The endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced pulmonary endothelial barrier disruption is a key pathogenesis of acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). However, the molecular mechanisms underlying LPS-impaired permeability of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVECs) are not fully understood.
MethodsRat PMVECs were isolated and monolayered cultured, then challenged with different doses of LPS (0.1mg/L, 1mg/L, and 10mg/L). Trans-endothelial electrical resistance (TER) was utilized to measure the integrity of the endothelial barrier. Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1) activity and the phosphorylation of Ezrin/Radixin/Moesin proteins (ERM) were assessed by pulldown assay and Western Blotting. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) inhibition of Rac1 and Moesin were applied to evaluate the effect of PMVEs permeability and related pathway.
ResultsLPS induced dose and time-dependent decreases in TER and increase in ERM threonine phosphorylation, while inactivated Rac1 activity in PMVEC. siRNA study demonstrated that both Rac1 and Moesin were involved in the mediation of the LPS-induced hyperpermeability in PMVECs monolayers, and Rac1 and Moesin could regulate each other.
ConclusionPhosphorylated ERM mediates LPS induced PMVECs permeability through negatively regulating Rac1 activity.
La disrupción de la barrera endotelial pulmonar inducida por endotoxina o lipopolisacárido (LPS) es un factor patogénico clave en la lesión pulmonar aguda (LPA) y el síndrome de distrés respiratorio agudo (SDRA). Sin embargo, los mecanismos que subyacen al empeoramiento de la permeabilidad de las células endoteliales de la microvasculatura pulmonar (PMVECs, por sus siglas en inglés) no se conocen.
MétodosSe aislaron y cultivaron en monocapa PMVEC de rata, y se expusieron a diferentes dosis de LPS (0,1, 1 y 10mg/l). Se utilizó la resistencia eléctrica transendotelial (TER, por sus siglas en inglés) para medir la integridad de la barrera endotelial. Se analizó la actividad del sustrato 1 de la toxina botulínica C3 relacionado con Ras (Rac1) y la fosforilación de las proteínas erzina/raxidina/moesina (ERM) mediante ensayos pulldown y Western blot. Para evaluar la permeabilidad de las PMVEC y las vías relacionadas se inhibieron Rac1 y moesina mediante ARN pequeño de interferencia (siRNA, por sus siglas en inglés).
ResultadosEl LPS indujo una disminución dependiente de dosis y tiempo de la TER e incrementó la fosforilación en treonina de ERM, al mismo tiempo que inactivó a Rac1 en las PMVEC. El estudio con siRNA demostró que, tanto Rac1 como la moesina estaban implicadas en la mediación de la permeabilidad de las PMVEC en monocapa inducida por LPS, y que Rac1 y la moesina podrían regularse mutuamente.
ConclusiónLa fosforilación de ERM media la permeabilidad de las PMVECs inducida por LPS mediante la regulación negativa de la actividad de Rac1.
Previous studies have shown that lipopolysaccharide (LPS), the endotoxin released from the gram-negative bacterial cell wall, is a key pathogenesis to induce an increased permeability of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVECs) that causes pulmonary edema, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).1–4 Therefore, the preservation of vascular endothelial cells (ECs) barrier integrity has the potential for profound clinical impact. Multiple studies have demonstrated that inflammation-induced ECs barrier dysfunction involves cytoskeletal rearrangement, equilibrium of competing for contractile and adhesive forces, and intercellular gap formation.5–8 However, the molecular mechanisms underlying LPS-impaired permeability of PMVECs are not fully understood.
The widely distributed ERM family of membrane-associated proteins (Ezrin, Radixin, Moesin), which share 70–85% of amino acid identity, are actin-binding linkers that connect filamentous (F)-actin and the plasma membrane.9–11 Binding of ERM to membrane lipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) and subsequent phosphorylation of a conserved C-terminal threonine (T567 in Ezrin, T564 in Radixin, and T558 in Moesin) are believed to unmasking sites for interactions with other proteins through conformational changes, thus regulating the activation state of ERM proteins.12 In addition to phosphorylation, ERM proteins also associate with cytoplasmic signaling molecules to integrate membrane transport with signaling pathways.13–15 However, information is limited concerning the possible role of ERM proteins in the remodeling of endothelial cytoskeleton in response to LPS-induced hyperpermeability in PMVECs.
Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1), a small GTPase belonging to the 21kDa Rho-GTPase family, is a multifunctional switch involved in epithelial development, differentiation and an important regulator of endothelial contraction, actin cytoskeleton dynamics and hence plays a pivotal role in the maintenance of endothelial integrity. The present study was designed to determine whether Rac1 and or ERM were involved in LPS-induced hyperpermeability in PMVECs.
Methods and materialsLPSLPS (Escherichia coli 0111: B4) was purchased from Sigma (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) and dissolved in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) at concentrations of 0.1mg/L, 1mg/L, and 10mg/L.
Isolation and culture of PMVECsPMVECs were isolated and cultured as described previously.16 Briefly, male Sprague-Dawley rats (Peking Vital River Laboratory Animal Ltd, Beijing, China) were sacrificed and outer edges of the remaining lung tissue, which did not contain large blood vessels, were harvested. All experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University. The tissues were then washed with serum-free Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's medium (DMEM), minced with scissors, and cultured with DMEM containing 20% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 2.5μg/mL amphotericin B in a humidified 37°C, 5% CO2 incubator. After 60h, the tissue was removed and the culture media was replaced every 3 days. Cells were morphologically identified as ECs by cobblestone shapes under an optical microscopy (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
Trans-endothelial electrical resistance measurementsThe ECs (5×105) were plated directly onto the gold micro-electrodes (10–4cm2) of the ECIS arrays (8W10E, Applied Biophysics, Troy, NY, USA), and cultured for a minimum of 2 days to establish confluency. Measurements of trans-endothelial electrical resistance (TER) across confluent PMVEC monolayers were performed in real time without cell damage.
Rac1 activity assayThe activity of Rac1 in the PMVECs subjected to LPS was assessed by pulldown assay. PMVECs were lysed with lysis buffer and incubated with 10μg of GST-PAK beads (Rac1) at 4°C for 40min. The beads were washed four times with wash buffer, heated to 95°C for 5min with 40μL of Laemelli buffer, and loaded on a 12.5% SDS gel. Bound Rac1 protein was then detected by Western Blotting using a polyclonal antibody against Rac1. The total amount of Rac1 in cell lysates was used as a control for the cross-comparison of Rac1 activity (level of GTP-bound Rac1).
siRNA treatmentsiRNA targeting Rac1 and Moesin or a control siRNA were purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA). PMVECs were pretreated with 10nM siRNA premixed with 10μg/mL lipofectin for 4h, then incubated with normal culture medium for 72h before experiments.
Western Blotting for phosphorylated ERMThe level of phosphorylated ERM was examined by immunoblot using a single Ab that recognized any of the three ERM proteins only when they are phosphorylated on the threonine residue: Ezrin (T567)/Radixin (T564)/Moesin (T558) (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, USA).17,18 The level of total ERM was similarly examined using a single Ab that recognizes any of the three ERM proteins regardless of their phosphorylation state (Cell Signaling). The membranes were then incubated in peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (Sigma-Aldrich) and developed with an ECL system (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Chalfont, UK). The relative intensity of the bands of interest was calculated by correcting for total ERM from the same sample with NIH-Image J1.51p 22 (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Statistical analysisAll the results are represented as the mean±standard deviation. The data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance followed by the Newman–Keuls posthoc tests (for multiple group comparisons) in the GraphPad Prism 5.01 software. Values of P<0.05 were considered to be statistically significant.
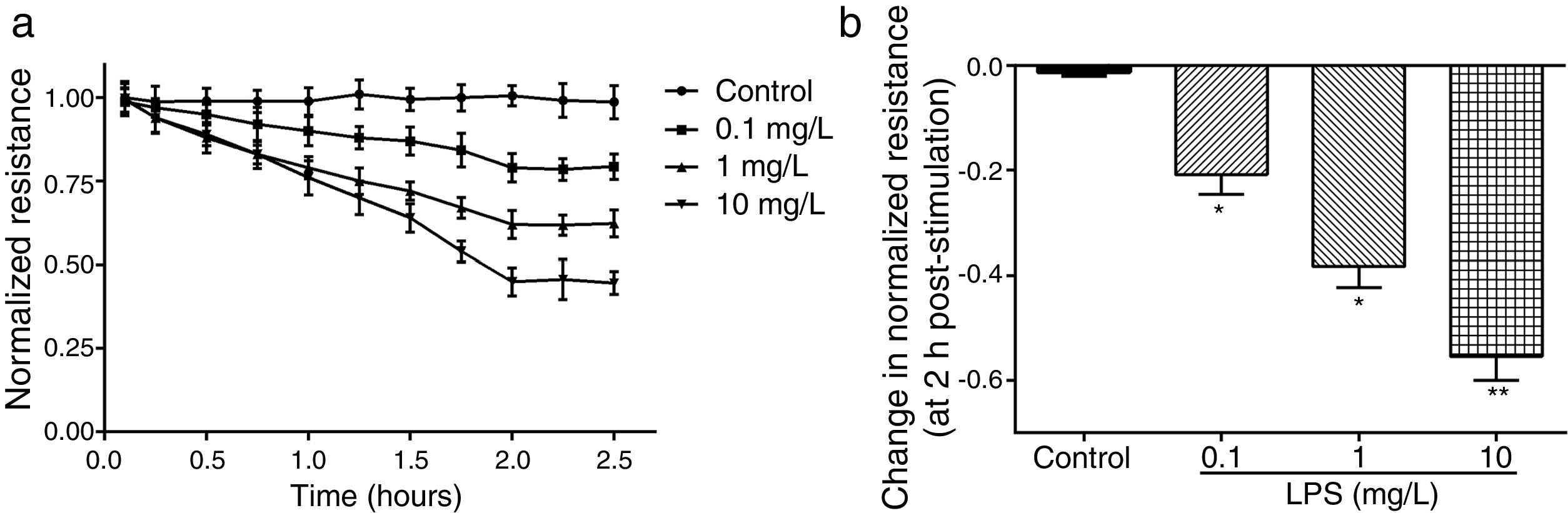
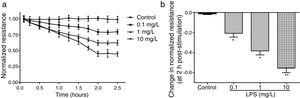
ResultsLPS induces dose and time-dependent decreases in TERECIS arrays system makes continuous TER measurement possible, which are strong indicators of the integrity of the cellular barriers before they are evaluated for transport of drugs or chemicals. When challenged with LPS, cultured PMVECs grown on gold microelectrodes produced dose-dependent (0.1–10mg/L) and time-dependent (0–2.5h) decreases in TER (Fig. 1a and b), indicating attenuated ECs barrier integrity or increased vascular permeability compared with the control.
LPS induces dose and time-dependent decreases in TER. (a) Cultured PMVECs grown to confluency on gold electrodes were treated with recombinant LPS (0.1, 1, 10mg/L), and changes in TER were measured over time, between 0 and 2.5h. Decreased TER represents endothelial barrier dysfunction or increased vascular permeability. (b) Dose-dependent changes in resistance 2h post-LPS stimulation. Data were presented as the mean±SD. N=6, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. untreated control.
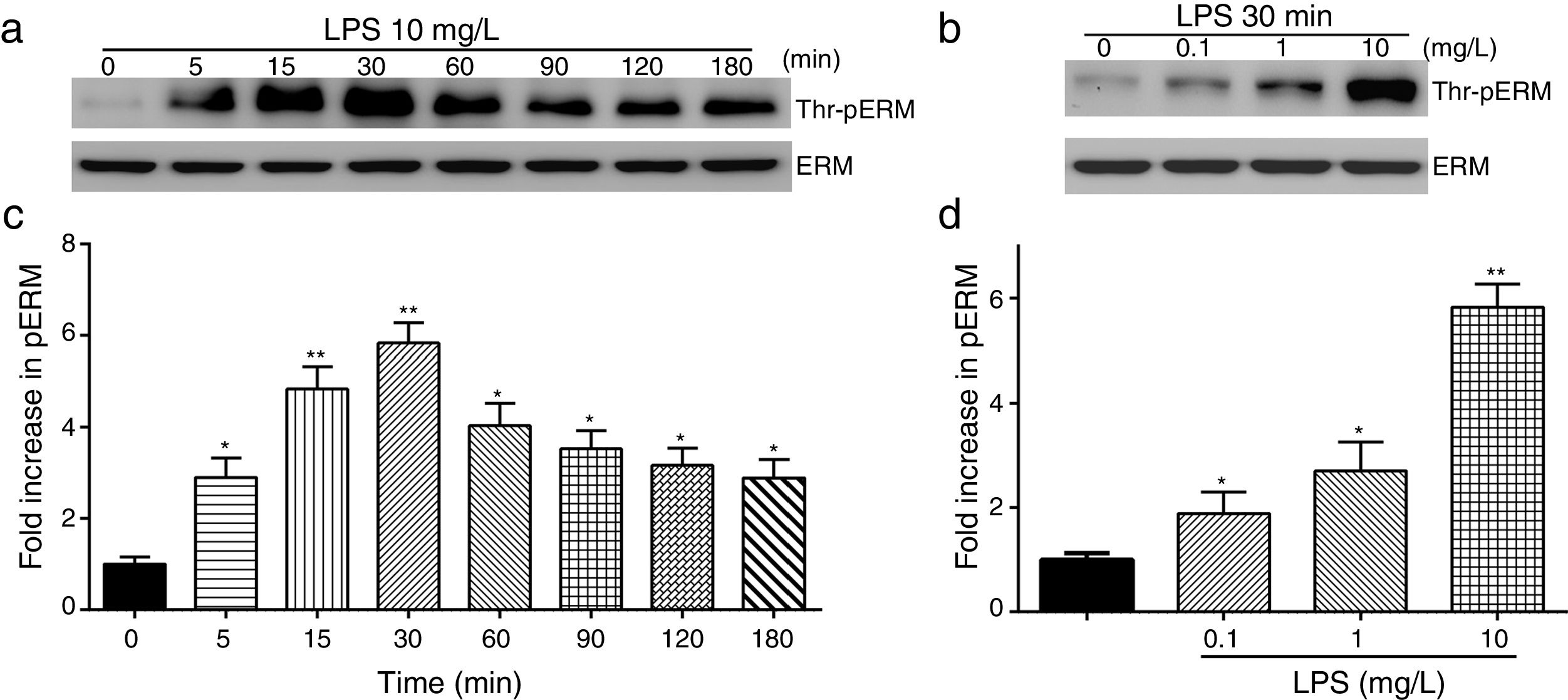
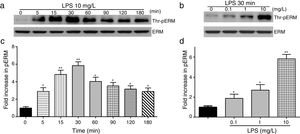
To elucidate the effect of LPS on phosphorylation of ERM at its critical COOH-terminal threonine, phospho-specific ERM antibody (phospho-Ezrin Thr567/Radixin Thr564/Moesin Thr558) was utilized to evaluate threonine phosphorylation of ERM by Western Blot. Treatment with 10mg/L LPS induced a significant increase in ERM phosphorylation in a time-dependent manner without detectable changes in the total ERM expression, which increased after 5min, reached maximum levels by 30min, and remained elevated for at least 180min (Fig. 2a and c). A dose response assay indicated that the most consistent and significant increase induced by LPS was detected at 10mg/L when compared with 0.1mg/L (2 folds) and 10mg/L groups (3 folds) (Fig. 2b and d).
LPS induces dose and time-dependent changes in threonine phosphorylation of ERM in PMVECs. (a) Time-dependent changes in threonine phosphorylation of ERM induced by 10mg/L LPS and relative expressions from the Western Blotting (c). (b) Dose-dependent changes in threonine phosphorylation of ERM following LPS treatment for 30min and relative expressions from the Western Blotting (d). Data were presented as the mean±SD. N=6, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. untreated control or the beginning time.
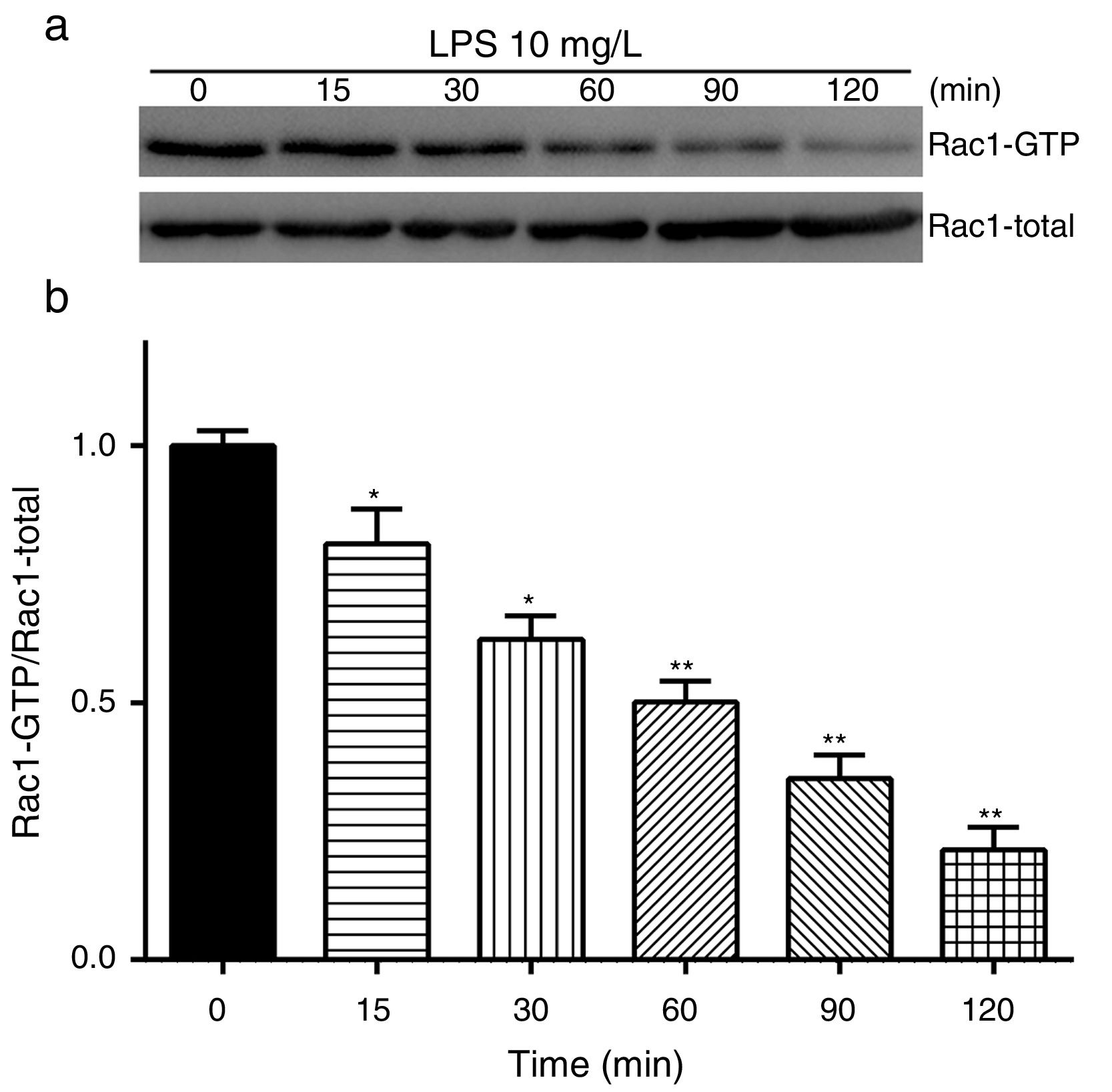
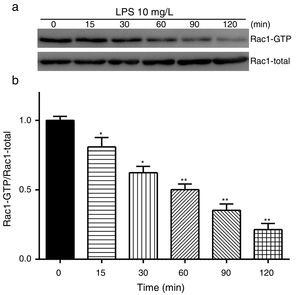
Exposure of PMVECs to 10mg/L LPS caused a strong reduction in Rac1 activity. Such reduction happened after 15min exposure and lasted to 120min in a time-dependent manner (Fig. 3a and b). Rac1 activity decreased nearly to 23±5% after 120min exposure when compared with the control group.
LPS inactivates Rac1 activity in PMVECs. (a) Representative Western Blots of Rac1 activity after 10mg/L LPS treatment. Active Rac1 was pulled down by a pull-down assay. Whole-cell lysate was used as a loading control. (b) Densitometric analysis of the Western Blots presented in a. Data were presented as the mean±SD. N=6, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. the beginning time.
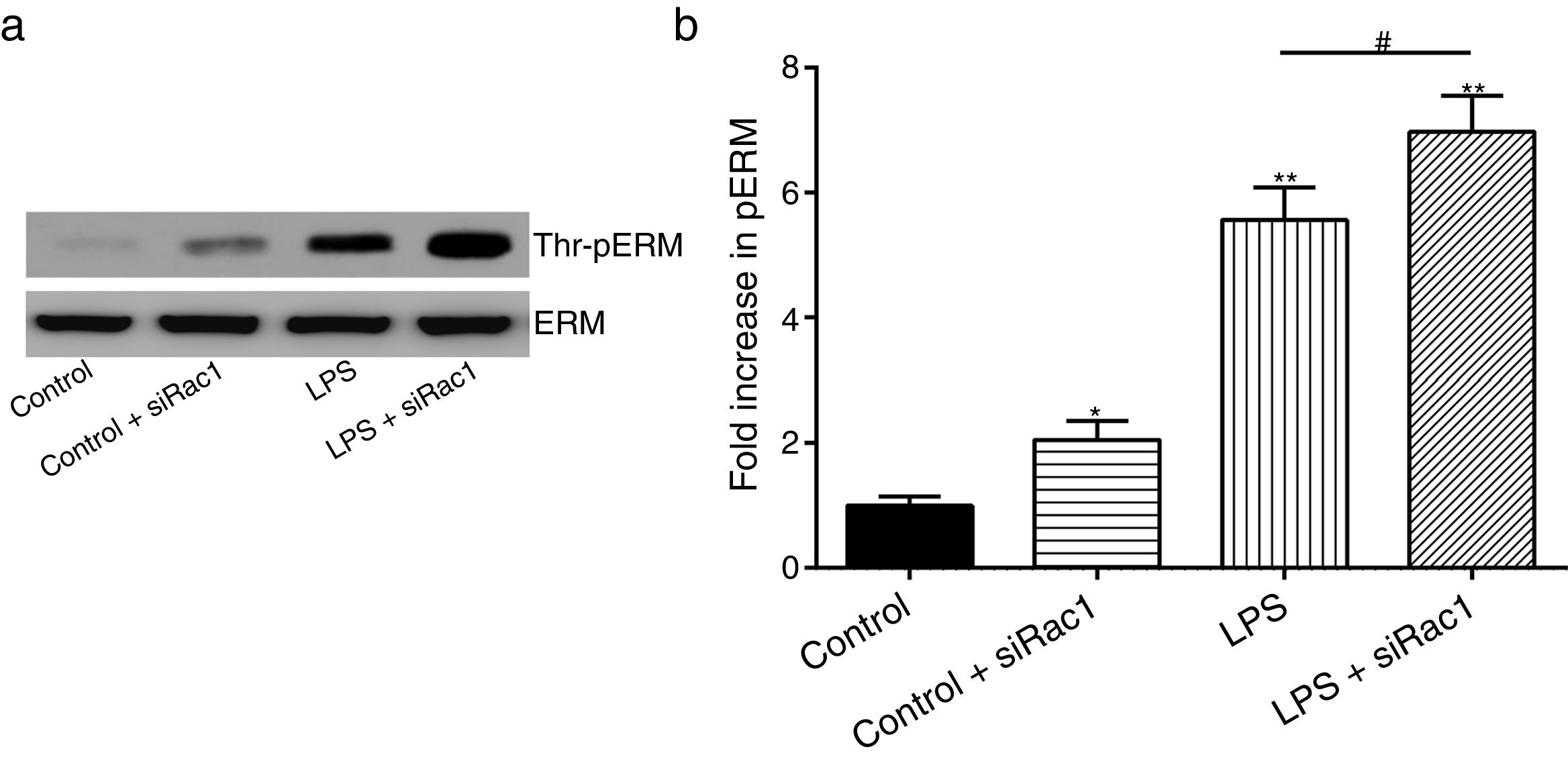
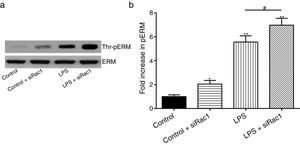
In order to further testify the effect of Rac1 on vascular permeability, siRNA against Rac1 was used. SiRac1 combined with LPS can significantly increase threonine phosphorylation of ERM in PMVECs (7 folds) and SiRac1 alone also can cause some increase of threonine phosphorylation of ERM (2 folds) when compared with control group (Fig. 4a and b). All of these suggested the possibility that the activity of Rac1 might negatively regulate the phosphorylation of ERM during LPS induced vascular hyperpermeability process.
Rac1 inhibition and LPS stimulation (10mg/L) together increase threonine phosphorylation of ERM in PMVECs. (a) Western Blotting was used to assay the expressions of Thr-pERM and normal ERM in different groups and relative expressions from the Western Blotting (b). Data were presented as the mean±SD. N=6, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared to control group. #P<0.05 between LPS group and LPS+siRac1 group.
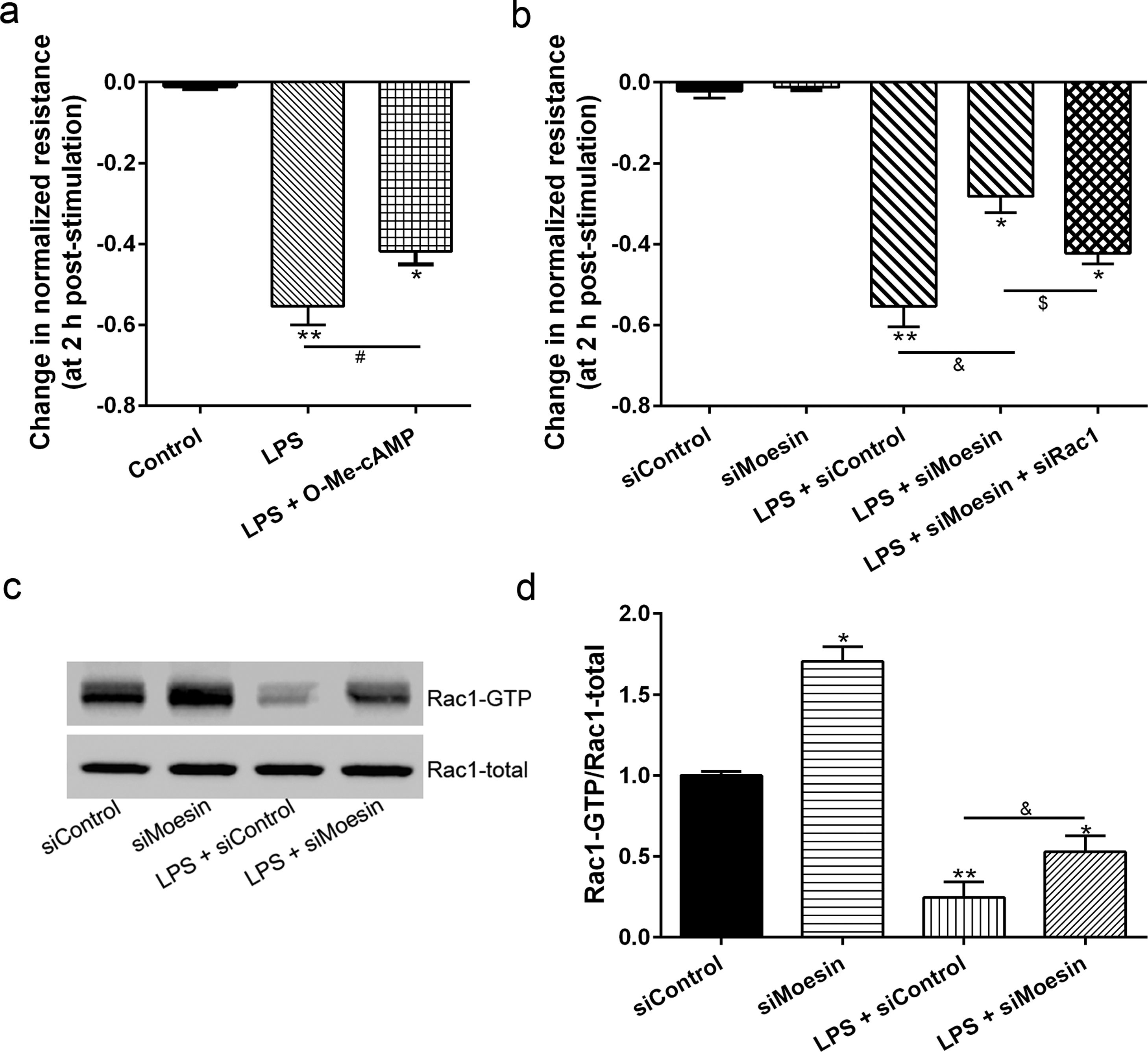
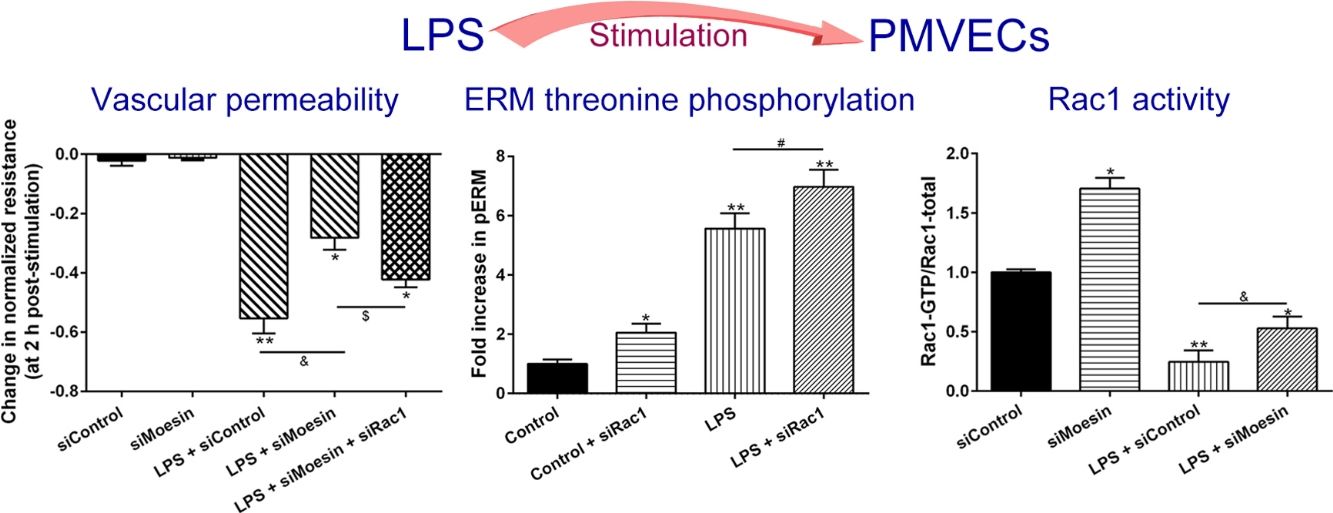
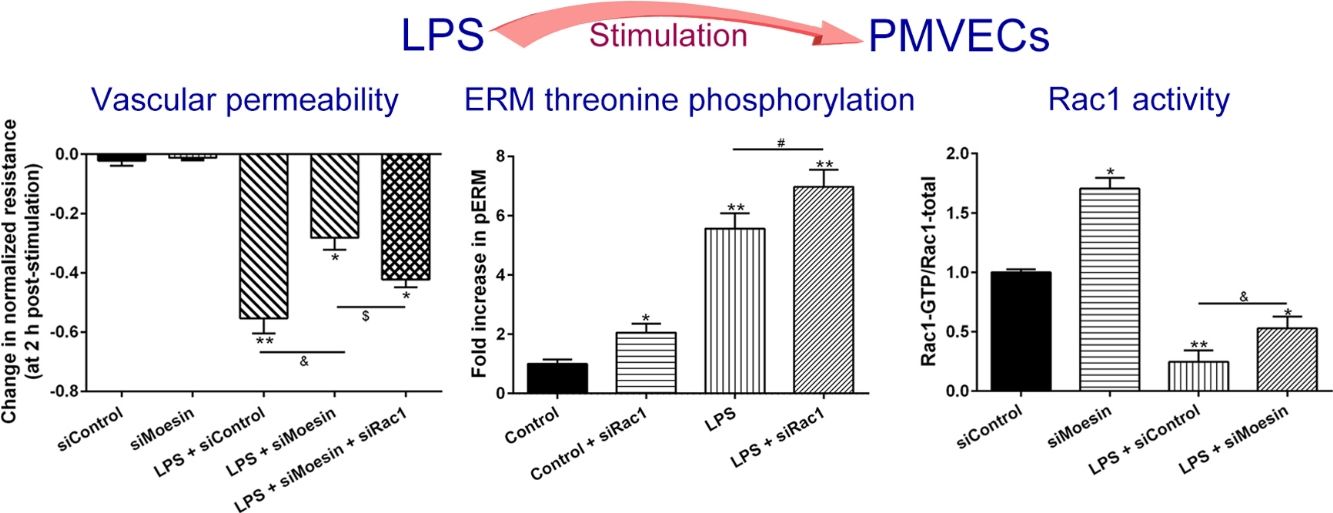
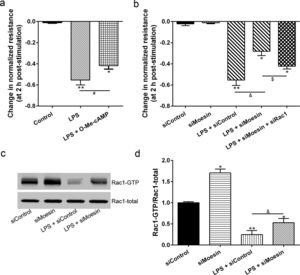
The Rho-family of GTPases (RhoA, Rac1, and cdc42) are considered to be important regulators of endothelial contraction, actin cytoskeleton dynamics and play a pivotal role in the maintenance of endothelial integrity.19,20 In order to specify the role of Rac1 in the LPS induced hyperpermeability, without interfering with RhoA activity, 8-CPT-O′-Me-cAMP (O-Me-cAMP), a cAMP analog, which specifically activated Epac/Rap1 and downstream Rac1 signaling and restored peripheral localization of action and VE-cadherin at cellular junctions was utilized. Challenge with O-Me-cAMP can restore decreased TER caused by LPS exposure (Fig. 5a), indicating Rac1 activity can abrogate hyperpermeability. siRNA against Moesin could recover the decreased TER caused by LPS exposure (Fig. 5b) and up-regulate Rac1 activity (Fig. 5c), while the adding of siRac1 could further lower the decreased TER induced by LPS and siMoesin (Fig. 5d), all of these suggested that LPS could downregulate the activity of Rac1 and Moesin could downregulate the activity of Rac1.
Moesin inhibition protects the LPS induced vascular hyperpermeability and increases Rac1 activity in PMVECs. (a) O-Me-cAMP protected LPS (10mg/L) induced vascular hyperpermeability. (b) TER changed between LPS stimulation, Moesin inhibition, and Rac1 inhibition. (c) Pull-down and Western Blotting assay were used to analyzed the Rac1 activity after LPS stimulation and Moesin inhibition and relative densitometric analysis of the Western Blots (d). Data were presented as the mean±SD. N=6, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared to control group. #P<0.05 between LPS group and LPS+O-Me-cAMP group. &P<0.05 between LPS+siControl group and LPS+siMoesin group. $P<0.05 between LPS+siMoesin group and LPS+siMoesin+siRac1 group.
Multiple mechanisms of PMVEC injury in sepsis and in ARDS have been postulated, which include altered actin cytoskeleton, gaps formation of between previously confluent cells, loss of tight junctions and cell-extracellular matrix, activated leukocytes and platelets, and paracrine exposure to injurious molecules released by these cells. While in our present study, cytoskeletal rearrangement associated Rac1 and ERM are further investigated. The results of the present study demonstrate that LPS induces dose and time-dependent decrease in TER and increase in ERM threonine phosphorylation, strongly suggest the important roles for ERM proteins in mediating endothelial barrier dysfunction induced by LPS. Using small interfering RNA against Rac1 and Moesin, the results demonstrate that both Rac1 and Moesin are involved in the mediation of LPS-induced hyperpermeability in PMVECs monolayers, and Rac1 and Moesin can regulate each other. All of these results advance our mechanistic understanding of ECs barrier regulation and identify Rac1 and Moesin as potential clinically important targets for therapeutic manipulation during permeability processes.
The ERM proteins (Ezrin, Radixin, and Moesin) are adaptor proteins that link plasma membrane receptors to the actin cytoskeleton. While the phosphorylation of ERM via the p38 MAPK and Rho/ROCK pathways can also participate in the modulation of endothelial permeability.21 Ezrin and Radixin have been implicated in cell polarization and cell migration, but little is known about the involvement of Moesin in these processes.22,23 Our results indicate that Moesin, known as actin-binding protein, is a cytoskeletal protein involved in cytoskeletal changes and paracellular gap formation, plays an important role in ECs barrier regulation which may regulate Rac1-mediated epithelial polarity and formation of adherent junctions.
It is now well established that the Rho family of GTPases (RhoA, Rac1, and cdc42) participate to the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton, cell adhesion, and other fundamental biological processes such as cell cycle progression, gene expression, vesicle trafficking and cell polarity.19,20,24,25 Some inhibitor may result in complete inhibition of the actin polymerizing machinery and a collapse of actin cytoskeleton, thereby worsening the interaction of another molecule binding with cytoskeleton. Therefore, a cAMP analog, O-Me-cAMP, which specifically activates Epac/Rap1 and downstream Rac1 signaling is used to activate Rac1 without interfering RhoA activity,26 which indicates that the activity of Rac1 can abrogate the LPS induced PMVECs permeability. Similarly, various barrier-protective mediators, as well as the barrier-stabilizing cAMP signaling pathway are found to reduce vascular permeability at least in part via the activation of Rac1. Thus, besides its role for the maintenance of barrier properties under resting conditions, activation of Rac1 appears to be a suitable approach to protect barrier functions under LPS exposure conditions.27,28
An important feature of ERM proteins is their ability to act as both upstream and downstream elements of Rho GTPases,29–31 which suggests the existence of a positive feedback loop between these two types of proteins in response to LPS stimulation. To test this hypothesis, we study the effects of ERM and Rac1 in response to LPS exposure using siRNA targeting Moesin and Rac1. siRac1 can induce a significant increase of ERM phosphorylation, and siMoesin can slightly increase Rac1 activation. These results demonstrate that during ECs barrier permeability induced by LPS, Rac1 is not only an upstream regulator of Moesin phosphorylation, but it may also serve as a downstream target for Moesin-mediated signaling.
The understanding of ECs barrier regulation may help to improve the therapeutic approaches to plug leaky endothelium in inflammation. There are some limitations we should indicate that the endothelial layer we utilize in this study is basically two-dimensional which may not mimic the actual “in vivo” pulmonary endothelial barrier. All in all, given the important role of Rac1 activation for the stabilization of the endothelial barrier, altering Rac1 mediated signaling would be a desirable approach.
ConclusionIn conclusion, our current data suggest that both ERM and Rac1 are involved in the LPS induced PMVECs permeability and phosphorylated ERM can negatively regulating Rac1 activity.
FundingThis study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81370170).
Conflict of interestsThe authors declare no conflict of interest.