Cough during childhood is very common, and is one of the most frequent reasons for consultation in daily pediatric practice. The causes differ from those in adults, and specific pediatric guidelines should be followed for correct diagnosis and treatment. The most common cause of cough in children is viral infection producing “normal cough”, but all children with persistent cough, i.e. a cough lasting more than 4–8weeks or “chronic cough”, must be carefully evaluated in other to rule out specific causes that may include the entire pediatric pulmonology spectrum. The treatment of cough should be based on the etiology. Around 80% of cases can be diagnosed using an optimal approach, and treatment will be effective in 90% of them. In some cases of “nonspecific chronic cough”, in which no underlying condition can be found, empirical treatment based on the cough characteristics may be useful. There is no scientific evidence to justify the use of over-the-counter cough remedies (anti-tussives, mucolytics and/or antihistamines), as they could have potentially serious side effects, and thus should not be prescribed in children.
La tos en la infancia es un síntoma muy frecuente, y constituye uno de los motivos de consulta más comunes en la práctica pediátrica diaria. Las causas de tos en el niño son diferentes a las del adulto y se deben seguir las guías específicas de la edad pediátrica para su diagnóstico y tratamiento. En la mayoría de casos la causa son infecciones respiratorias banales que producen una «tos normal o esperada», pero todo niño con tos que persiste más allá de las 4 a 8semanas se considera que tiene «tos crónica» y debe ser evaluado para descartar patologías específicas que abarcan todo el espectro de la neumología pediátrica. El tratamiento de la tos debe realizarse en función de la etiología. Con un abordaje adecuado se puede identificar la misma hasta en el 80% de los casos y el tratamiento será efectivo en el 90% de ellos. En algunos casos de «tos crónica inespecífica», tos en la que se ha descartado patología subyacente, se puede realizar un tratamiento empírico en función de las características de la tos. No hay evidencia científica que justifique el empleo de tratamientos sintomáticos que alivien la tos, como jarabes antitusivos, mucolíticos y/o antihistamínicos, ya que pueden tener efectos secundarios potencialmente graves, por lo que no se deben emplear.
Cough is a complex physiological reflex that consists of a violent expiration to release secretions, foreign matter, overcome bronchospasm or relieve diseases of the airways and protect the respiratory system.1,2 Cough receptors, located along the length of the airway from the larynx to the segmentary bronchi, are stimulated by chemical irritation, tactile stimulation and mechanical forces. The cough reflex consists of an afferent pathway, where impulses travel via the branches of the vagal and laryngeal nerves to the brainstem and are modulated in the cerebral cortex, followed by a motor efferent pathway that includes the respiratory muscles. Upper respiratory tract infections (URTI), bronchial hyperactivity (BHR), asthma, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and angiotensin converter enzyme inhibitor therapy, among others, increase the sensitivity of the cough receptors.3–5 A healthy school-aged child with no history of URTI in the previous 4 weeks can cough up to 34 times a day.6,7 However, coughing is one of the most common reasons for consultation in routine pediatric practice and becomes very worrying when it persists for a prolonged period of time; it impacts negatively on sleep and daily activities and affects the quality of life of the child and the parents or caregivers.8,9 Management of cough in children must be carried out in accordance with applicable pediatric guidelines, that are notably different from those used in adults.10,11 In recent years, specific guidelines have been developed for the management of cough in children in America,12 the United Kingdom13 and Australia and New Zealand.14 The aim of this review is to update the evidence on the etiology, diagnosis and treatment of cough in children.
Etiology of Cough in ChildrenIn pediatrics, the causes of cough vary clearly according to age, as discussed below.11–20 Exposure to tobacco smoke and other environmental contaminants and smoking by the children and adolescents themselves are a common cause of cough or the failure of cough to resolve at all ages.4 Sometimes there may be more than one underlying cause, and an integral etiological approach to this disease in children is fundamental in order to assign appropriate treatment.16–21
Evaluation of the Child With CoughOne way of approaching cough in children is to evaluate it according to the length of time that symptoms have been present. Thus, cough is classified as acute, subacute or chronic.
Acute CoughThe definition of acute cough varies depending on the guidelines: the US and Australian-New Zealand guidelines establish the duration of acute cough as 2 weeks,12,14 while the UK guidelines suggest 4 weeks.13 In most children, cough is caused by URTI that normally resolves spontaneously. Preschoolers may have up to 8–10 episodes of URTI a year, and coughing may last for more than 2 weeks.22 In this setting, the possibility of inhalation of a foreign body or bacterial infections must be taken into consideration.13
Diagnostic Evaluation of Acute CoughChildren with acute cough do not generally require any complementary examination, since progress is usually self-limiting. A chest X-ray would be indicated if there is a clinical suspicion of pneumonia or a chronic respiratory disorder, hemoptysis, sudden onset of cough or an episode of choking that might suggest aspiration of a foreign body.22 In this case, inspiration and expiration X-rays should be taken, and if there is a clear suspicion, a rigid bronchoscopy should be performed, although a flexible bronchoscopy may initially be considered. In this setting, the characteristics of the cough may sometimes assist in the diagnostic procedure: for example, cough accompanied by wheezing suggests asthma; a hacking or metallic cough may be indicative of tracheomalacia, laryngomalacia or croup; a paroxystic cough with or without stridor may suggest pertussoid syndromes; a staccato cough may be due to Chlamydia trachomatis or Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection; and a croaking, strident cough may be psychogenic.
Treatment of Acute CoughTreatment of URTIs requires antipyretics, good hydration and aspiration of secretions. There is no placebo-controlled evidence to suggest the usefulness of antitussive syrups, antihistamines or combinations of these; indeed the adverse effects are potentially very serious, so these products should be avoided.23–26 Honey has been shown to be more effective than placebo in the treatment of cough associated with URTI.27 Bronchodilators are ineffective in non-asthmatic children, and antibiotics are recommended if bacterial infection, streptococcal tonsillitis or pneumonia is suspected.4 Educating the public and healthcare professionals about the natural history of cough associated with URTI is very important for avoiding unnecessary consultations and examinations, since in the majority of the cases, the cough will resolve two weeks after onset.28
Subacute CoughBetween acute cough and chronic cough lies a gray area, known as subacute cough. The US and Australian-New Zealand guidelines define it as cough lasting 4 weeks12,14 and the UK guidelines set the limit at 8 weeks.13 In most cases, it is caused by prolonged or overlapping URTIs or bacterial infections.29 The recommended approach is observation, and if the cough persists more than 4 weeks, a chest X-ray should be performed. If it is normal, the child should be monitored up for 6–8 weeks. If it does not abate, the cough should be considered from its duration as chronic, and the appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic procedures should be initiated.
Chronic CoughChronic cough in children is cough persisting more than 4 weeks, according to the US and Australian-New Zealand guidelines, or more than 8 weeks, according to the UK guidelines.12–14 The causes of chronic cough in children vary depending on age. Marchant et al.17 carried out an etiological study in preschoolers with chronic cough, finding that the most common cause was persistent bacterial bronchitis (PBB) (40%). The next most common cause was spontaneously resolving prolonged or overlapping URTIs, while only 10% of cases were caused by asthma, upper airway cough syndrome or GERD. In the study by Asiloy et al.16 in schoolchildren, the most common causes of cough were asthma (25%), PBB (23%), upper airways syndrome (20%) and GERD (5%). After adolescence, the causes of chronic cough are similar to those in adults.2,10,30,31
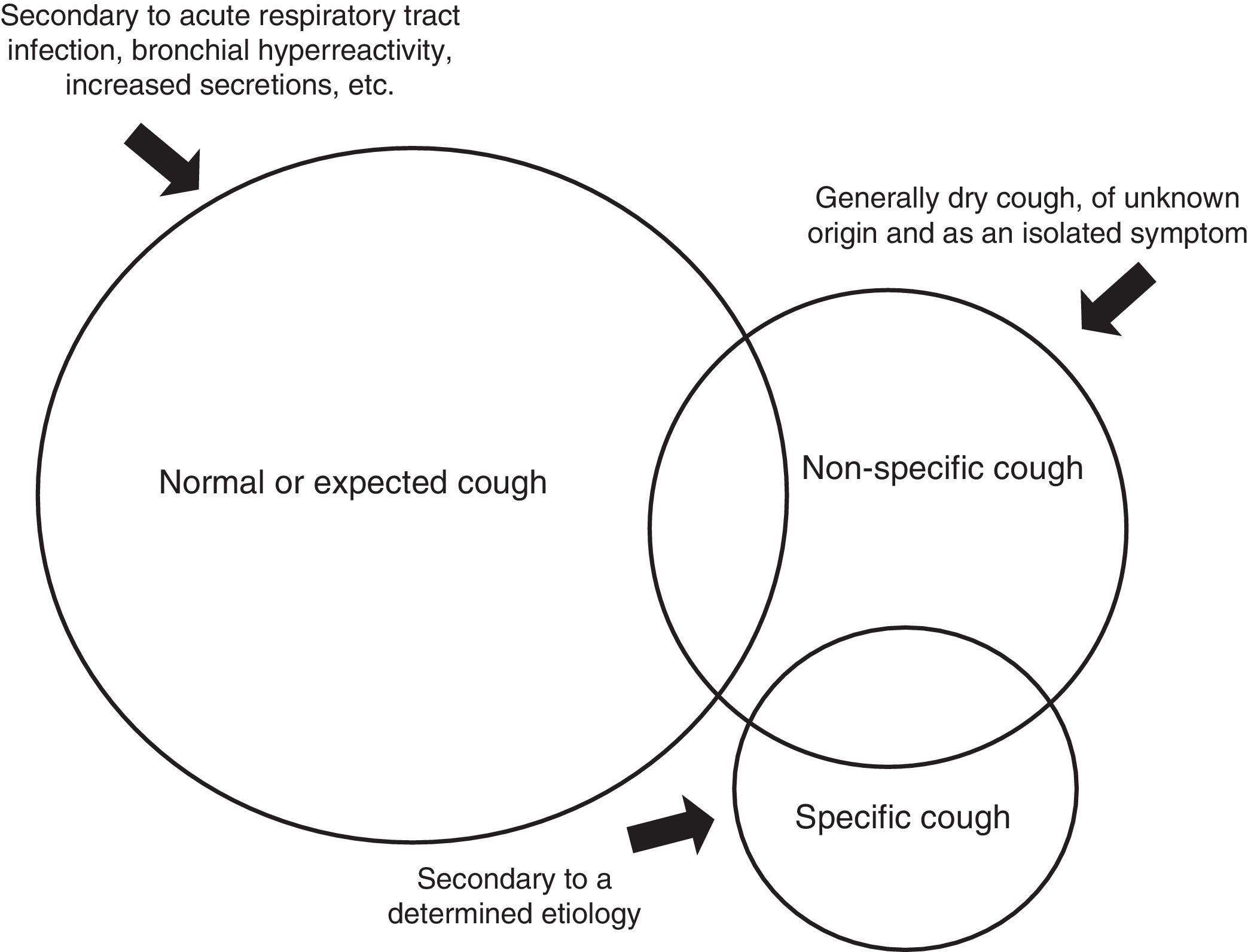
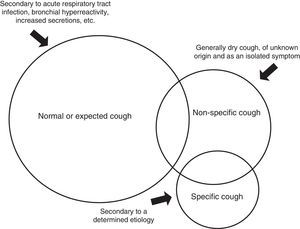
Chronic cough in children can be classified into 3 etiological groups (Fig. 1).
- 1.
Normal or expected cough: The cause is known, so the cough is considered expected and no specific studies are required.
- 2.
Specific cough: This is cough that occurs with signs and symptoms suggesting a specific diagnosis that has been reached after thorough examination. This group includes asthma, bronchiectasis (BE), cystic fibrosis (CF), aspiration of a foreign body, aspirative symptoms, atypical respiratory infections, cardiac abnormalities and pulmonary interstitial disease, among others (Table 1).32
Table 1.Differential Diagnosis of Specific Causes of Chronic Cough in Children.
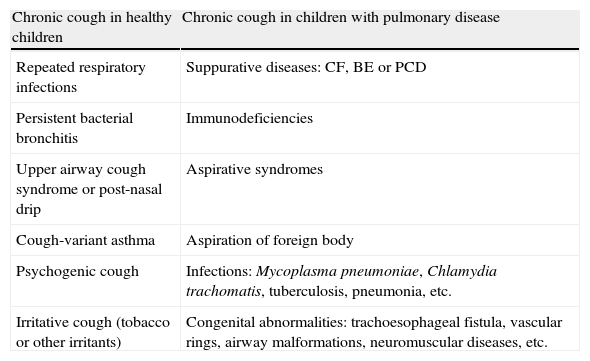
Chronic cough in healthy children Chronic cough in children with pulmonary disease Repeated respiratory infections Suppurative diseases: CF, BE or PCD Persistent bacterial bronchitis Immunodeficiencies Upper airway cough syndrome or post-nasal drip Aspirative syndromes Cough-variant asthma Aspiration of foreign body Psychogenic cough Infections: Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia trachomatis, tuberculosis, pneumonia, etc. Irritative cough (tobacco or other irritants) Congenital abnormalities: trachoesophageal fistula, vascular rings, airway malformations, neuromuscular diseases, etc. BE: bronchiectasis; C. trachomatis: Chlamydia trachomatis; PCD: primary ciliary dyskinesia; CF: cystic fibrosis; M. pneumoniae: Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
- 3.
Non-specific cough: This includes syndromes that present with predominantly dry isolated cough, with no signs or symptoms suggestive of disease in a child who feels well and in whom complementary studies (at least spirometry, if feasible, and chest X-ray) are normal.11–13 In most cases, it is secondary to protracted URTI, it is not serious and resolves spontaneously. Sometimes persistent cough is due to an increase in sensitivity of the cough receptors after a viral infection,5 but factors such as environmental contamination and exposure to tobacco smoke may be observed in this entity, and may contribute to its persistence.33 Many of these cases are treated incorrectly with inhaled corticosteroids, having been classified as “cough variant asthma”.4,34,35
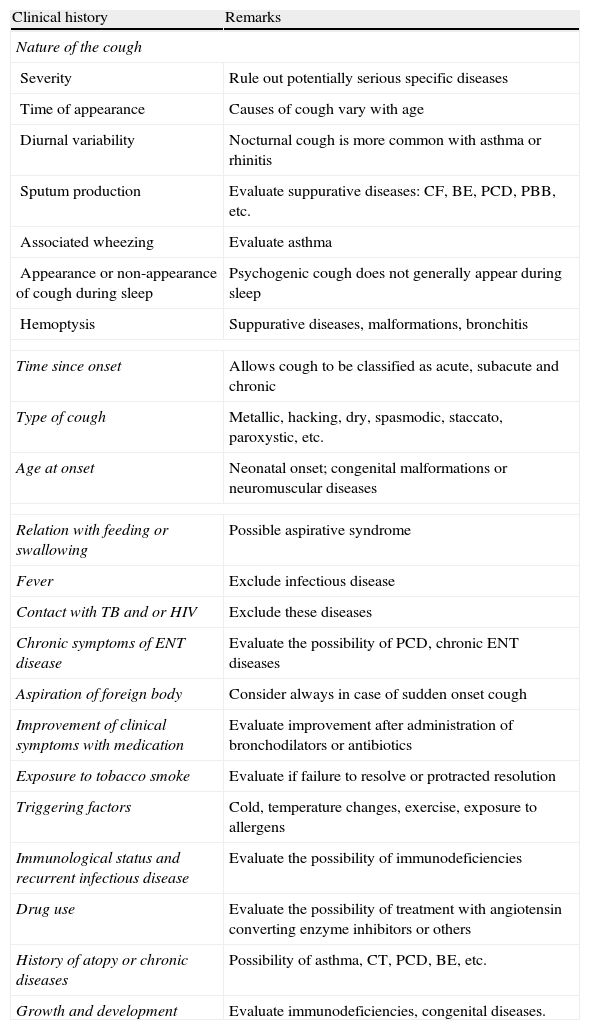
The time and evolution, type of cough, diurnal pattern, aggravating factors and triggers, quality of the cough (dry or productive) and associated symptoms should be evaluated from the clinical records4,36,37 (Table 2). It is essential that the characteristics of the cough, whether dry or productive, are evaluated, since productive, purulent chronic cough is pathological and requires investigation for suppurative diseases. If cough is accompanied by wheezing or breathing difficulties, the spectrum of possible etiological causes is wide: asthma, foreign body, recurrent aspirations, tracheobronchomalacia, bronchiolitis obliterans, interstitial diseases, chronic pulmonary disease in pre-term infants and heart diseases, among others. When it is associated with atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis or sensitivity to allergens, personal and family history of allergy or asthma, occurs at night and is exacerbated with exercise, cold or exposure to irritants or allergens, a diagnosis of asthma is more probable.35 If hemoptysis is observed, pneumonia, pulmonary abscesses, BE, CF, foreign bodies, tuberculosis, pulmonary hemosiderosis, tumors, pulmonary hypertension or pulmonary arteriovenous malformations must be excluded. Nasal obstruction, mucopurulent rhinorrhea and halitosis would suggest upper airway cough syndrome or posterior nasal drip.38 Persistent headache may be a symptom of sinusitis.39 Recurrent febrile syndrome, general malaise, constitutional symptoms and a generally productive cough would indicate the need for a contact study to rule out tuberculosis.40 In aspirative syndromes, cough is generally associated with food-related regurgitation and choking.41 Psychogenic cough is dry, hacking, repetitive and frequent during the day, and calms down or disappears during sleep; it is exacerbated in the presence of parents or caregivers and diminishes with distraction and sport. It is diagnosed exclusively in a healthy child who does not improve with medication.19,20 Finally, to guide diagnosis, it is always important to determine if the patient has received any type of treatment and what effect it has had on the cough, to enquire about environmental factors (smoking in the family, daycare attendance, animals, environmental irritants, etc.) and to look for alarm signs or symptoms (neonatal onset, cough during feeding, cough with sudden onset, suppurative cough with expectoration, nocturnal sweating, associated weight loss or signs of chronic pulmonary disease, etc.). Alarm signs and symptoms in the study of children with chronic cough are listed in Table 3.
Key Points in the Clinical History of the Child With Chronic Cough.
| Clinical history | Remarks |
| Nature of the cough | |
| Severity | Rule out potentially serious specific diseases |
| Time of appearance | Causes of cough vary with age |
| Diurnal variability | Nocturnal cough is more common with asthma or rhinitis |
| Sputum production | Evaluate suppurative diseases: CF, BE, PCD, PBB, etc. |
| Associated wheezing | Evaluate asthma |
| Appearance or non-appearance of cough during sleep | Psychogenic cough does not generally appear during sleep |
| Hemoptysis | Suppurative diseases, malformations, bronchitis |
| Time since onset | Allows cough to be classified as acute, subacute and chronic |
| Type of cough | Metallic, hacking, dry, spasmodic, staccato, paroxystic, etc. |
| Age at onset | Neonatal onset; congenital malformations or neuromuscular diseases |
| Relation with feeding or swallowing | Possible aspirative syndrome |
| Fever | Exclude infectious disease |
| Contact with TB and or HIV | Exclude these diseases |
| Chronic symptoms of ENT disease | Evaluate the possibility of PCD, chronic ENT diseases |
| Aspiration of foreign body | Consider always in case of sudden onset cough |
| Improvement of clinical symptoms with medication | Evaluate improvement after administration of bronchodilators or antibiotics |
| Exposure to tobacco smoke | Evaluate if failure to resolve or protracted resolution |
| Triggering factors | Cold, temperature changes, exercise, exposure to allergens |
| Immunological status and recurrent infectious disease | Evaluate the possibility of immunodeficiencies |
| Drug use | Evaluate the possibility of treatment with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or others |
| History of atopy or chronic diseases | Possibility of asthma, CT, PCD, BE, etc. |
| Growth and development | Evaluate immunodeficiencies, congenital diseases. |
PBB: persistent bacterial bronchitis; BE: bronchiectasis; PCD: primary ciliary dyskinesia; CF: cystic fibrosis; ENT: ear, nose, throat; TB: tuberculosis; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus.
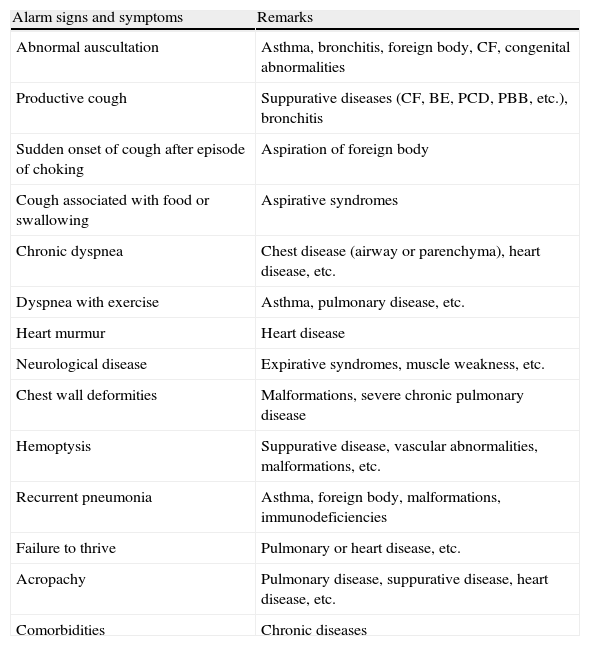
Alarm Signs and Symptoms in Children With Chronic Cough.
| Alarm signs and symptoms | Remarks |
| Abnormal auscultation | Asthma, bronchitis, foreign body, CF, congenital abnormalities |
| Productive cough | Suppurative diseases (CF, BE, PCD, PBB, etc.), bronchitis |
| Sudden onset of cough after episode of choking | Aspiration of foreign body |
| Cough associated with food or swallowing | Aspirative syndromes |
| Chronic dyspnea | Chest disease (airway or parenchyma), heart disease, etc. |
| Dyspnea with exercise | Asthma, pulmonary disease, etc. |
| Heart murmur | Heart disease |
| Neurological disease | Expirative syndromes, muscle weakness, etc. |
| Chest wall deformities | Malformations, severe chronic pulmonary disease |
| Hemoptysis | Suppurative disease, vascular abnormalities, malformations, etc. |
| Recurrent pneumonia | Asthma, foreign body, malformations, immunodeficiencies |
| Failure to thrive | Pulmonary or heart disease, etc. |
| Acropachy | Pulmonary disease, suppurative disease, heart disease, etc. |
| Comorbidities | Chronic diseases |
PBB: persistent bacterial bronchitis; BE: bronchiectasis; PCD: primary ciliary dyskinesia; CF: cystic fibrosis.
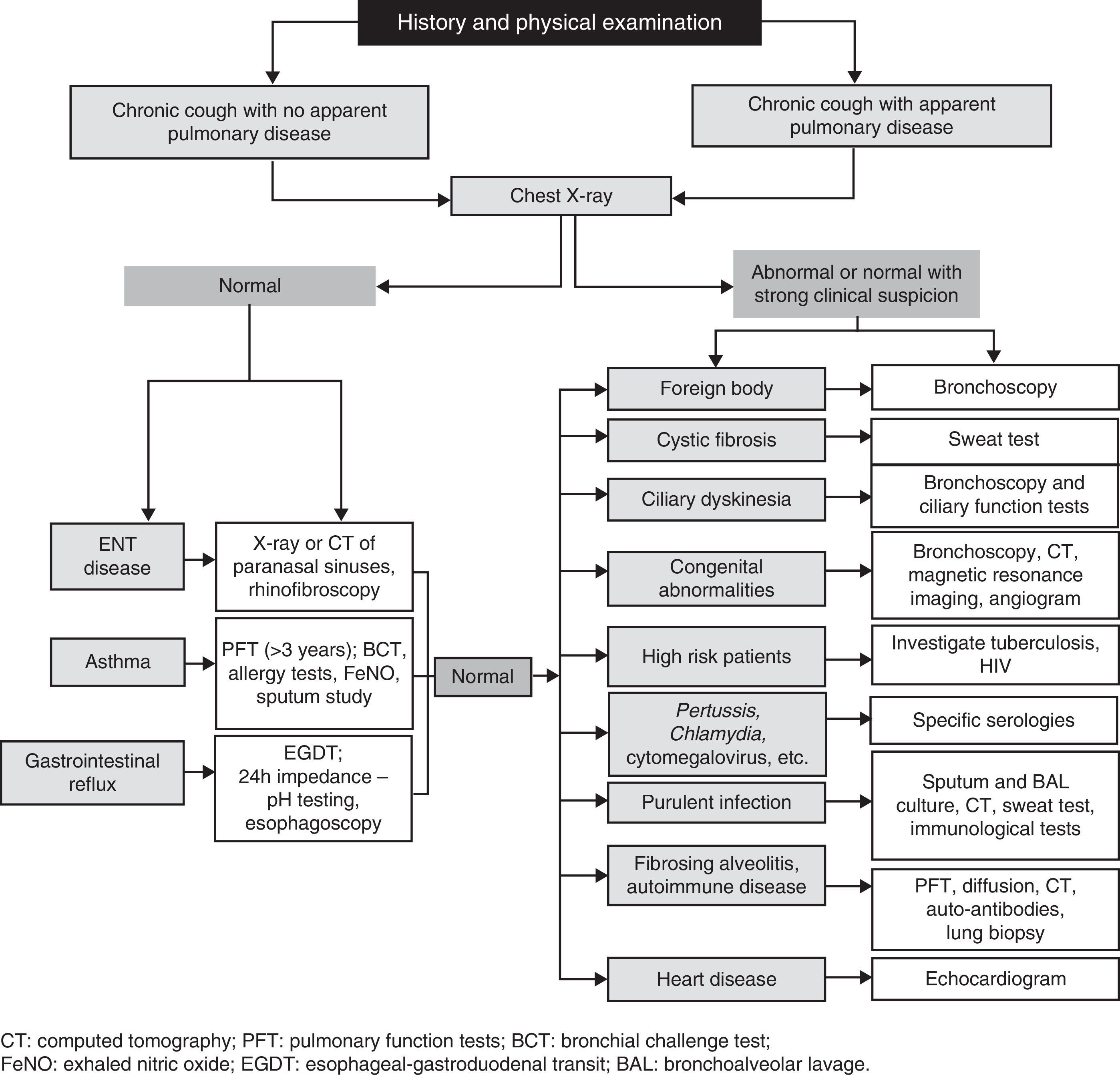
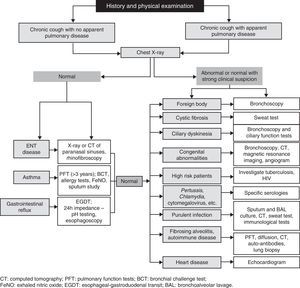
Physical examination must be complete and detailed, including the ear, nose and throat. Diagnostic tests should be requested after a full history and clinical examination have been obtained.10,15 Chest X-ray is the first study12,13,36 and, depending on the results, the following tests should be considered (Fig. 2).
- a.
Laboratory tests: full blood panel with immunoglobulins, in case of suspected immunodeficiencies in children with cough and recurrent bacterial infections.36
- b.
Skin tests: tuberculin sensitivity test, sweat test (electrolytes in sweat with determination of chloride) and allergy study.13
- c.
Microbiological study: sputum or nasopharyngeal aspirate culture for study of respiratory viruses, bacterial cultures and/or cellularity studies.12–14
- d.
Other radiological studies: chest X-ray in inspiration and expiration in case of suspected foreign body. High-resolution computed axial tomography for suspected suppurative diseases, pulmonary malformations or severe infections. Upper gastrointestinal transit (UGT) for suspected foreign bodies in the esophagus, tracheoesophageal fistulas and extrinsic compressions.12–14
- e.
Pulmonary function: spirometry can be carried out from the age of 3–4 years with appropriate training. A positive bronchodilator test suggests asthma, but to reach a diagnosis, complementary studies (metacholine, exhaled nitric oxide or induced sputum) are required when it is normal.13,42
- f.
Fiberoptic bronchoscopy: this should be performed in all children with chronic cough and suspicion of airway abnormalities, foreign body inhalation, aspirations, if localized radiological changes are observed or for performing bronchoalveolar lavage and microbiological studies.12,13,39
- g.
pH monitoring: this should be performed if GERD is suspected, even though normal results do not exclude the presence of non-acid reflux, which should be evaluated with impedance testing.13,38,43
Asthma. Children with asthma can begin with cough, but most children with non-specific cough do not have asthma.44 Recurrent dry cough may be due to increased sensitivity of cough receptors,5 frequently caused by URTI. BHR is associated with wheezing but not with persistent dry cough or nocturnal cough.45 Risk factors, the characteristics of the cough, presence of wheezing and spirometry can assist in reaching a diagnosis.13,14,35,42
Persistent Bacterial Bronchitis. Until recently, persistent bacterial bronchitis was understudied and underdiagnosed. It is defined as productive chronic cough secondary to airway infection that resolves with long-term antibiotic treatment, after other diseases have been ruled out.46 The most commonly involved microorganisms are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis, and in some cases, more than one pathogen is isolated.29,47 Definitive diagnosis is carried out by bronchoscopy and bronchoalveolar lavage, but administration of antibiotics for 2–4 weeks can be tried to see if the clinical picture resolves before carrying out a bronchoscopy. Some patients with recurrent PBB require long and repeated cycles of antibiotics, for which reason some authors propose the possibility of long-term treatment with inhaled antibiotics.48 This is a disease entity that may be associated with asthma and involves a high level of morbidity, so it should be diagnosed and treated appropriately to avoid it progressing to BE.
Upper Airway Cough Syndrome or Posterior Nasal Drip. This is one of the main causes of chronic cough in adults, but it is less common in the pediatric population.15 It is due to mechanical stimulation of the afferent branch of the cough reflex in the upper airway by secretions that descend from the nose and/or the paranasal sinuses. In preschoolers, it is caused by repeated infections due to adenotonsillar hypertrophy and/or seromucous otitis. In schoolchildren, persistent rhinitis and/or turbinate hypertrophy should suggest atopy, and if nasal polyps are observed, CF should be ruled out.2,49
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. The association between GERD and non-specific chronic cough in children is widely debated, since there is little evidence that this disease alone causes cough.32 For the determination of acid GERD, 24-h pH testing is sensitive and specific, while impedance is required for the diagnosis of non-acid GERD.30 UGT assists in the diagnosis of vascular rings and other causes of mechanical compression.12–14
Functional Respiratory Disorders. It is important to recognize psychogenic cough and other functional respiratory disorders in pediatric patients, since they are difficult to diagnose and are frequently labeled as asthma or upper airway cough syndrome. Psychogenic cough is less common in males, and generally occurs in schoolchildren or teenagers who, after a URTI, begin with a dry, harsh, croaking cough that occurs intermittently during the day but then disappears when the subject is distracted or sleeping. It is generally very alarming for parents, teachers and others to observe, but the patient is usually surprisingly indifferent.19,20
Treatment of Chronic Cough in ChildrenChronic cough should be treated after a thorough etiological study, the aim being to eliminate the causative agent, following clinical practice guidelines.12–14 The family must be reminded to avoid exposing the child to tobacco smoke and other environmental irritants.15
Treatment of Specific Cough. Chronic cough due to asthma requires treatment with bronchodilators and, depending on classification, with inhaled corticosteroids.42 In cases of allergic rhinitis, antihistamines and nasal steroids will be required.38 Sinusitis will require treatment with antibiotics.39 GERD should be treated with proton pump inhibitors and/or surgery.50 PBB needs long-term treatment (between 2 and 6 weeks) with amoxicillin–clavulanate or clarithromycin.29,46–48 Psychogenic cough requires investigation of the causes of stress or anxiety and subsequent psychological support.12–14,19,20
Treatment of Non-specific Cough. If the cough has a moderate impact, there is no underlying disease and the child is healthy, a period of observation is recommended before diagnostic tests or treatment are initiated, with a follow-up examination of the child after 6–8 weeks. If a decision is taken to carry out a trial treatment, the duration should be empiric and based on the recommendations of experts, given the lack of controlled studies in the pediatric population.4,12,16 A trial treatment with inhaled corticosteroids at half doses is recommended for predominantly dry cough (budesonide 400μg/day or equivalent) for 2–12 weeks, depending on the guidelines. The patient should be reassessed after 2–3 weeks and if there has been no response to treatment, it should be discontinued12,13 (Fig. 3). In cases of non-specific productive cough, initiating a course of antibiotics (amoxicillin–clavulanate) for 2–3 weeks may be considered. Chang et al.51 carried out a study in children with cough of more than 4 weeks’ duration, who were randomized to follow a previously defined treatment algorithm after 4 weeks or to continue the untreated observation period for 6–8 weeks. The primary endpoint of the study was resolution of cough at 6 weeks. The duration of cough was shorter in the early treatment group. In some patients, cough resolves spontaneously, irrespective of treatment, and the diagnosis of cough as “cough variant asthma” can only be established if symptoms recur after treatment withdrawal and respond again after it is reintroduced, so a positive response with inhaled corticosteroids does not confirm the diagnosis of asthma. The use of central action antitussives, non-opiate antitussives, mucolytics or expectorants is not indicated.4 The presence of more than one cause of cough may lead to a delay in response or treatment failure if underlying conditions are not treated.
ConclusionsCough in childhood is a common symptom that, in most cases, is due to banal respiratory infections, but all children with chronic cough must be thoroughly studied to determine the underlying cause. Detailed history and physical examinations, with chest X-ray and spirometry (if possible) are recommended. Specific chronic cough should be treated according to the underlying disease. If diagnosis is unclear, the characteristics of the cough, whether dry or productive, can help in evaluating possible treatment: inhaled corticosteroids for dry cough or antibiotics for productive cough. If no improvement is observed, these treatments should be discontinued and alternative diagnoses explored, bearing in mind that in some cases the cause of cough may be more than one disease. There is no evidence that the use of antitussive syrups and/or antihistamines or other cough remedies are effective, and, with the exception of honey for URTI, they may have serious adverse effects in children, so they must not be used.
FundingThis review was conducted without funding.
Conflict of InterestsThe authors state that they have no conflict of interest.
Please cite this article as: Lamas A, Ruiz de Valbuena M, Máiz L. Tos en el niño. Arch Bronconeumol. 2014;50:294–300.