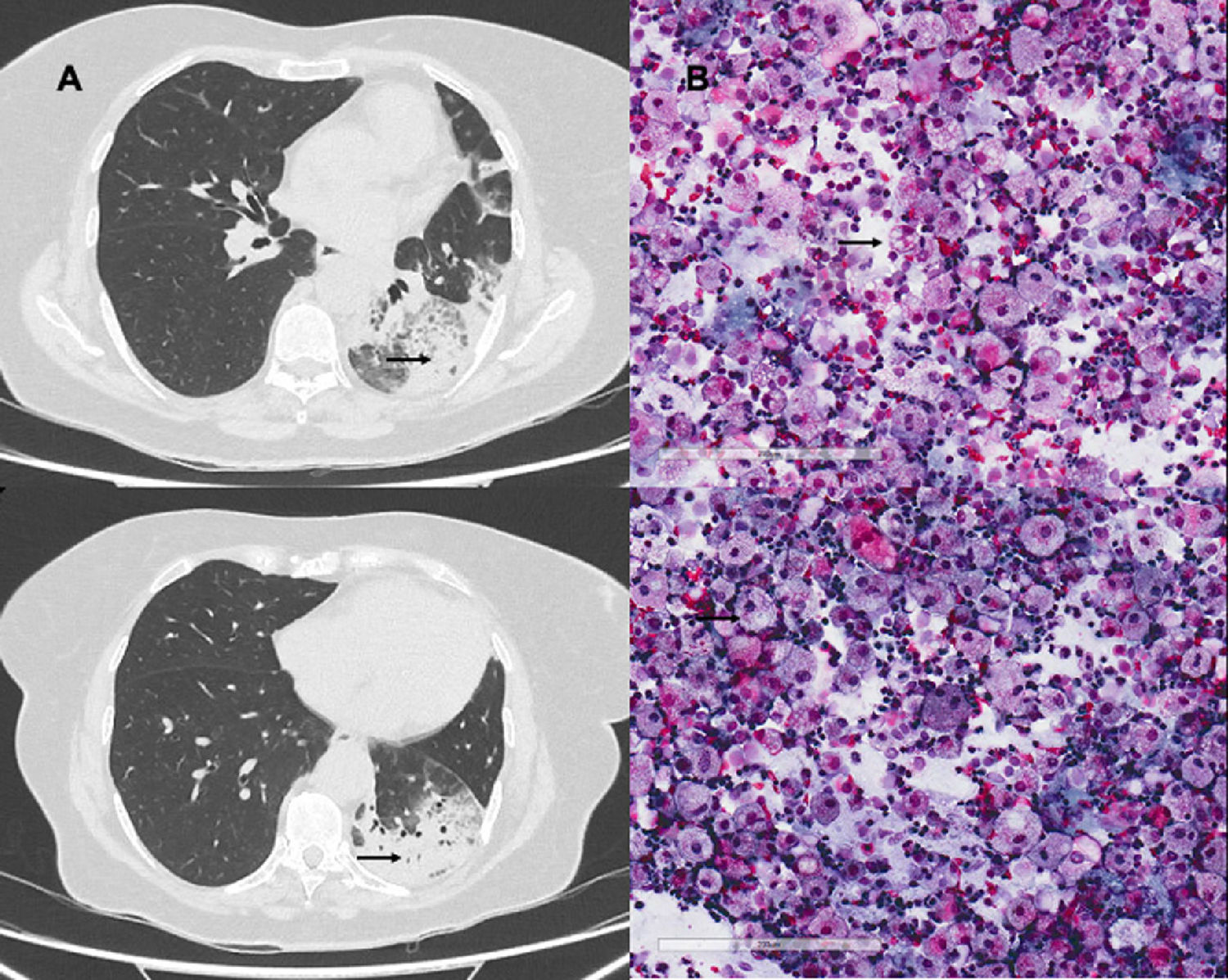
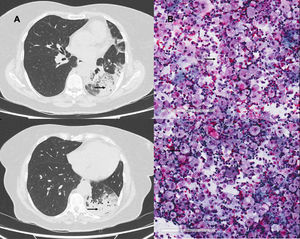
A 69-year-old woman, former smoker who stopped 20 years previously, with no other background of interest, had a 30-year history of using of Vaseline lip balm up to 6 times a day. She presented in the respiratory medicine clinic with a 2-month history of non-productive cough, dyspnea on minimal exertion, and temperature of 37 °C in the last few days. Examination showed an oxygen saturation of 93% in room air and bilateral crackles. Chest X-ray revealed bilateral multiple consolidations. Chest computed tomography located these multifocal consolidations in the left hemitorax and basal segments of the right lower lobe consistent with pneumonic changes.1 Treatment began with dual antibiotic therapy, with little clinical and radiological improvement. Bronchoscopy was performed with bronchoalveolar lavage that was negative for microbiological culture, fungi and mycobacteria, while bronchial cytology findings showed abundant macrophages with foamy vacuolated cytoplasm consistent with lipoid pneumonia associated with the excessive use of petroleum jelly. Discontinuation of this product resulted in clinical and radiological improvement in subsequent follow-ups (Fig. 1).
Exogenous lipoid pneumonia is an uncommon disease caused by lipid deposition within the pulmonary alveoli, which may be caused by absorption of oily agents such as Vaseline lip balm.2
FundingThe current manuscript had no source of funding.
Conflict of interestsThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interests directly or indirectly related with the contents of this manuscript.
We thank all the people who collaborated in this study.
Please cite this article as: Wangüemert Pérez AL. Neumonía lipoidea exógena secundario a uso de vaselina labial. Arch Bronconeumol. 2021;57:298.