Las bronquiectasias son el resultado final de enfermedades diferentes que tienen puntos de manejo comunes. Suelen cursar con infección e inflamación bronquiales crónicas que se asocian con progresión. Siempre debe investigarse la etiología, en especial de las tributarias de tratamiento. Para valora r la gravedad y hacer el seguimiento, recomendamos evaluar la etiología, la clínica, la colonización-infección bronquial, la función respiratoria, la inflamación, el daño estructural, el estado nutricional y la calidad de vida. Su atención debería realizarse en unidades especializadas, al menos en casos de infección bronquial crónica, agudizaciones repetidas o etiología susceptible de tratamiento. El tratamiento tiene como objetivo mejorar la clínica y detener la progresión, y se basa en el tratamiento de la etiología, de la infección aguda y crónica, en el drenaje de secreciones y en el tratamiento de las complicaciones. La pauta de administración del antibiótico depende del control de la infección, que se comprueba con el color del esputo y la disminución de las agudizaciones. Recomendamos los antibióticos inhalados en la infección bronquial crónica sin respuesta clínica o con efectos secundarios al antibiótico oral, en la causada por Pseudomonas, en la causada por microorganismos resistentes a los antibióticos orales y en la colonización inicial por Pseudomonas.
Bronchiectasis is the end result of several different diseases that share principles of management. The clinical course usually involves chronic bronchial infection and inflammation, which are associated with progression. The cause of bronchiectasis should always be investigated, particularly when it can be treated. We recommend evaluating etiology, symptoms, bronchial colonization and infection, respiratory function, inflammation, structural damage, nutritional status, and quality of life in order to assess severity and to monitor clinical course. Care should be supervised by specialized units, at least in cases of chronic bronchial infection, recurrent exacerbations, or when there is a cause that is likely to respond to treatment. Improving symptoms and halting progression are the goals of management, which is based on treatment of the underlying cause and of acute or chronic infections and on the drainage of secretions. Complications that arise must also be treated. Antibiotic prescription is guided by how well infection is being controlled, and this is indicated by the color of sputum and a reduction in the number of exacerbations. We recommend inhaled antibiotics in cases of chronic bronchial infection that does not respond to oral antibiotics, when these cause side effects, or when the cause is Pseudomonas species or other bacteria resistant to oral antibiotics. Inhaled administration is also advisable to treat initial colonization by Pseudomonas species.
Las bronquiectasias (BQ) son dilataciones anormales e irreversibles de los bronquios con alteración del epitelio ciliar. No son una enfermedad en sí mismas, sino el resultado final de enfermedades diferentes que tienen puntos de manejo en común. Sin embargo, clásicamente se han diferenciado en BQ debidas a fibrosis quística (FQ) y BQ no FQ. Las primeras afectan a una población homogénea de pacientes en quienes la afectación respiratoria es el principal factor predictor de mortalidad, el control se realiza en unidades especializadas, la investigación e interés comerciales han sido mayores, y se dispone de conferencias de consenso que facilitan su manejo1-4. No obstante, sólo representan un pequeño porcentaje del total de BQ5. Por el contrario, las BQ no FQ afectan a una población heterogénea de pacientes y tienen etiologías muy diferentes, incluidas las de causa no conocida, cada una con sus propias características; el control se realiza con frecuencia en unidades no especializadas; la investigación y el interés comercial han sido muy inferiores, y no se dispone de conferencias de consenso que faciliten su manejo. La prevalencia no se conoce y probablemente varía en diferentes poblaciones; en EE.UU. se ha estimado una prevalencia de 53 casos por 100.000 adultos, con un coste anual medio por paciente de 13.244 dólares, ligeramente superior al de los pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica, y el 25% de ellos son responsables del 80% del coste total6.
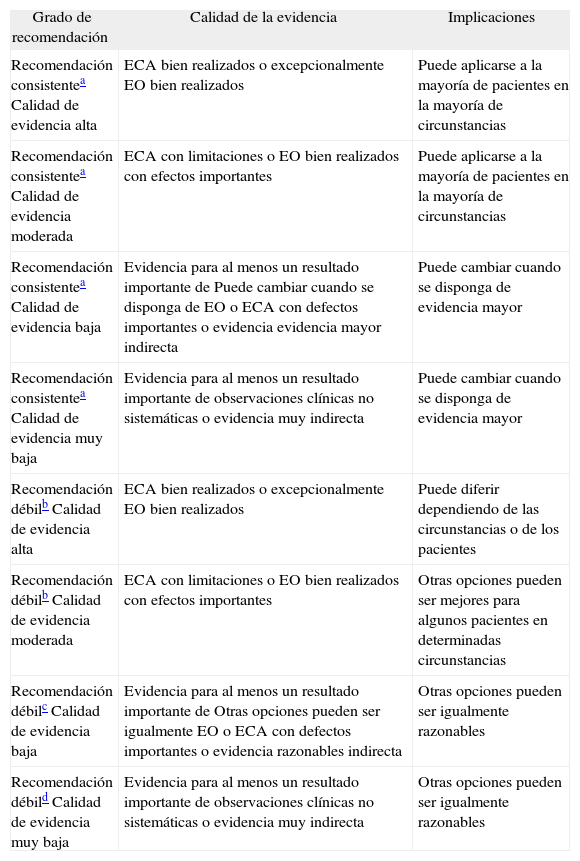
Sea cual sea la etiología, los pacientes con BQ son susceptibles de contraer infecciones bronquiales y desarrollar una respuesta inflamatoria que favorece la progresión de la lesión pulmonar. Dado que es una afección crónica y progresiva, es importante establecer las estrategias de manejo más efectivas para aplicarlas lo antes posible. La ausencia de una normativa sobre BQ en general y el hecho de que las guías actuales de BQ no FQ no reflejen las necesidades de tratamiento de estos pacientes7,8 han motivado la elaboración de la presente normativa. El objetivo es mejorar, facilitar y unificar el manejo de los pacientes con BQ. Las recomendaciones se han establecido con el sistema GRADE9 (tabla I). En los aspectos en que la evidencia científica es insuficiente se han incluido las recomendaciones acordadas por consenso de los autores.
Clasificación de las recomendaciones y calidad de la evidencia según el sistema GRADE9
| Grado de recomendación | Calidad de la evidencia | Implicaciones |
| Recomendación consistentea Calidad de evidencia alta | ECA bien realizados o excepcionalmente EO bien realizados | Puede aplicarse a la mayoría de pacientes en la mayoría de circunstancias |
| Recomendación consistentea Calidad de evidencia moderada | ECA con limitaciones o EO bien realizados con efectos importantes | Puede aplicarse a la mayoría de pacientes en la mayoría de circunstancias |
| Recomendación consistentea Calidad de evidencia baja | Evidencia para al menos un resultado importante de Puede cambiar cuando se disponga de EO o ECA con defectos importantes o evidencia evidencia mayor indirecta | Puede cambiar cuando se disponga de evidencia mayor |
| Recomendación consistentea Calidad de evidencia muy baja | Evidencia para al menos un resultado importante de observaciones clínicas no sistemáticas o evidencia muy indirecta | Puede cambiar cuando se disponga de evidencia mayor |
| Recomendación débilb Calidad de evidencia alta | ECA bien realizados o excepcionalmente EO bien realizados | Puede diferir dependiendo de las circunstancias o de los pacientes |
| Recomendación débilb Calidad de evidencia moderada | ECA con limitaciones o EO bien realizados con efectos importantes | Otras opciones pueden ser mejores para algunos pacientes en determinadas circunstancias |
| Recomendación débilc Calidad de evidencia baja | Evidencia para al menos un resultado importante de Otras opciones pueden ser igualmente EO o ECA con defectos importantes o evidencia razonables indirecta | Otras opciones pueden ser igualmente razonables |
| Recomendación débild Calidad de evidencia muy baja | Evidencia para al menos un resultado importante de observaciones clínicas no sistemáticas o evidencia muy indirecta | Otras opciones pueden ser igualmente razonables |
ECA: estudios controlados y aleatorizados; EO: estudios observacionales.
El espectro clínico es muy variado. Suelen cursar con infecciones respiratorias de repetición y entre estos episodios los pacientes pueden permanecer asintomáticos o presentar expectoración crónica, que puede ser mucosa, mucopurulenta o purulenta. Deben sospecharse especialmente si no hay exposición tabáquica. Pueden cursar con expectoración hemoptoica o hemoptisis recidivante, clínica de hiperreactividad bronquial, disnea según el grado de afectación de la función pulmonar, dolor torácico de carácter pleurítico por afectación de la pleura visceral, astenia y pérdida de peso. Pueden asociarse a sinusitis, en especial las debidas a FQ, discinesia ciliar primaria, inmunodeficiencias primarias, síndrome de Young, síndrome de las uñas amarillas o panbronquiolitis difusa.
La exploración respiratoria puede ser normal o puede haber estertores crepitantes, roncus y/o sibilancias. En la enfermedad avanzada los pacientes pueden presentar acropaquías, caquexia, signos de insuficiencia respiratoria o cor pulmonale.
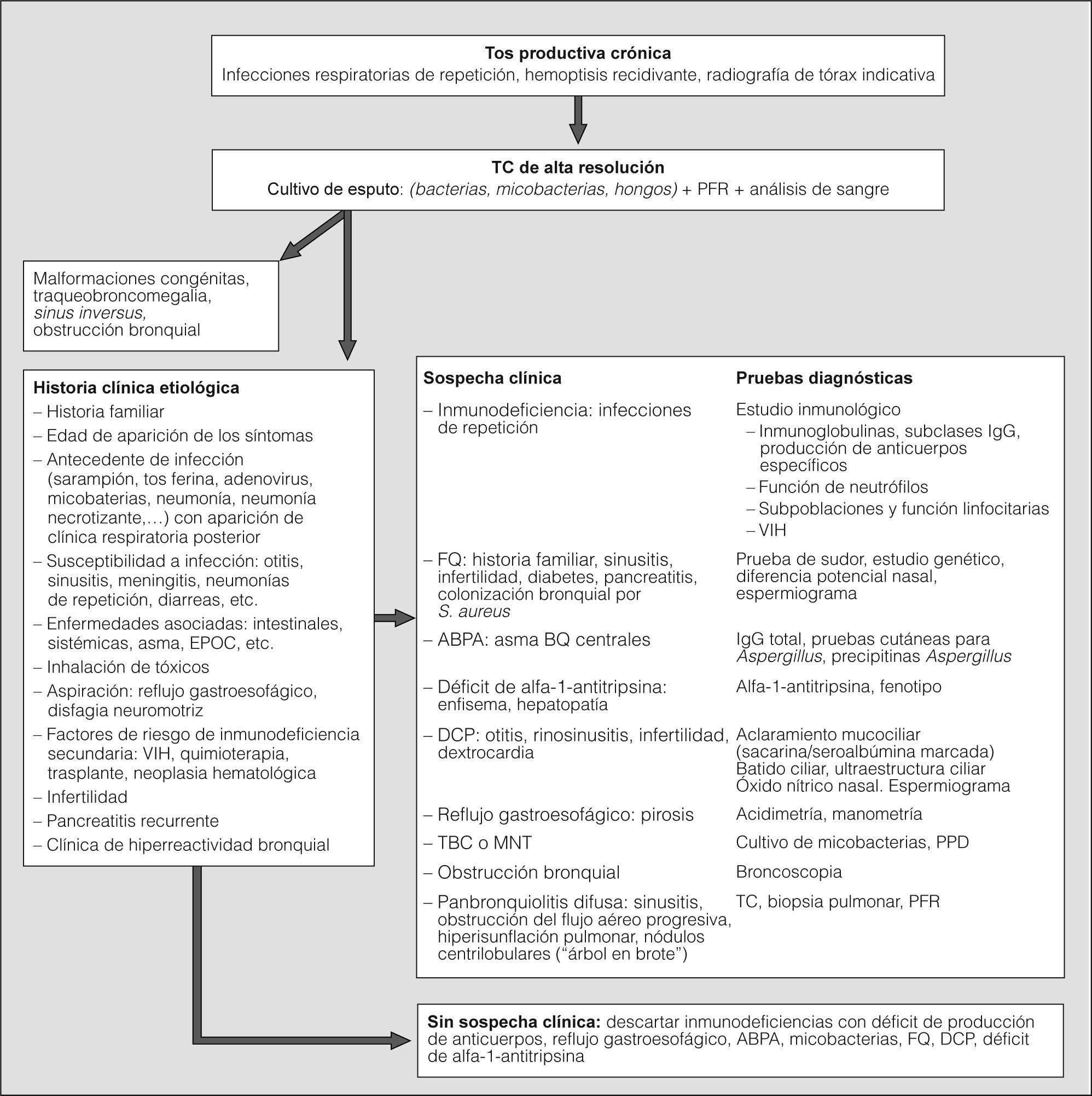
El diagnóstico se realiza por tomografía computarizada (TC) de alta resolución sin contraste, con cortes de 1 mm a intervalos de 10 mm, en inspiración máxima10. (Recomendación consistente. Calidad de evidencia alta.) La TC permite además valorar la extensión y morfología de las BQ (cilindricas, varicosas o quísticas). Los criterios diagnósticos de BQ por TAC son: a) signos directos, tales como dilatación bronquial con una relación broncoarterial mayor de 1–1,5 (signo de anillo de sello), falta de afilamiento de los bronquios y visualización de bronquios a 1 cm de la pleura, y b) signos indirectos, como engrosamiento de la pared bronquial, pérdida de volumen lobular, patrón en mosaico, nódulos en árbol en brote y tapones de moco. La TC puede asimismo indicar la etiología en casos de malformaciones congénitas, situs inversus, traqueobroncomegalia, obstrucción bronquial o enfisema por déficit de alfa-1-antitripsina. Las BQ debidas a tuberculosis predominan en los campos superiores, y en la aspergilosis broncopulmonar alérgica (ABPA) son centrales. La presencia de múltiples nódulos pequeños asociados, de predominio en la língula y lóbulo medio, indica infección por micobacterias no tuberculosas (MNT).
Diagnóstico etiológicoLas etiologías de las BQ se muestran en la tabla II. Su frecuencia ha cambiado con el tiempo en los países desarrollados. Mientras que las causas postinfecciosas han disminuido, las producidas por enfermedades subyacentes que predisponen a la infección y a la inflamación bronquiales se han incrementado5. Todavía hay un porcentaje considerable de pacientes en los que se desconoce la causa (un 26-53% según las series). Una historia clínica detallada y la realización de una TC permiten en muchos casos sospechar la causa e indicar las pruebas diagnósticas necesarias5. Es muy importante la búsqueda sistemática de la etiología, especialmente de las tributarias de un tratamiento específico2,5,11-16, ya que tiene importantes implicaciones clínicas en el manejo y en el pronóstico5,12. Las causas que siempre hay que descartar ante unas BQ de etiología no conocida son las siguientes: inmunodeficiencias con déficit de producción de anticuerpos, reflujo gastroesofágico, ABPA, infección por micobacterias, FQ, discinesia ciliar primaria y déficit de alfa-1-antitripsina. (Recomendación consistente. Calidad de evidencia alta.)
Etiología de las bronquiectasias
| Postinfección |
| Bacterias: neumonía necrosante |
| Micobacterias: tuberculosis, micobacterias no tuberculosas |
| Virus (Adenovirus, sarampión) |
| Hongos |
| Obstrucción bronquial |
| Intrínseca: estenosis cicatricial, broncolitiasis, cuerpo extraño, tumor |
| Extrínseca: adenopatías, tumor, aneurisma |
| Inmunodeficiencias |
| Primarias |
| Déficit de anticuerpos (agammaglobulinemia, inmunodeficiencia común variable, déficit de activación de desaminasa citidina inducida, déficit de anticuerpos con inmunoglobulinas normales, etc.) |
| Inmunodeficiencias combinadas (déficit de TAP, etc.) |
| Otras (síndrome de Wiskott-Aldrich, síndrome de hiperinmunoglobulinemia E, disfunción de los neutrófilos, etc.) |
| Secundarias: quimioterapia, trasplante, neoplasias hematológicas, VIH |
| Alteración de la escalera mucociliar |
| Fibrosis quística |
| Discinesia ciliar primaria |
| Síndrome de Young |
| Neumonitis inflamatoria |
| Aspiración, reflujo gastroesofágico |
| Inhalación de tóxicos (drogas, gases, etc.) |
| Anormalidad del árbol traqueobronquial |
| Traqueobroncomegalia (síndrome de Mounier-Kuhn) |
| Defectos del cartílago (síndrome de Williams-Campbell) |
| Secuestro pulmonar |
| Traqueobroncomalacia |
| Bronquio traqueal |
| Asociada a otras enfermedades |
| Enfermedades sistémicas: artritis reumatoide, lupus eritematoso sistémico, síndrome de Sjogren, síndrome de Marfan, policondritis recidivante, espondilitis anquilosante, sarcoidosis |
| Enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal: colitis ulcerosa, enfermedad de Crohn |
| Otras enfermedades respiratorias: asma, EPOC, síndrome de Swyer-James |
| Déficit de alfa-1-antitripsina, síndrome de las uñas amarillas |
| Aspergilosis o micosis broncopulmonar alérgica |
| Panbronquiolitis difusa |
| Etiología no conocida |
EPOC: enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica: TAP: transportador asociado al procesamiento de antígenos; VIH: virus de la inmunodeficiencia humana.
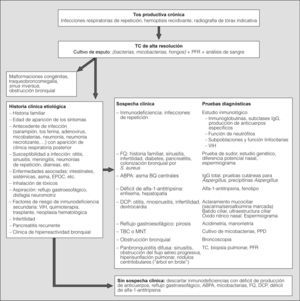
En la figura 1 se muestra el algoritmo diagnóstico propuesto.
Algoritmo diagnóstico. ABPA: aspergilosis broncopulmonar alérgica; BQ: bronquiectasias; DCP: discinesia ciliar primaria; EPOC: enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica; FQ: fibrosis quística; IgE: inmunoglobulina E; IgG: inmunoglobulina G; MNT: micobacterias no tuberculosas; PFR: pruebas de función respiratoria; PPD: derivado proteico purificado RT-23; TC: tomografía computarizada; TBC: tuberculosis; VIH: virus de la inmunodeficiencia humana.
La agudización la definimos como la presentación de forma aguda y mantenida de cambios en las características del esputo (incremento del volumen, la consistencia, la purulencia o hemoptisis), y/o aumento de la disnea no debidos a otras causas7. Puede acompañarse de incremento de la tos, fiebre, astenia, mal estado general, anorexia, pérdida de peso, dolor torácico pleurítico, cambios en la exploración respiratoria, alteraciones en la radiografía de tórax indicativas de infección, deterioro de la función respiratoria o incremento de los marcadores sistémicos de inflamación. La agudización puede asociarse a cambios en la densidad bacteriana de la flora colonizadora o a la adquisición de un microorganismo nuevo.
Se considera agudización grave cuando cursa con taquipnea, insuficiencia respiratoria aguda, insuficiencia respiratoria crónica agudizada, deterioro significativo de la saturación de oxígeno o de la función respiratoria, hipercapnia, fiebre de más de 38 °C, hemoptisis, inestabilidad hemodinámica y/o deterioro del estado cognitivo.
Diagnóstico de colonización, infección e inflamación bronquialesLas BQ son un nicho ecológico ideal para la colonización por diferentes microorganismos, ya que la alteración del sistema mucociliar dificulta la eliminación de las se creciones y facilita el sobrecrecimiento bacteriano. En general, las bacterias que colonizan la mucosa respiratoria son menos virulentas que las que producen enfermedad invasiva y no se adhieren al epitelio bronquial, pero tienen la capacidad de desarrollar mecanismos que facilitan su persistencia al entorpecer la acción de los mecanismos de defensa y de los antimicrobianos (formación de biopelículas, hipermutabilidad, formación de cápsula, etc.). El desarrollo de las bacterias se produce en la superficie de la mucosa respiratoria sin invadir los tejidos adyacentes, lo que da lugar a un proceso de "patogenia pasiva"4. El elevado inóculo bacteriano que normalmente se alcanza y el proceso crónico de colonización son capaces de provocar un efecto inflamatorio sin necesidad de que se produzca una agresión directa4. La diferenciación entre colonización e infección es complicada, y es preferible referirse a la persistencia bacteriana como "colonización patógena"4. Sin embargo, desde el punto de vista clínico se podrían diferenciar varias situaciones:
- 1.
Colonización bronquial: presencia de una población bacteriana que no induce una respuesta inflamatoria con repercusión clínica, a excepción de expectoración mucosa. Puede ser
Inicial: primer cultivo positivo en fase estable de un microorganismo no aislado en cultivos periódicos previos.
Intermitente: cultivos positivos y negativos para un mismo microorganismo, con al menos un mes de diferencia, en pacientes que no están recibiendo antibiótico contra el mismo. En general refleja una colonización crónica con bajos valores cuantitativos, no siempre detectables en el cultivo de esputo4.
Crónica: 3 o más cultivos consecutivos positivos para un mismo microorganismo en un período de 6 meses, en muestras separadas entre sí por al menos un mes4.
- 2.
Infección bronquial crónica: presencia de población bacteriana que induce una respuesta inflamatoria que se manifiesta clínicamente con expectoración purulenta persistente17. Puede acompañarse de infecciones respiratorias de repetición y afectación sistémica, con febrícula, astenia y/o pérdida de peso.
El diagnóstico de colonización y de infección bronquial crónica se realiza con la clínica y el cultivo microbiológico de las secreciones respiratorias. La determinación de anticuerpos anti-Pseudomonas puede ayudar a detectar la colonización crónica por este microorganismo, especialmente en pacientes pediátricos con BQFQ, pero no aporta ventajas sobre los cultivos bacteriológicos.
- 3.
Inflamación bronquial: reacción bronquial inespecífica frente a la infección bacteriana con el objetivo de eliminar el microorganismo. Cuando no se consigue su eliminación, la inflamación se cronifica, se produce una gran acumulación de leucocitos, que son los responsables de las secreciones purulentas17, y se asocia con la progresión del daño pulmonar. La respuesta inflamatoria puede ser sólo local18 o también sistémica19. La primera puede verificarse por el color del esputo: el blanco (mucoso) contiene escaso número de células inflamatorias; el verde pálido o amarillo (mucopurulento), una cantidad moderada, y el verde (purulento), una gran cantidad17. La determinación de mediadores inflamatorios en las secreciones respiratorias18 no se realiza de forma sistemática. La inflamación sistémica puede medirse mediante el recuento de leucocitos y neutrófilos, la velocidad de sedimentación globular, la proteína C reactiva y la inmunoglobulina A11,19.
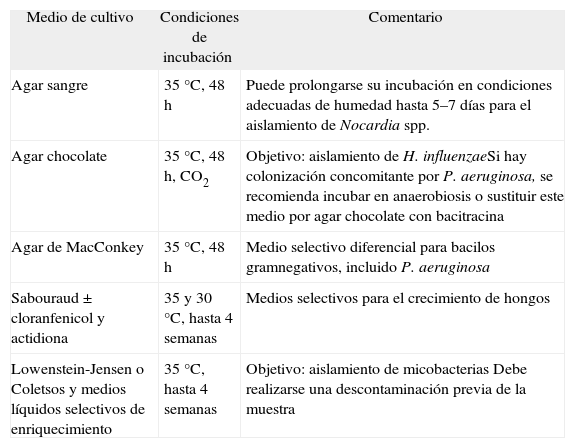
Se realiza preferentemente en esputo tras una valoración microscópica que excluya contaminaciones de la vía respiratoria superior (> 25 leucocitos y < 10 células epiteliales por campo microscópico con bajo aumento). Se recomienda incluir medios generales y selectivos diferenciales para incrementar su rentabilidad y favorecer la diferenciación de los distintos microorganismos (tabla III). Los recuentos bacterianos sistemáticos son controvertidos por el tiempo necesario para su realización y la potencial utilidad de los datos obtenidos, pero deberían utilizarse en la evaluación de nuevos tratamientos, entre ellos las asociaciones de antimicrobianos. Si se sospecha colonización o infección por Nocardia20, es importante avisar al microbiólogo de la sospecha. Una tinción de Gram previa al cultivo puede ser útil para orientar el estudio microbiológico, al igual que incluir la muestra en medios selectivos y establecer condiciones de incubación que aseguren su aislamiento.
Medios de cultivo recomendables, condiciones óptimas de incubación y objetivo de éstos
| Medio de cultivo | Condiciones de incubación | Comentario |
| Agar sangre | 35 °C, 48 h | Puede prolongarse su incubación en condiciones adecuadas de humedad hasta 5–7 días para el aislamiento de Nocardia spp. |
| Agar chocolate | 35 °C, 48 h, CO2 | Objetivo: aislamiento de H. influenzaeSi hay colonización concomitante por P. aeruginosa, se recomienda incubar en anaerobiosis o sustituir este medio por agar chocolate con bacitracina |
| Agar de MacConkey | 35 °C, 48 h | Medio selectivo diferencial para bacilos gramnegativos, incluido P. aeruginosa |
| Sabouraud ± cloranfenicol y actidiona | 35 y 30 °C, hasta 4 semanas | Medios selectivos para el crecimiento de hongos |
| Lowenstein-Jensen o Coletsos y medios líquidos selectivos de enriquecimiento | 35 °C, hasta 4 semanas | Objetivo: aislamiento de micobacterias Debe realizarse una descontaminación previa de la muestra |
En los cultivos pueden aparecer variantes de colonias con morfotipos diferentes de un mismo microorganismo, con el mismo o diferente patrón de sensibilidad frente a los antimicrobianos; por ello se recomienda realizar antibiograma de cada uno de ellos. La infección crónica, los recuentos elevados, la presión selectiva con antimicrobianos y la farmacocinética poco favorable de algunos antibióticos en la mucosa respiratoria favorecen el desarrollo de resistencias. En algunos de los patógenos aislados se ha encontrado un número de mutantes resistentes más alto de lo normal (de 10 a 1.000 veces), lo que, junto al inóculo elevado, facilita la selección de mutantes resistentes durante el tratamiento antimicrobiano21.
Los resultados obtenidos en el antibiograma son esenciales para establecer el tratamiento antimicrobiano. Sin embargo, no siempre hay una buena correlación entre la sensibilidad in vitro convencional y la respuesta al tratamiento, como ocurre con los microorganismos capaces de crecer en biopelículas que reducen la actividad de muchos antibacterianos22. Por otra parte, cuando se utilizan antimicrobianos nebulizados, los criterios de interpretación del antibiograma deberían adecuarse al hecho de que con esta vía de administración se alcanzan concentraciones de antibiótico en la mucosa bronquial mucho más elevadas23.
Las MNT requieren cultivos con medios especiales y una petición expresa al microbiólogo para establecer condiciones que aseguren su aislamiento. Debe aplicarse un proceso de descontaminación que elimine otras bacterias y posibles hongos (tabla III). Una tinción específica para bacterias ácido-alcohol resistentes (Ziehl-Neelsen o preferentemente fluorescente con auramina) puede ser útil, pero debe realizarse una amplificación genómica que excluya la presencia de Mycobacterium tuberculosis. (Recomendaciones consistentes. Calidad de evidencia moderada.)
Valoración de la gravedad y seguimiento. PronósticoLas BQ son una afección crónica, irreversible y progresiva. El pronóstico depende de la enfermedad subyacente, la extensión de las lesiones, la repercusión en la función respiratoria y la gravedad de las agudizaciones1. La infección bronquial crónica, especialmente por Pseudomonas, las agudizaciones graves y la inflamación sistémica se asocian con progresión de la enfermedad24. El diagnóstico precoz de BQ, el diagnóstico y tratamiento precoces de su etiología, el tratamiento adecuado de la infección bronquial crónica, los controles clínicos programados y las medidas preventivas pueden retrasar la progresión de la enfermedad y mejorar la supervivencia1. La atención médica y de enfermería de estos pacientes debería realizarse en unidades especializadas en casos de BQ con una etiología susceptible de tratamiento específico1,2,11-16, con infección bronquial crónica y/o con agudizaciones repetidas.
Los aspectos que hay que considerar y controlar para valorar la gravedad e iniciar intervenciones precoces que minimicen la morbimortalidad son:
La etiología. Hay que considerar si persiste la causa que las ha producido, si ésta recibe el tratamiento adecuado y qué repercusión tienen las BQ en la enfermedad de base. En este sentido, la evolución de las BQ es la principal causa de morbimortalidad en la FQ y en pacientes con inmunodeficiencias, por lo que su tratamiento y control debe ser más agresivo1,12,15.
La clínica. Es recomendable efectuar controles cada 1-6 meses dependiendo de la morbilidad, gravedad y progresión. Deben comprobarse el color y volumen del esputo en fase estable (cuanto más mucoso sea, menor es la inflamación17); el número y la gravedad de las agudizaciones (un mayor número de agudizaciones graves se asocia con un mayor descenso de la función pulmonar24); el grado de disnea; los síntomas y signos de hiperreactividad bronquial; la frecuencia e intensidad de las hemoptisis; la afectación sistémica (astenia, pérdida de peso, febrícula persistente) y la exploración cardiorrespiratoria.
La colonización-infección bronquial. Se recomienda realizar un cultivo de esputo con antibiograma en cada visita y en las agudizaciones. Los microorganismos que colonizan con mayor frecuencia son Haemophilus influenzae no tipificable y Pseudomonas aeruginosa18. Staphylococcus aureus es más frecuente en la FQ y en casos de ABPA; cuando se aísla en otros pacientes, es recomendable revaluarlos para descartar estas etiologías25. La detección precoz de Pseudomonas es muy importante para intentar erradicarla, ya que una vez establecida es muy difícil de eliminar. Se recomienda instaurar medidas para prevenir la transmisión de infección por microorganismos multirresistentes entre pacientes. El aislamiento de MNT se está incrementando, por lo que es recomendable su investigación anual de forma sistemática y siempre que haya un deterioro clínico no justificado26. La colonización fúngica puede darse en etapas avanzadas de la enfermedad sin tener un efecto patógeno en la mayoría de las ocasiones, excepto en el caso de Aspergillus fumigatus, que puede producir ABPA; es aconsejable su investigación anual.
La afectación de la función respiratoria. Es aconsejable el estudio, como mínimo anual, de la función pulmonar con espirometría y prueba broncodilatadora, y en cada visita, la medida de la saturación de oxihemoglobina. La gasometría arterial y una prueba de esfuerzo (prueba de la marcha de 6 min) deben valorarse dependiendo de la afectación de la función pulmonar. En pacientes con riesgo de deterioro acelerado es recomendable efectuar una espirometría en cada control clínico. La obstrucción al flujo aéreo de carácter progresivo es el hallazgo predominante y se relaciona con el engrosamiento de la pared bronquial. El volumen espiratorio forzado en el primer segundo (FEV1) es el factor predictor de mortalidad más importante. El grado de afectación de la función pulmonar es mayor en los pacientes con infección crónica por Pseudomonas24,27 y con mayor inflamación sistémica24, pero el deterioro progresivo disminuye si se tratan de manera adecuada27,28.
La inflamación sistémica. Se recomienda realizar un análisis de sangre anual con marcadores de inflamación sistémica (hemograma, velocidad de sedimentación globular, proteína C reactiva, inmunoglobulina A) y parámetros nutricionales, especialmente en los pacientes con infección bronquial crónica. Otros parámetros específicos se solicitarán en función de la sospecha clínica (p. ej., inmunoglobulina E específica por sospecha de ABPA).
El daño estructural. La TC de alta resolución es más sensible que las pruebas de función respiratoria en la detección de la alteración pulmonar y de su progresión12. Su uso repetido debe valorarse en función de la información que puede aportar y la exposición a la radiación. Se recomienda efectuarla cada 2 años en los pacientes con mayor riesgo de progresión, y siempre que aparezcan nuevas lesiones en la radiografía de tórax27. Esta última se recomienda en casos de sospecha de complicaciones pulmonares agudas (hemoptisis, neumonía, neumotórax, etc.).
La valoración nutricional. Debe formar parte del manejo de las BQ, dado el riesgo de desnutrición. Puede realizarse por diferentes métodos en función de la disponibilidad del centro29. Son indispensables en cada consulta y/o ingreso: peso, índice de masa corporal (IMC) y pérdida de peso en relación con el tiempo. El IMC mínimo que se recomienda alcanzar y mantener es de 22 kg/m2 en mujeres y 23 kg/m2 en varones. Un IMC inferior a 18,5 kg/m2 y/o pérdidas de peso superiores al 5% en 2 meses o al 10% en 6 meses deben considerarse criterio absoluto de desnutrición. Es recomendable realizar anualmente una valoración detallada de la dieta habitual (encuesta dietética de 3 días), albúmina (al menos anualmente y en ingresos) y prealbúmina (sobre todo en pacientes ingresados o con agudización para valorar la eficacia del tratamiento nutricional). Para una valoración nutricional más completa, en pacientes desnutridos o con riesgo de desnutrición se recomienda la evaluación en una unidad de nutrición y dietética.
La calidad de vida. La aplicación de cuestionarios validados (St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire) permite valorar la percepción de gravedad que tiene el paciente, en la cual los factores que más influyen son la disnea, el FEV1 y el volumen de esputo30.
Recomendaciones de tratamientoEl objetivo es mejorar la clínica y prevenir la progresión de la enfermedad.
Tratamiento de la etiologíaSe realizará siempre que se haya identificado la etiología y sea posible, especialmente en casos de déficit de producción de anticuerpos12, ABPA5, reflujo gastroesofágico5, obstrucción bronquial, infección por micobacterias26, déficit de alfa-1-antitripsina, FQ1,15, enfermedades asociadas5 (enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal, autoinmunitarias, panbronquiolitis, entre otras). (Recomendación consistente. Calidad de evidencia alta.)
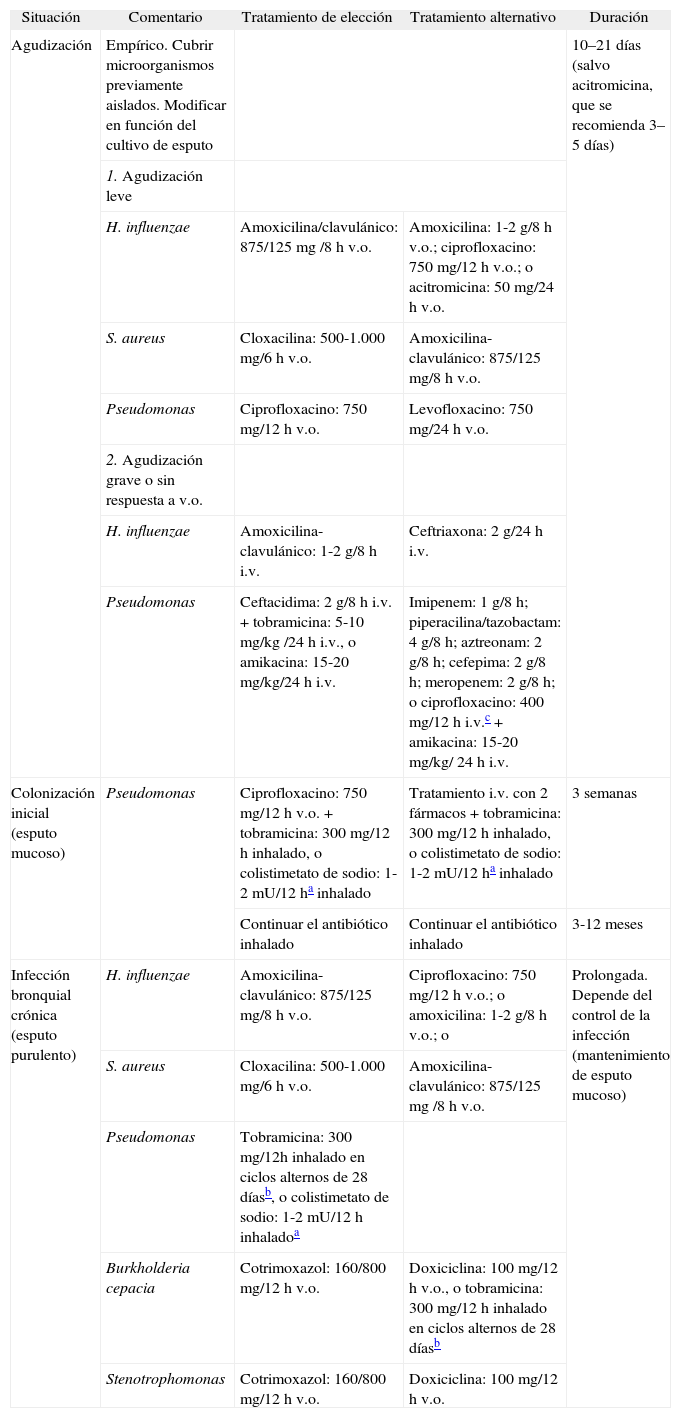
Tratamiento de la agudizaciónLos antibióticos, facilitar la eliminación de las secreciones y el tratamiento del broncoespasmo asociado constituyen la base del tratamiento de las agudizaciones. La elección del antibiótico depende de la presencia o no de una colonización o infección bronquial crónica conocida. En el primer caso hay que adecuar el antibiótico a los microorganismos previamente aislados; en el segundo, debe iniciarse un antibiótico empírico. Siempre debe tenerse en cuenta el riesgo de colonización por P. aeruginosa (antibioterapia u hospitalización reciente, enfermedad grave, aislamientos previos de Pseudomonas7). El antibiótico debe modificarse dependiendo del microorganismo aislado en el cultivo de esputo durante la agudización y su antibiograma. Hay que usar antibióticos con alto grado de penetración en las secreciones respiratorias, a dosis elevadas, y administrarlos hasta que el esputo deje de ser purulento, con un mínimo de 10 días, y en casos de infección por Pseudomonas, durante 14–21 días2,4. El lugar y la vía de administración dependen de la gravedad de la agudización y de la presencia de infección bronquial crónica previa por microorganismos multirresistentes. Las agudizaciones leves pueden tratarse ambulatoriamente por vía oral2. La vía intravenosa se utilizará en casos de agudizaciones graves, infección bronquial crónica por microorganismos resistentes a los antibióticos por vía oral, falta de respuesta al antibiótico oral y en agudizaciones por Pseudomonas en pacientes con FQ cuando no se haya aislado con anterioridad4. Puede administrarse en el hospital o en el domicilio dependiendo del estado del paciente y de los recursos disponibles, siempre con supervisión apropiada31. En casos de agudizaciones moderadas-graves por Pseudomonas se recomienda utilizar 2 antibióticos por vía intravenosa (generalmente un betalactámico y un aminoglucósi-do)2,4. Es mejor administrar los aminoglucósidos en una sola dosis32. Añadir un antibiótico por vía inhalada al tratamiento antibiótico oral o intravenoso no ha demostrado aportar beneficios clínicos33 (tabla IV). (Recomendaciones consistentes. Calidad de evidencia moderada.)
Tratamiento antibiótico en diferentes situaciones clínicas
| Situación | Comentario | Tratamiento de elección | Tratamiento alternativo | Duración |
| Agudización | Empírico. Cubrir microorganismos previamente aislados. Modificar en función del cultivo de esputo | 10–21 días (salvo acitromicina, que se recomienda 3–5 días) | ||
| 1. Agudización leve | ||||
| H. influenzae | Amoxicilina/clavulánico: 875/125 mg /8 h v.o. | Amoxicilina: 1-2 g/8 h v.o.; ciprofloxacino: 750 mg/12 h v.o.; o acitromicina: 50 mg/24 h v.o. | ||
| S. aureus | Cloxacilina: 500-1.000 mg/6 h v.o. | Amoxicilina-clavulánico: 875/125 mg/8 h v.o. | ||
| Pseudomonas | Ciprofloxacino: 750 mg/12 h v.o. | Levofloxacino: 750 mg/24 h v.o. | ||
| 2. Agudización grave o sin respuesta a v.o. | ||||
| H. influenzae | Amoxicilina-clavulánico: 1-2 g/8 h i.v. | Ceftriaxona: 2 g/24 h i.v. | ||
| Pseudomonas | Ceftacidima: 2 g/8 h i.v. + tobramicina: 5-10 mg/kg /24 h i.v., o amikacina: 15-20 mg/kg/24 h i.v. | Imipenem: 1 g/8 h; piperacilina/tazobactam: 4 g/8 h; aztreonam: 2 g/8 h; cefepima: 2 g/8 h; meropenem: 2 g/8 h; o ciprofloxacino: 400 mg/12 h i.v.c + amikacina: 15-20 mg/kg/ 24 h i.v. | ||
| Colonización inicial (esputo mucoso) | Pseudomonas | Ciprofloxacino: 750 mg/12 h v.o. + tobramicina: 300 mg/12 h inhalado, o colistimetato de sodio: 1-2 mU/12 ha inhalado | Tratamiento i.v. con 2 fármacos + tobramicina: 300 mg/12 h inhalado, o colistimetato de sodio: 1-2 mU/12 ha inhalado | 3 semanas |
| Continuar el antibiótico inhalado | Continuar el antibiótico inhalado | 3-12 meses | ||
| Infección bronquial crónica (esputo purulento) | H. influenzae | Amoxicilina-clavulánico: 875/125 mg/8 h v.o. | Ciprofloxacino: 750 mg/12 h v.o.; o amoxicilina: 1-2 g/8 h v.o.; o | Prolongada. Depende del control de la infección (mantenimiento de esputo mucoso) |
| S. aureus | Cloxacilina: 500-1.000 mg/6 h v.o. | Amoxicilina-clavulánico: 875/125 mg /8 h v.o. | ||
| Pseudomonas | Tobramicina: 300 mg/12h inhalado en ciclos alternos de 28 díasb, o colistimetato de sodio: 1-2 mU/12 h inhaladoa | |||
| Burkholderia cepacia | Cotrimoxazol: 160/800 mg/12 h v.o. | Doxiciclina: 100 mg/12 h v.o., o tobramicina: 300 mg/12 h inhalado en ciclos alternos de 28 díasb | ||
| Stenotrophomonas | Cotrimoxazol: 160/800 mg/12 h v.o. | Doxiciclina: 100 mg/12 h v.o. | ||
Los antibióticos referidos son los más utilizados. La selección de éstos, de otros o de sus combinaciones depende del microorganismo aislado y de su antibiograma. Las dosis referidas son las recomendadas en población adulta.
i.v.: vía intravenosa; v.o.: vía oral.
La dosis de colistimetato de sodio depende del tipo de nebulizador utilizado. Un nebulizador con menor volumen residual como I-neb permite utilizar menor dosis (1 mU/12 h).
Colonización bronquial inicial. No existe evidencia para indicar tratamiento antibiótico, excepto en el caso del primer aislamiento de Pseudomonas en BQ debidas a FQ, con el objetivo de erradicarla para retrasar la colonización crónica4. Se recomienda la administración de ciprofloxacino oral junto a un antibiótico inhalado (tobramicina o colistimetato de sodio) durante 3 semanas y continuar con el inhalado de 3 a 12 meses4,34, o bien 2 antibióticos intravenosos durante 14–21 días y continuar con el inhalado también de 3 a 12 meses (tabla IV). (Recomendación consistente. Calidad de evidencia moderada.)
Aunque no hay estudios en otras etiologías, es recomendable administrar ciprofloxacino oral durante 3 semanas y, si no se consigue la erradicación, aplicar la misma pauta que en la FQ. Con el aislamiento de otros microorganismos se recomienda efectuar una valoración individualizada. (Recomendación consistente. Calidad de evidencia baja.)
Colonización bronquial intermitente o crónica. Se debe considerar el tratamiento antibiótico prolongado ante cualquiera de las siguientes situaciones: agudizaciones repetidas, recaídas tempranas, ingresos hospitalarios, deterioro de la función pulmonar o colonización crónica por Pseudomonas, con las mismas pautas que en la infección bronquial crónica. (Recomendación consistente. Calidad de evidencia baja.)
Infección bronquial crónica. El tratamiento se basa en la administración prolongada de antibiótico35 y en facilitar el drenaje de secreciones. El objetivo es romper el círculo vicioso de infección-inflamación reduciendo tanto la carga bacteriana como la respuesta inflamatoria y, con ello, el volumen y la purulencia del esputo, el número y la gravedad de las agudizaciones, así como el deterioro de la función pulmonar. La elección del antibiótico depende del microorganismo causante de la infección y de su antibiograma. La pauta y el tiempo de administración dependen del control de la infección, que se verifica con la obtención y el mantenimiento de un esputo lo más mucoso posible y la disminución de las agudizaciones. La vía de administración puede ser oral o inhalada. Esta última se recomienda en caso de no respuesta clínica con el antibiótico oral o de efectos secundarios con el mismo, en la infección por Pseudomonas1-4,28,36 o en la infección por microorganismos resistentes a los antibióticos por vía oral37. Los antibióticos disponibles por vía inhalada son el colistimetato de sodio y la tobramicina sin aditivos; si se precisara utilizar otros antibióticos, puede considerarse el uso de las preparaciones intravenosas, que deben ser lo más isotónicas posibles y sin aditivos37 (amoxicilina, ceftacidima, aztreonam), aunque hay pocos estudios que demuestren su eficacia. Dado que la tobramicina sin aditivos se administra en períodos intermitentes de 28 días28, hay que valorar si los pacientes con infección bronquial de difícil control pueden requerir otro antibiótico, oral o inhalado, durante los períodos de descanso. Los antibióticos inhalados deben administrarse con nebulizadores específicos para este fin —compresor de alto flujo con nebulizador a chorro PARI LC PLUS (Pari)28,33,36, o nebulizadores electrónicos: eFlow (Pari), I-neb (Respironics)—. Pueden producir broncoespasmo, aumento de la disnea o molestias torácicas que deben controlarse. Son recomendables la administración de un broncodilatador de acción rápida y el drenaje de secreciones antes de su administración. Los aminoglucósidos deberían evitarse en pacientes con hipoacusia o insuficiencia renal (tabla IV). (Recomendaciones consistentes. Calidad de evidencia moderada.)
Tratamiento de la inflamación bronquialEl tratamiento prolongado con corticoides orales o ibuprofeno no está recomendado por los efectos secundarios.
Macrólidos. Son efectivos en el tratamiento de la panbronquiolitis difusa y disminuyen el número de agudizaciones en las BQ de otras etiologías38,39. Su efecto probablemente se debe a su acción moduladora de la respuesta inflamatoria y a la capacidad de interferir con la formación de biopelículas. Se recomienda su administración en la infección bronquial crónica por Pseudomonas1,38 o por otros microorganismos con control clínico difícil a pesar de un tratamiento adecuado39. El fármaco con el que se dispone de mayor experiencia es la acitromicina a dosis de 250 a 500 mg en función del peso, 3 días por semana durante períodos de 3 a 6 meses. No se han realizado estudios que demuestren su eficacia y seguridad en tratamientos de más de 12 meses de duración. La pauta óptima (duración, dosis, periodicidad) todavía debe establecerse. Es recomendable el control de la función hepática en las primeras semanas del tratamiento y a intervalos regulares de 6 meses, así como la investigación de MNT en secreciones respiratorias antes de iniciar el tratamiento y cada 6 meses. Los pacientes en que se aíslen MNT no deberían recibir monoterapia con macrólidos26. (Recomendaciones consistentes. Calidad de evidencia moderada.)
Corticoides inhalados. Están indicados especialmente en pacientes con clínica de hiperreactividad bronquial40. Han demostrado ser eficaces en aquéllos con mayor volumen de esputo41, si bien no se recomienda su uso sistemático sin que se objetive un efecto beneficioso en cada caso individual40,41. (Recomendación consistente. Calidad de evidencia moderada.)
Tratamiento de la hiperreactividad bronquialSe utilizarán broncodilatadores y corticoides inhalados. Los broncodilatadores también mejoran la movilidad ciliar y facilitan el aclaramiento de secreciones. Se recomienda la administración de broncodilatadores de acción rápida antes de la realización de fisioterapia y de la aerosolterapia antibiótica3. (Recomendaciones consistentes. Calidad de evidencia moderada.)
Tratamiento nutricionalDebe ofrecerse consejo dietético individualizado lo antes posible con el objetivo de mejorar la ingesta calórica, sobre todo en pacientes con enfermedad grave o mayor riesgo de desnutrición29. Se recomienda añadir suplementos orales en personas con IMC menor de 20 kg/m2, o bien mayor de 20 kg/m2 si están perdiendo peso de forma aguda (especialmente en las agudizaciones e ingresos). Se utilizarán fórmulas poliméricas e hipercalóricas, sobre todo si se requiere restricción de líquidos. En situaciones de alto estrés metabólico (valores de albúmina < 3 g/dl) es recomendable que sean, además, hiperproteicas. El empleo de fórmulas altas en grasas no debe ser la norma. En caso de diabetes concomitante, las fórmulas con alto contenido en ácidos grasos monoinsaturados mejoran el control metabólico42. (Recomendaciones consistentes. Calidad de evidencia baja.)
Rehabilitación respiratoria. MucolíticosLos pacientes deben entrar en programas de rehabilitación respiratoria dirigidos por profesionales especializados, con el objetivo de facilitar la eliminación de secreciones y mejorar tanto la tolerancia física como la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud42. Tanto en el nivel ambulatorio como en el hospitalario hay que aplicar medidas efectivas para evitar las infecciones cruzadas, además de mantener una oxigenación adecuada en pacientes con enfermedad moderada-grave. (Recomendación consistente. Calidad de evidencia moderada.)
Fisioterapia respiratoria. Se recomienda en pacientes con hipersecreción bronquial (≥ 30 ml/día)42, de una a 3 veces al día, después del tratamiento broncodilatador y previa a los antibióticos inhalados3. Incluye varias técnicas que pueden combinarse (tabla V), sin que haya evidencia de cuál es la más efectiva. La elección dependerá de la edad del paciente y de su capacidad para realizar la técnica. Se recomiendan las técnicas autoadministradas para facilitar el cumplimiento a largo plazo. (Recomendaciones consistentes. Calidad de evidencia baja.)
Técnicas para el aclaramiento mucociliar de la vía aérea
| Técnicas asistidas |
| Fisioterapia respiratoria convencional (drenajes bronquiales, tos eficaz, percusión-vibraciones torácicas) |
| Técnicas de ciclo activo |
| Drenaje autógeno |
| Técnica de espiración lenta con glotis abierta y en decúbito lateral |
| Dispositivo de oscilación de la vía aérea: ventilador de percusión intrapulmonar |
| Técnicas no asistidas |
| Dispositivos de oscilación de la vía aérea: Flutter®, Cornet®, Acapella® |
| Técnica de espiración forzada |
| Presión positiva espiratoria |
| Compresor de alta frecuencia del tórax |
Ejercicio. El ejercicio físico aeróbico (caminar, correr, ciclismo o natación) mejora la tolerancia física y la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud. Se recomienda a todos los pacientes practicar ejercicio de moderado a intenso durante 30 min al día, de 3 a 4 veces por semana, o, en su defecto, una actividad física moderada todos los días, además de las técnicas de fisioterapia43. (Recomendación consistente. Calidad de evidencia moderada.)
Mucolíticos. La bromhexina o el manitol pueden facilitar la eliminación de secreciones44,45. La solución salina hipertónica nebulizada y la desoxirribonucleasa pueden reducir las agudizaciones en la FQ con afectación pulmonar leve o moderada1. (Recomendación consistente. Calidad de evidencia moderada.) En otras etiologías la desoxirribonucleasa no se ha demostrado efectiva46; sin embargo, mantener una buena hidratación y la solución salina hipertónica nebulizada pueden ser beneficiosos45.
Tratamiento de las complicacionesHemoptisis. Generalmente se produce en una agudización. Requiere, además de las medidas habituales, administrar antibiótico intravenoso, evitar fármacos inhalados y la fisioterapia, al menos durante las primeras 24–48 h. La embolización de las arterias bronquiales patológicas de la zona de la hemorragia es el tratamiento de elección. La cirugía sólo está indicada cuando hay riesgo vital y el origen de la hemorragia está bien localizado, sin que pueda controlarse la hemoptisis con las medidas anteriores2,47. (Recomendación consistente. Calidad de evidencia moderada.)
Amiloidosis. La inflamación crónica incrementa la producción hepática de amiloide A, un reactante de fase aguda, que es degradado por macrófagos circulantes en fragmentos que se depositan en los tejidos. El diagnóstico se realiza por biopsia del órgano afectado. El análisis de orina sirve de cribado, ya que el 95% de los pacientes tiene proteinuria. El tratamiento es el del órgano afectado y el de la infección-inflamación crónica. (Recomendación consistente. Calidad de evidencia moderada.)
Insuficiencia respiratoria. Requiere oxígeno y ventilación mecánica no invasiva en caso de acidosis respiratoria aguda o crónica. Las indicaciones de valoración de trasplante pulmonar son: FEV1 inferior al 30% o pérdida rápida de la función pulmonar en pacientes con afectación grave, insuficiencia respiratoria crónica, hipercapnia, hipertensión pulmonar, agudizaciones o complicaciones graves frecuentes48. La colonización por microorganismos multirresistentes es una contraindicación relativa.
CirugíaEs el único tratamiento curativo en caso de BQ localizadas que causen problemas de manejo clínico, siempre que se descarten las enfermedades subyacentes que favorecen su aparición. Está indicada con intención paliativa en casos de hemoptisis grave con embolización inefectiva, o de zonas abscesificadas no curables con tratamiento antibiótico49. (Recomendación consistente. Calidad de evidencia baja.)
Criterios de ingreso hospitalarioSe considerará el ingreso en caso de: agudizaciones graves, falta de mejoría con tratamiento ambulatorio, necesidad de tratamiento intravenoso, deterioro progresivo de la función pulmonar, pérdida de peso progresiva no controlada, comorbilidad, carencia de apoyo social, hemoptisis moderadas-graves u otras complicaciones. Los criterios de ingreso en unidades de cuidados intensivos son los mismos que en otras enfermedades respiratorias7. Se recomienda aplicar medidas preventivas para evitar las infecciones cruzadas.
Profilaxis de la infecciónSe siguen las mismas recomendaciones que para la prevención de infecciones del aparato respiratorio inferior7. Se aconseja la administración de las vacunas antigripal y antineumocócica. (Recomendaciones consistentes. Calidad de evidencia baja.)
Educación del pacienteLas BQ son una enfermedad crónica cuyo manejo puede ser complejo. Se recomienda que los pacientes con una etiología susceptible de tratamiento específico1,2,11-16, con infección bronquial crónica y/o con agudizaciones repetidas sean controlados en unidades especializadas que dispongan de neumólogo, de enfermería y de rehabilitación especializados en su cuidado. Son importantes la educación y supervisión en: el reconocimiento de la agudización y su automanejo inicial50, la administración de antibióticos inhalados e intravenosos en el domicilio, el mantenimiento y la limpieza de los equipos, la administración de otros tratamientos (oxígeno, ventilación mecánica, vacunas, etc.), la nutrición, la fisioterapia y el cumplimiento del tratamiento. (Recomendación consistente. Calidad de evidencia moderada.)
Aspectos a tener en cuenta en población infantilMuchas de las BQ del adulto tienen su origen en la edad pediátrica5, por lo que una intervención precoz podría minimizar su morbilidad y mortalidad a largo plazo. La inmadurez inmunológica puede ser un importante factor propiciador, ya que la mayoría de las BQ en la infancia son adquiridas, siendo la más frecuente la infecciosa. El patrón bacteriológico es distinto del que se observa en el adulto; H. influenzae y Streptococcus pneumoniae son los patógenos predominantes. El aislamiento de P. aeruginosa no es común y obligaría a descartar la FQ.
Las BQ consecutivas a neumonía pueden desaparecer en algunos casos51, por lo que algunos autores proponen una nueva definición para la población infantil, que distinguiría: a) pre-BQ (inflamación bronquial persistente sin alteración estructural), que pueden resolverse, persistir o progresar a b) BQ detectadas por TC, donde ya hay dilatación bronquial, y que a su vez pueden resolverse, retornar al estadio previo, persistir o progresar a c) BQ establecidas, que ya serían irreversibles.
Queremos dar las gracias al Dr. Pedro Ortuño (Servicio de Radiología del Hospital Josep Trueta de Girona) por la revisión del diagnóstico radiológico de bronquiectasias.