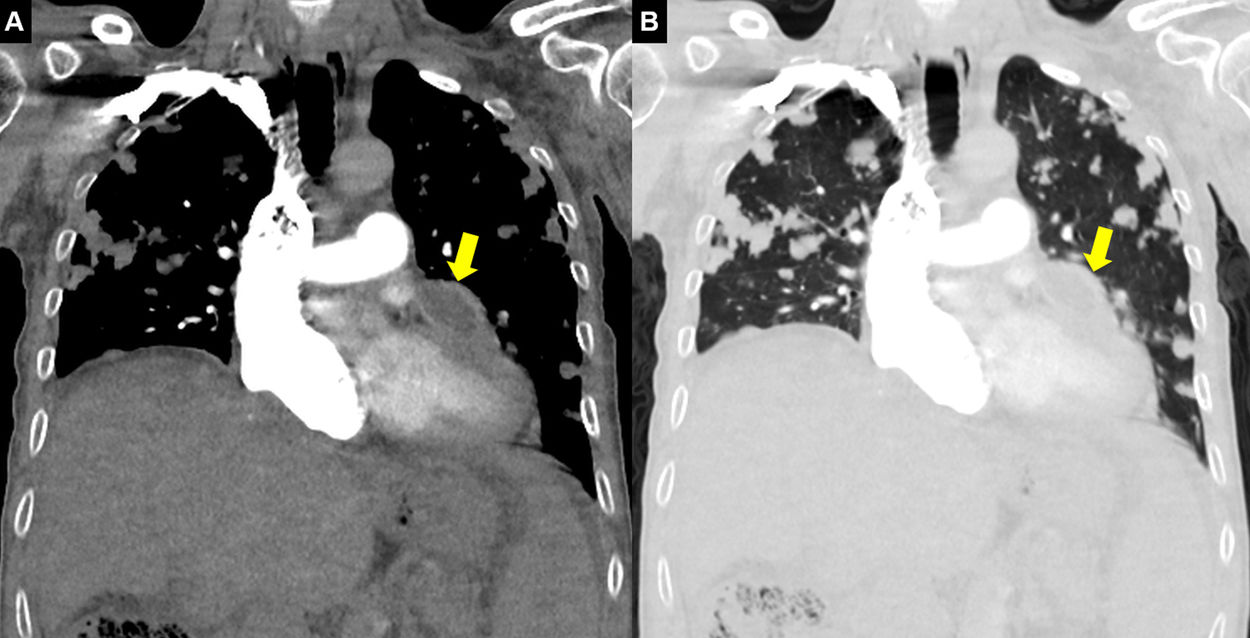
A 65-year-old man with a histopathologic diagnosis of hepatic alveolar echinococcus ten years ago presented with progressive dyspnea. The patient's electrocardiogram showed atrial fibrillation. Radiologic evaluation revealed extensive metastases in bilateral lungs and cardiac involvement secondary to echinococcus alveolaris (Fig. 1). The patient was followed for pulmonary metastases for about 10 years. Slow progression of pulmonary metastases was observed over time. However, cardiac involvement recently appeared. The patient was given albendazole 10mg/kg/day for three months every year and was followed up.
The lungs are involved in 7–20% of hepatic alveolar echinococcus cases and cardiac involvement is 0.5–2% with only a few cases reported in the literature.1–3 The prevalence of alveolar echinococcus has recently increased significantly.1 The incubation period ranges from five to fifteen years and diagnosis is difficult due to the long asymptomatic phase. In hepatic alveolar echinococcus and its metastases, surgical treatment should be considered first if surgical excision is possible. In cases where surgery is not appropriate, the progression of the disease can be slowed with albendazole treatment.
Financial SupportThe authors received no financial support for the research and/or authorship of this article.
Conflict of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication of this article.