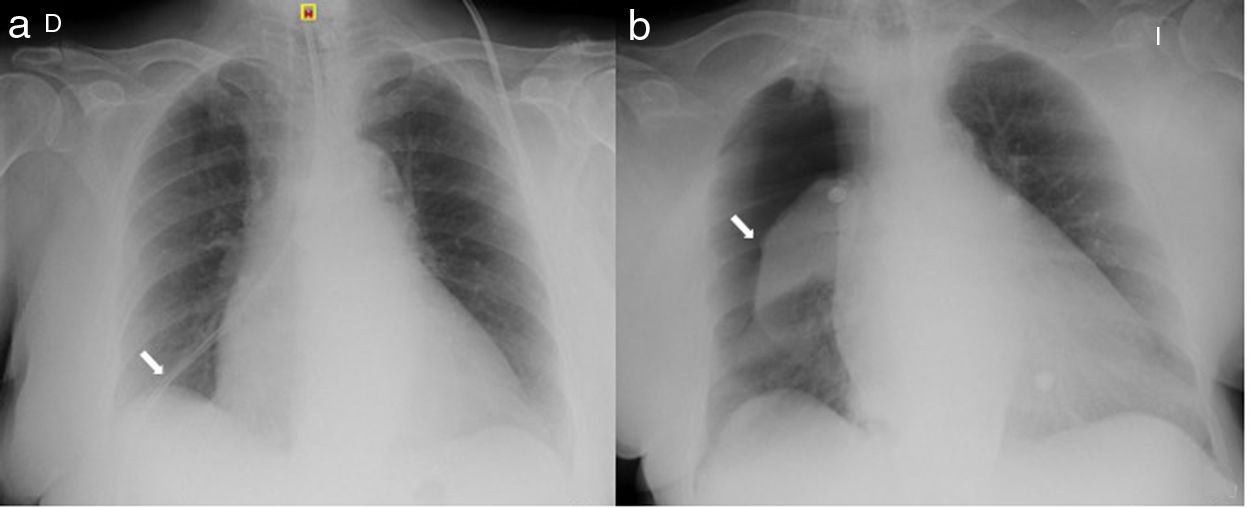
We report the case of a 73-year-old woman admitted to the neurology department with a suspected diagnosis of ischemic stroke in the middle cerebral artery accompanied by left hemiparesis, dysarthria, and impaired swallowing. Insertion of a nasogastric (NG) tube was indicated for nutritional purposes. After placement of the tube, air was instilled and gastric auscultation was performed, which was difficult to interpret. A follow-up chest X-ray showed the tip of the tube located in the right costophrenic angle (Fig. 1a). After removal of the NG tube, the patient developed dyspnea and tachypnea, requiring oxygen therapy with a fraction of inspired oxygen of 50% to maintain correct saturations. An urgent chest X-ray performed at the bedside showed complete right pneumothorax (Fig. 1b), so a chest tube was placed with subsequent resolution of the clinical picture.
The placement of an NG tube for nutritional or therapeutic purposes is common practice, although it is not free from complications. In fact, accidental introduction of the tube into the airway occurs in 0.3%–15% of cases.1 However, iatrogenic pneumothorax after NG tube insertion is rare.2 It should be suspected in patients with neurological disorders accompanied by a decreased cough reflex, since in this situation insertion of the NG tube in the airway may go unnoticed. Placement of the tube must be immediately confirmed with X-ray.
Please cite this article as: Granados G, Ojanguren A, Ojanguren I. Neumotórax iatrogénico tras malposición de sonda nasogástrica. Arch Bronconeumol. 2020;56:117.