 3).
The DLCO test was performed by 128 (42%) individuals, but it was not possible to evaluate the existing acceptability criteria because of uncertain, likely underestimated, vital capacity due to short expirations. However, the DLCO results of most participants were within normal limits (Table 2). In this case, 39% of participants reached a DLCO ≥80% of predicted according to Mexican reference values.9 Only 26% of 19–29 age group achieved an inspiratory volume >85% of FVC; results were lower for the other age groups (Table 3). Similarly, the proportion of participants with a CV <10% was the lowest index determined in all age groups (Fig. 1). However, the apnea time of 10±2s and the expiratory time <3s were accomplished by almost all participants in each age group.
Most participants (75%) performed the 6MWT, but 13 stopped before 6min, and 4 tests were canceled because of dyspnea. The 6MWT was not performed by 75 participants for the following reasons: 54 refused; 13 had oxygen desaturation at rest (≤90%); and 8 were unable to walk. Table 2 describes the median (p25, p75) number of meters walked by the participants who completed the test. A statistically-significant increase in heart rate was observed after 6MWT, even though participants did not make maximum effort, according to the technicians’ reports.
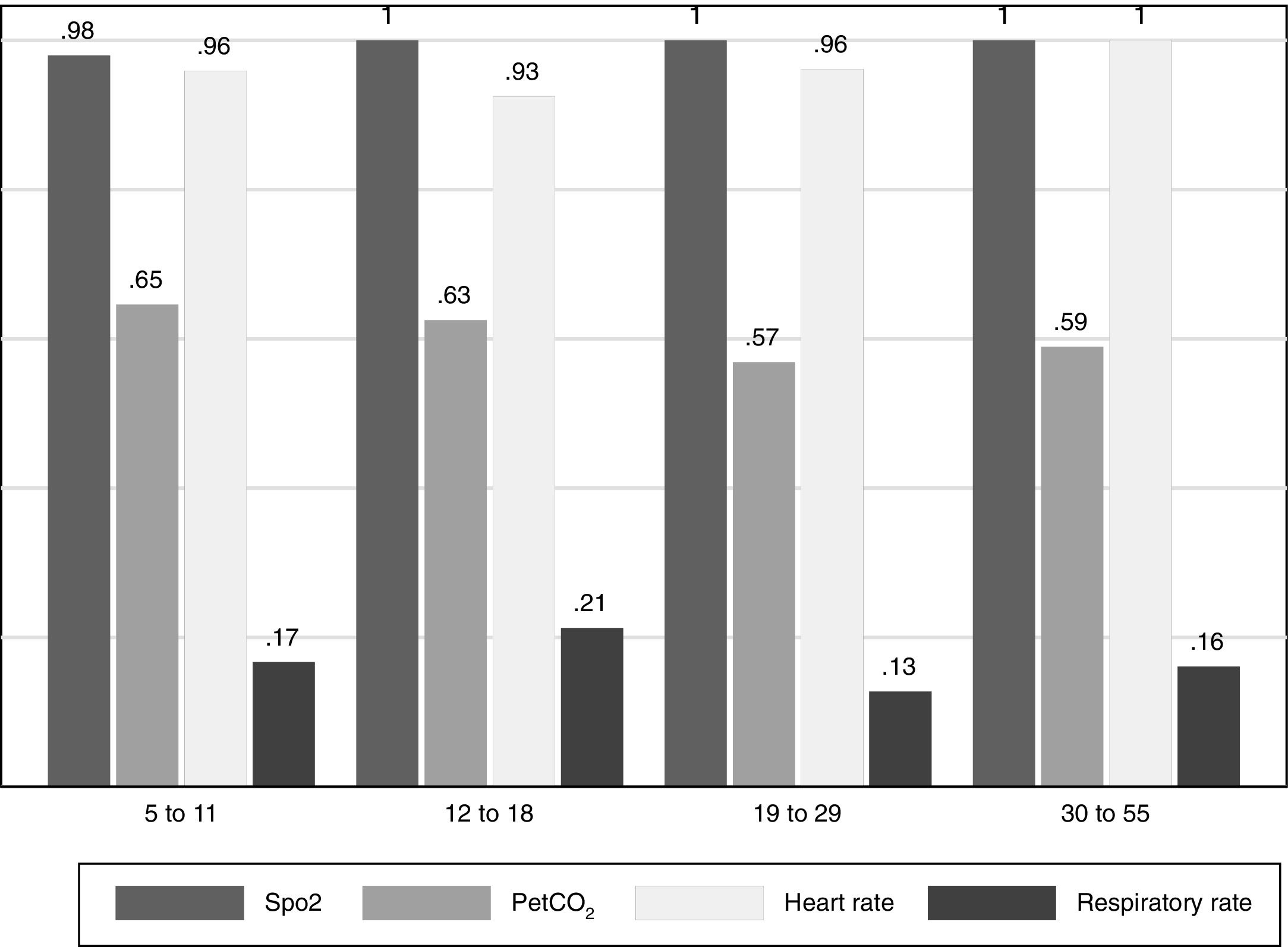
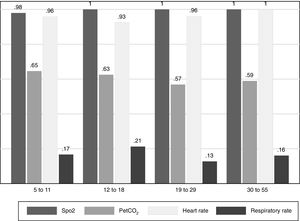
Although capnography variables (Table 1) do not require much collaboration on the part of patients, the proportion of participants with a breathing frequency CV<10% was very small (Fig. 3), whereas 65% in the 5–11 age group achieved repeatable PetCO2. Measurements of SpO2 and HR were acceptable in almost all participants.
4DiscussionThis study's most individuals with DS properly performed the IOS test and had acceptable SpO2 and HR measurements, though PeTCO2 and RR had poor repeatability. Ninety-one percent of participants had a Rrs5 with a CV<10% (Fig. 1); hence, this test could complement medical diagnoses in participants with DS, especially those with suspected airway obstruction, exhibited high variability in our participants, also true for healthy respiratory child populations.10
Forced spirometry was unsuccessful in participants primarily because of short expirations that led to underestimating FVC in a higher proportion than in children without DS.11 One study of DS participants showed a decrease in FVC and FEV1 compared to normal participants; however, no results on test quality criteria were reported there.12
We consider that participants’ physical characteristics (hypotonia, dysphagia, developmental delay, and craniofacial and cardiac anomalies), had a greater influence on FET.13 In addition, the condition known as alveolar simplification makes these participants more susceptible to mechanical stress,2,14 which explains why individuals with DS have worse FEV1 and FVC results than people without DS.12,15 Therefore, when evaluating individuals with DS, clinically-useful results will be more important than standard quality criteria. For example, a FEV1 or DLCO within normal range for height, age and sex may be clinically-relevant even though repeatability may be poor.
Since our participants’ FVC results were not reliable due to short expirations, it was not possible to evaluate the acceptability of DLCO using current criteria, including a vital capacity during DLCO close to maximal. Similarly, the lowest proportions of participants with CV <10% were recorded for this test (Fig. 1). In contrast, a high proportion of participants achieved the remaining quality criteria (Table 3).
Our participants also performed poorly on the 6MWT due to a slow pace that technicians attributed to poor collaboration and motivation, not to manifestations of respiratory symptoms. Unfortunately, we were only able to conduct one 6MWT, though we are aware that there is a training effect between the 1st and 2nd walk.16 In our study, the median number of meters walked was 372 (p25 325, p75 424) with a mean of 373m (±85.8 SD). These distances are similar to those reported for people with severe intellectual disabilities on their 2nd walk. Although a second walk may improve the quality and reliability of the 6MWT, and could be useful for detecting exercise-induced desaturation, it is generally considered unreliable to evaluate the performance of functional exercise in people with DS.17
Capnography is non-invasive and requires little collaboration by participants, but results of this procedure must be taken with caution because the nasal prongs used may modify breathing patterns and so alter PeTCO2 and RR measures.
4.1LimitationsOur participants were unable to perform all the components of this respiratory function test battery, but evaluating feasibility was, precisely, one of the main objectives of the study. We did not measure participants’ cognitive levels prior to performing the PFTs as a possible predictor of the inability to perform them.17 Finally, it is probable that we included participants with cardiac diseases and other undiagnosed comorbidities, which are very common in this population and could affect test performance and results.
5ConclusionMost individuals with DS may be able to perform IOS properly and achieve acceptable pulse oximetry tests that could help evaluate respiratory mechanics and gas exchange. The 6MWT could be useful for assessing desaturation induced by physical activity, but it would be advisable to evaluate its repeatability in more detail.
6FundingThis work was supported by Mexico's National Council for Science and Technology (CONACYT) [grant numbers 233621, 2014].
7Conflict of interestsThe authors declare no conflict of interests.