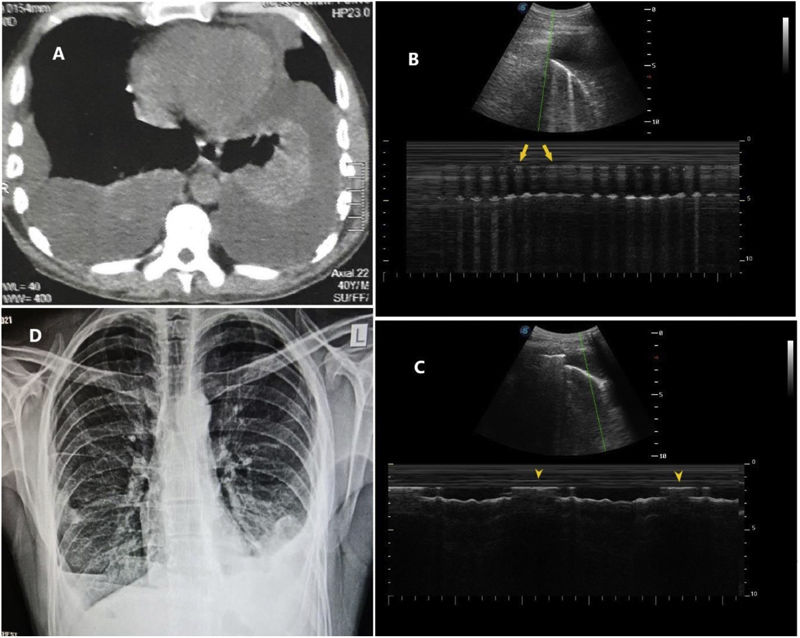
A 36 year-old male patient was admitted with bilateral pleural effusions (Fig. 1 panel A) and symptoms of chest pain, fever and night sweating. Right-side thoracentesis yielded a straw-coloured aspirate with pH 7.41. He was started on intravenous ampicillin-sulbactam and subsequent fluid results revealed LDH 1006IU/L, glucose 71g/dL and cultures growing Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella species. Ultrasound was done on both sides to evaluate the need for chest tube drainage. On the right-side just above the effusion, the ‘lung artefact’ appeared to move erratically and asynchronously relative to patient's breathing (supplementary video). This was shown using M-mode ultrasonography (panel B). In contrast, the lung artefact overlying the left effusion moved regularly and synchronously with breathing as demonstrated by M-mode (panel C). These findings suggested a right hydropneumothorax which was confirmed on chest radiography (panel D).
Panel A: chest computed tomography scan showing bilateral partially loculated pleural effusions. Panel B: top half: B-mode image of pleural effusion, underlying consolidated lung and an A-type artefact; bottom half: M-mode image showing rapid and irregular alternation between short runs of barcode sign (yellow arrows) and regions of blackness representing a hydropneumothorax. Panel C: top half: B-mode image of pleural effusion, underlying consolidated lung and an A-type artefact; bottom half: M-mode image showing regular alternation between the seashore sign (yellow arrowheads) with black effusion representing the expanding and receding aerated upper lobe. Panel D: chest radiograph shows right partially loculated hydropneumothorax and left partially loculated pleural effusion.
The case depicts the hydro-point,1 which is a sign described in B-mode ultrasound examination of hydropneumothorax where an A-type artefact (which could be mistaken for the lung) moves in a way that simulates the movement of liquid in partially filled glass that is shaken. To our knowledge, this is the first report to demonstrate the M-mode appearance of the sign by highlighting the rapid and erratic alternation between barcodes2 (representing air) and blackness (representing fluid) at the air-fluid level. This is in stark contrast to the regular alternation between the seashore sign(of sliding lung)2 and effusion.
Informed consentWritten informed consent was provided by the person subject of the report.
Conflict of interestNo conflict of interest to declare.