La disfunción muscular de pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica (EPOC) constituye una de las comorbilidades más importantes, con repercusiones negativas en su capacidad de ejercicio y calidad de vida. En la presente normativa se ha resumido la literatura publicada más recientemente sobre los diferentes aspectos del tema y se ha utilizado también la escala Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) de recomendaciones sobre el grado de evidencia de las diferentes propuestas de la normativa. Respecto a una población control, se estima que en un tercio de los pacientes EPOC la fuerza del cuádriceps es un 25% inferior incluso en estadios precoces de su enfermedad. Aunque tanto los músculos respiratorios como los de las extremidades están alterados, estos últimos suelen verse mayormente afectados. Diversos factores y mecanismos biológicos están involucrados en la disfunción muscular de los pacientes. Se proponen diversas pruebas para evaluar y diagnosticar el grado de afectación de los músculos respiratorios y de las extremidades (periféricos), así como identificar la capacidad de esfuerzo de los pacientes (prueba de marcha de 6min y cicloergometría). Se describen también las posibles estrategias terapéuticas vigentes que incluyen las diversas modalidades de entrenamiento y de soporte farmacológico y nutricional.
In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), skeletal muscle dysfunction is a major comorbidity that negatively impacts their exercise capacity and quality of life. In the current guidelines, the most recent literature on the various aspects of COPD muscle dysfunction has been included. The Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) scale has been used to make evidence-based recommendations on the different features. Compared to a control population, one third of COPD patients exhibited a 25% decline in quadriceps muscle strength, even at early stages of their disease. Although both respiratory and limb muscles are altered, the latter are usually more severely affected. Numerous factors and biological mechanisms are involved in the etiology of COPD muscle dysfunction. Several tests are proposed in order to diagnose and evaluate the degree of muscle dysfunction of both respiratory and limb muscles (peripheral), as well as to identify the patients’ exercise capacity (six-minute walking test and cycloergometry). Currently available therapeutic strategies including the different training modalities and pharmacological and nutritional support are also described.
En la presente normativa se describen los últimos avances sobre la disfunción muscular en los pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica (EPOC) por lo que respecta al problema general, etiología, diagnóstico, evaluación y tratamiento. Para ello, por parte de los autores expertos se ha resumido la literatura más reciente sobre los diferentes aspectos del tema y se ha utilizado también la escala Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) de recomendaciones sobre el grado de evidencia de las diferentes propuestas de la normativa1. Dadas las limitaciones de espacio, este documento se acompaña de una versión extensa en la que los contenidos de la normativa han sido explicados con más detalle (ver material adicional a este artículo en su versión electrónica).
Epidemiología, fisiopatología e implicaciones para los pacientesLos músculos de cualquier territorio poseen 2 propiedades funcionales fundamentales: la fuerza, o expresión máxima de su capacidad de contracción, y la resistencia, o capacidad de mantener en el tiempo un esfuerzo inferior al máximo2. La fuerza depende fundamentalmente de la masa muscular, mientras que la resistencia viene determinada por la capacidad aeróbica del músculo3. Estas 2 propiedades pueden medirse en diversos grupos musculares en la clínica diaria.
La disfunción muscular se define como la incapacidad de un músculo para cumplir su cometido2. La disfunción muscular es consecuencia de déficits en la fuerza, la resistencia o ambas. La disfunción muscular, tanto de los músculos ventilatorios como de las extremidades (también llamados periféricos), es frecuente en las enfermedades respiratorias. Cuando existe disfunción muscular en las extremidades, los pacientes pierden autonomía, y ello condiciona negativamente su calidad de vida4,5. La EPOC es probablemente la enfermedad respiratoria en que se ha estudiado más la disfunción muscular. Así, se ha publicado que hasta un tercio de los enfermos con EPOC, incluso en fases precoces de su enfermedad, muestran una función muscular deteriorada en sus extremidades (fuerza un 25% inferior a la desarrollada por los sujetos control)4. La disfunción muscular respiratoria se observa en pacientes con EPOC avanzada y oscila entre el 20 y el 30% de la fuerza diafragmática desarrollada por los sujetos control6-8.
Los estudios observacionales demuestran consistentemente que los pacientes EPOC tienen disfunción muscular independientemente de la gravedad de la obstrucción pulmonar. Evidencia GRADE 1A.
Fisiopatología de la disfunción muscularEn las 2 últimas décadas se ha demostrado la participación de diversos factores y mecanismos en la etiología multifactorial de la disfunción muscular de pacientes con EPOC.
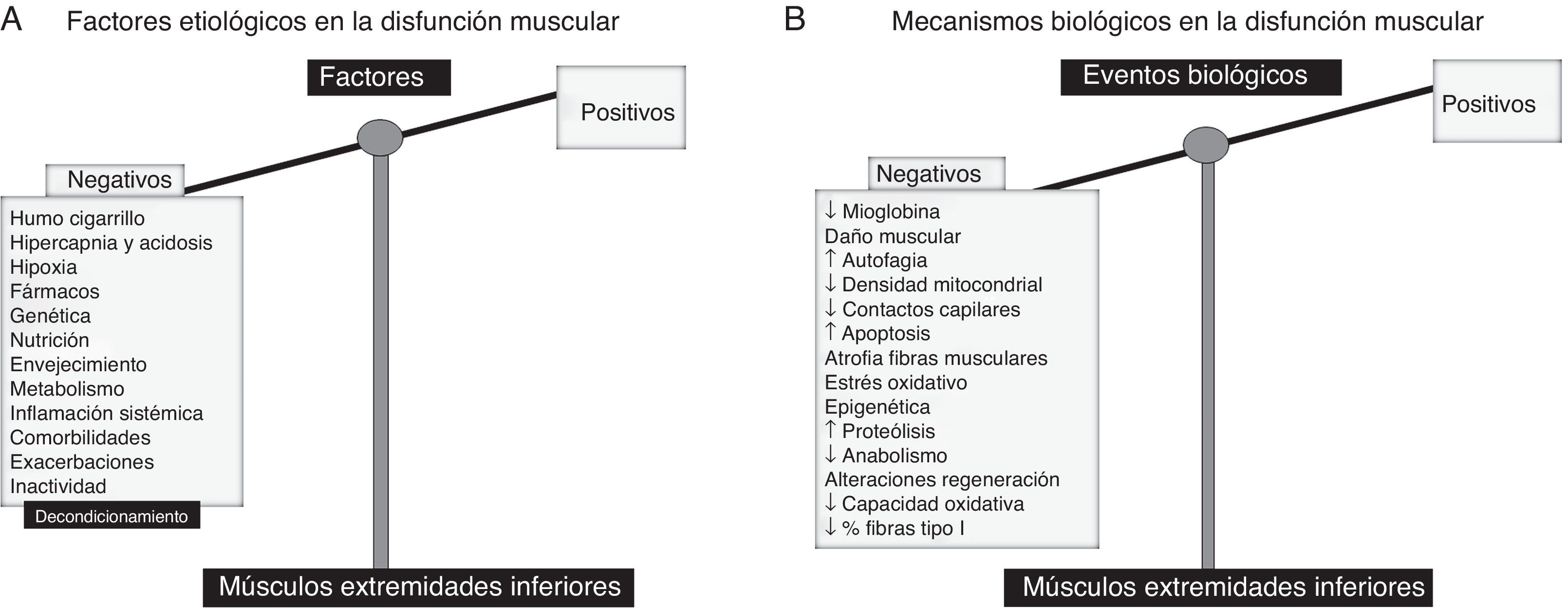
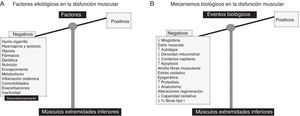
Disfunción muscular periférica (cuádriceps)Tal como se indica en la figura 1A, el humo del cigarrillo, las alteraciones genéticas y epigenéticas, los trastornos metabólicos incluidas las deficiencias de vitaminaD y testosterona, fármacos (corticoides), la presencia de comorbilidades, las exacerbaciones, la inflamación sistémica, la malnutrición, la inactividad física y el envejecimiento constituyen los factores implicados en la disfunción muscular periférica de los pacientes EPOC2,3. En cuanto a los eventos biológicos implicados en la disfunción muscular periférica, destacan una serie de alteraciones estructurales9-11, el estrés oxidativo9,11,12, la hipoxia crónica, la hipercapnia y acidosis, alteraciones estructurales y mitocondriales13,14 (fig. 1B). Finalmente, también se ha demostrado que mecanismos como la proteólisis, la apoptosis, la autofagia y la epigenética están involucrados en la fisiopatología de la disfunción muscular periférica de dichos enfermos9,15-19.
A)Factores etiológicos involucrados en la disfunción muscular periférica de los pacientes EPOC. Dichos factores ejercen efectos deletéreos en la función y en la masa muscular de los músculos de las extremidades inferiores, motivo por el que la balanza está totalmente decantada hacia el lado negativo (bandeja izquierda). B)En los músculos de las extremidades inferiores, diversos mecanismos biológicos median las acciones de los factores etiológicos, ejerciendo así los efectos deletéreos sobre la función muscular y masa, y la estructura. La balanza está inclinada totalmente hacia el lado izquierdo.
Los estudios observacionales demuestran consistentemente los factores y mecanismos biológicos implicados en el desarrollo de disfunción muscular en los pacientes EPOC. Evidencia GRADE 1A.
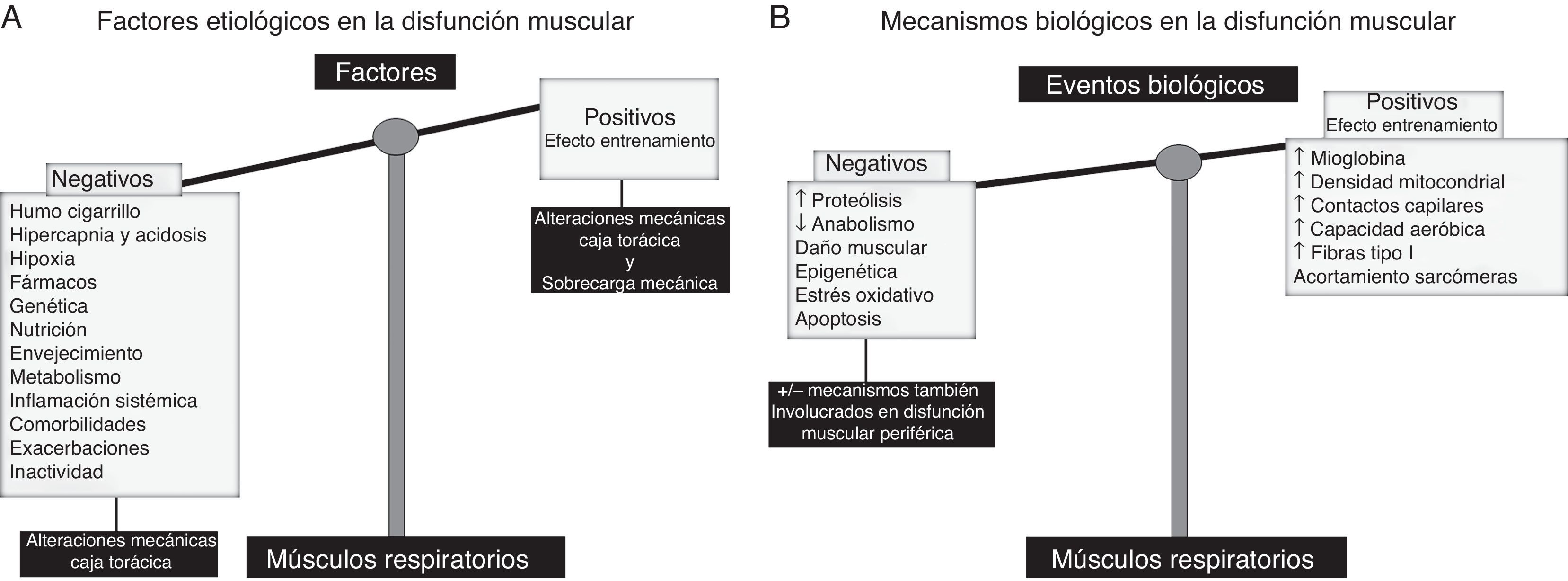
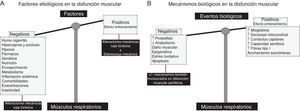
Disfunción muscular respiratoriaLos factores mayormente implicados en la disfunción muscular respiratoria de la EPOC se ilustran en la figura 2A. Entre ellos destacan especialmente los factores mecánicos. Por otro lado, también existen factores que inducen una adaptación positiva, la cual confiere cierta resistencia a los músculos respiratorios de estos pacientes3,20 (fig. 2A). Además, se ha podido confirmar la existencia de fenómenos biológicos adaptativos en el diafragma, contrarrestando así los potenciales efectos deletéreos: acortamiento de la longitud de las sarcómeras, aumento del contenido en mioglobina y mayores proporciones de fibras resistentes a la fatiga y del número de contactos capilares, incremento de la densidad mitocondrial, y mejorías en el potencial aeróbico del músculo3,21-25 (fig. 2B). En la EPOC, el fenotipo muscular final del diafragma resultará del balance entre los factores y mecanismos adaptativos y de los involucrados en la disfunción muscular, a la vez que entre situación estable y exacerbación (fig. 2B). Sin embargo, en la EPOC avanzada, idénticos mecanismos biológicos8,9,15-19,26 a los descritos en la disfunción muscular periférica afectarían al diafragma predominando sobre los mecanismos adaptativos (fig. 2B).
A)En los músculos respiratorios, los factores etiológicos como las alteraciones en la geometría del tórax y la sobrecarga mecánica pueden de alguna manera contrarrestar (efecto entrenamiento, bandeja derecha de la balanza) los efectos deletéreos de los otros factores etiológicos, de naturaleza más sistémica (bandeja izquierda de la balanza), puesto que también contribuyen a la disfunción muscular periférica. B)En los músculos respiratorios, diversos mecanismos celulares y moleculares ejercen efectos beneficiosos (mecanismos adaptativos, bandeja derecha de la balanza), responsables de contrarrestar los efectos deletéreos de los otros mecanismos biológicos (bandeja izquierda de la balanza).
Los estudios observacionales demuestran consistentemente los factores y mecanismos biológicos implicados en el desarrollo de disfunción muscular en los pacientes EPOC. Evidencia GRADE 1A.
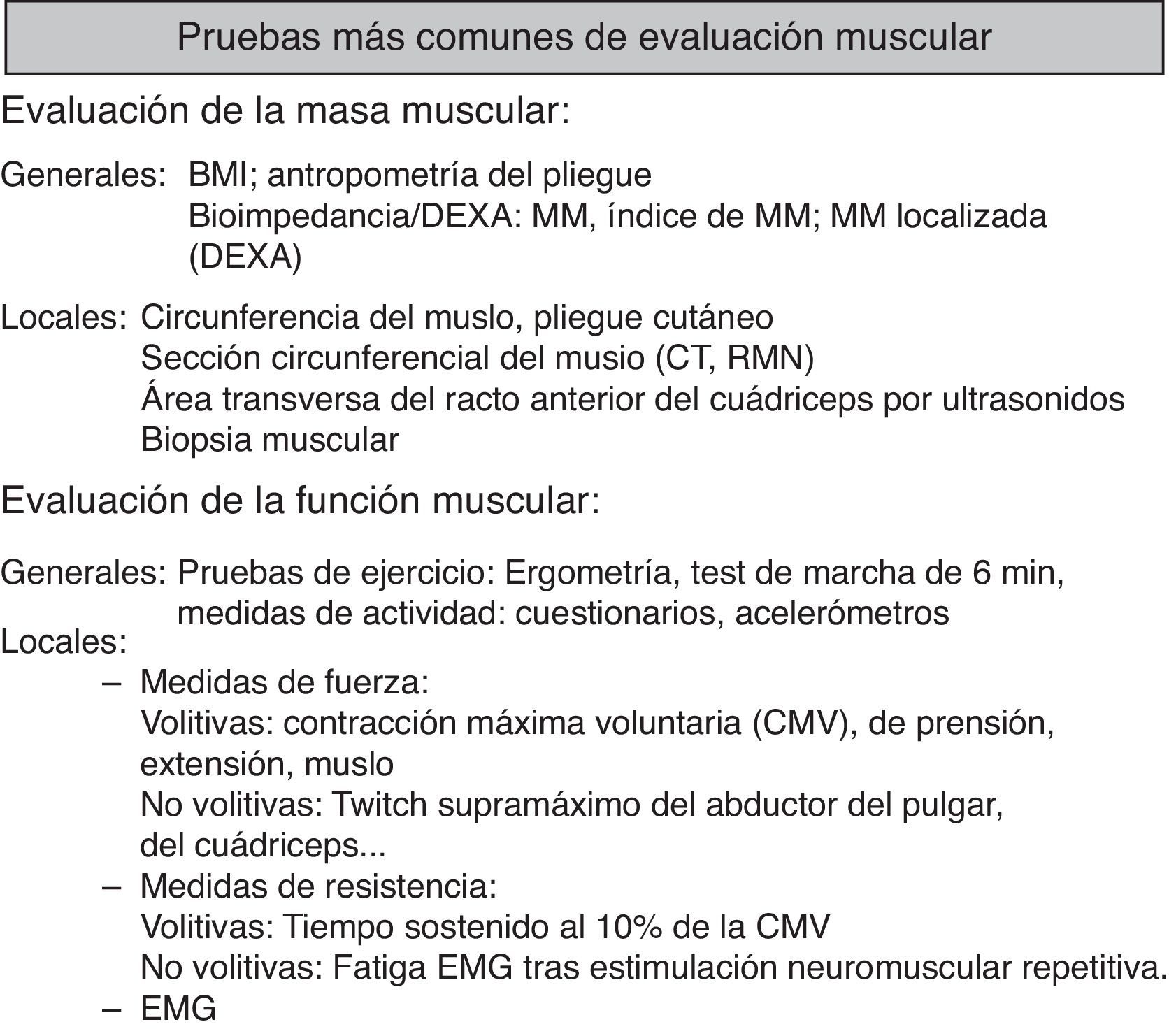
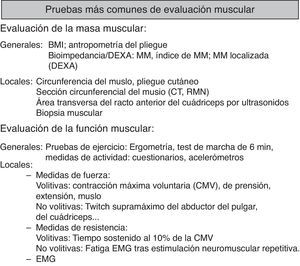
Evaluación de los músculos respiratorios: maniobras voluntarias e involuntarias (tabla 1)Evaluación de la fuerza de los músculos respiratorios: pruebas voluntarias de medición de la fuerza de los músculos respiratoriosPruebas no invasivasEspirometríaLa espirometría forzada27, aunque inespecífica, permite detectar un descenso en la capacidad vital forzada (FVC), que puede condicionar un trastorno ventilatorio no obstructivo28. Un descenso en la FVC mayor del 25% entre espirometrías realizadas en sedestación y en decúbito supino, o una FVC inferior al 75% de los valores de referencia en decúbito supino, con valores normales en sedestación, indican debilidad diafragmática29.
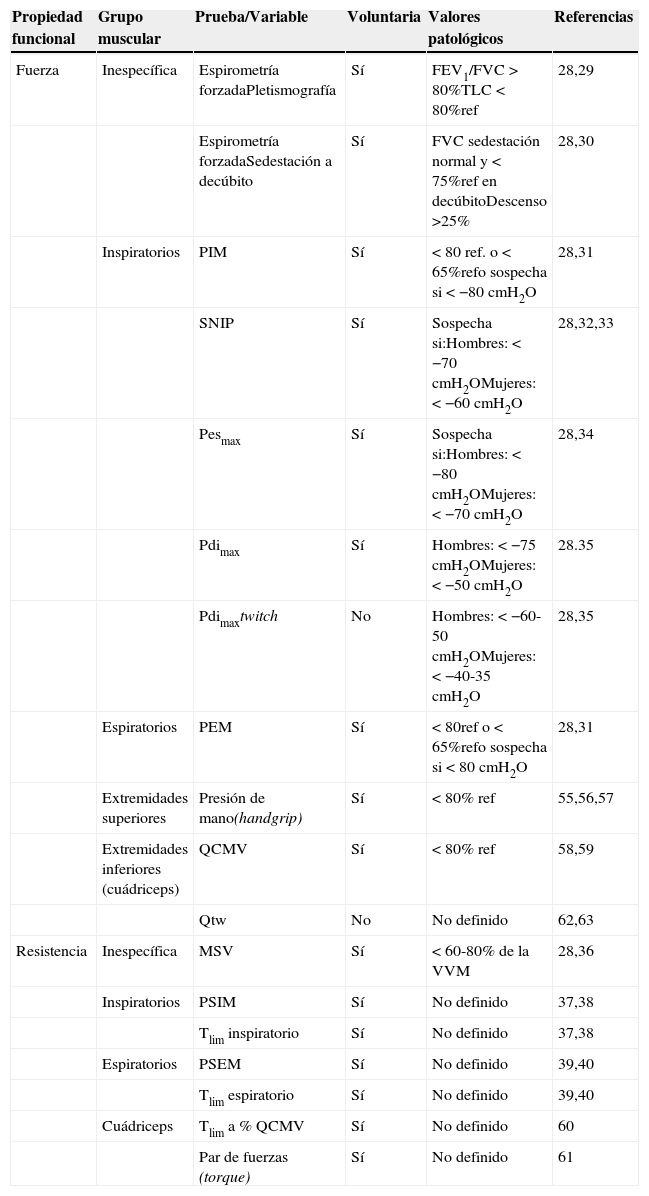
Tipos de pruebas de evaluación de la función muscular en sus componentes de fuerza y resistencia
| Propiedad funcional | Grupo muscular | Prueba/Variable | Voluntaria | Valores patológicos | Referencias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuerza | Inespecífica | Espirometría forzadaPletismografía | Sí | FEV1/FVC>80%TLC<80%ref | 28,29 |
| Espirometría forzadaSedestación a decúbito | Sí | FVC sedestación normal y <75%ref en decúbitoDescenso >25% | 28,30 | ||
| Inspiratorios | PIM | Sí | <80 ref. o <65%refo sospecha si <−80cmH2O | 28,31 | |
| SNIP | Sí | Sospecha si:Hombres: <−70cmH2OMujeres: <−60cmH2O | 28,32,33 | ||
| Pesmax | Sí | Sospecha si:Hombres: <−80cmH2OMujeres: <−70cmH2O | 28,34 | ||
| Pdimax | Sí | Hombres: <−75cmH2OMujeres: <−50cmH2O | 28.35 | ||
| Pdimaxtwitch | No | Hombres: <−60-50cmH2OMujeres: <−40-35cmH2O | 28,35 | ||
| Espiratorios | PEM | Sí | <80ref o <65%refo sospecha si <80cmH2O | 28,31 | |
| Extremidades superiores | Presión de mano(handgrip) | Sí | <80% ref | 55,56,57 | |
| Extremidades inferiores (cuádriceps) | QCMV | Sí | <80% ref | 58,59 | |
| Qtw | No | No definido | 62,63 | ||
| Resistencia | Inespecífica | MSV | Sí | <60-80% de la VVM | 28,36 |
| Inspiratorios | PSIM | Sí | No definido | 37,38 | |
| Tlim inspiratorio | Sí | No definido | 37,38 | ||
| Espiratorios | PSEM | Sí | No definido | 39,40 | |
| Tlim espiratorio | Sí | No definido | 39,40 | ||
| Cuádriceps | Tlim a % QCMV | Sí | No definido | 60 | |
| Par de fuerzas (torque) | Sí | No definido | 61 |
FEV1: volumen espiratorio máximo en el primer segundo; FVC: capacidad vital forzada; MSV: ventilación máxima sostenible; Pdimáxtwitch: presión transdiafragmática máxima en inspiración inducida por estimulación eléctrica o magnética; Pdimax: presión transdiafragmática máxima en inspiración (generalmente obtenida durante la maniobra de sniff); PEM: presión espiratoria máxima en boca (maniobra estática o de Valsalva); Pesmax: presión esofágica máxima en inspiración (generalmente obtenida durante la maniobra de sniff); PIM: presión inspiratoria máxima en boca (maniobra estática o de Müller); PSEM: presión espiratoria sostenible máxima ante cargas umbral incrementales; PSIM: presión inspiratoria sostenible máxima ante cargas umbral incrementales; QCMV: contracción isométrica máxima del cuádriceps; Qtw: contracción inducida twitch del músculo cuádriceps; SNIP: presión inspiratoria nasal por inhalación brusca (maniobra dinámica de sniff); TLC: capacidad pulmonar total; Tlim: tiempo límite o tiempo de aguante ante cargas submáximas constantes (generalmente un porcentaje de la PSIM o de la PIM para la prueba inspiratoria, de la PSEM o de la PEM para la prueba espiratoria, y del QCMV (generalmente un 10%) para el cuádriceps; VVM: ventilación voluntaria máxima.
Las presiones máximas generadas en boca, tanto inspiratoria (PIM) como espiratoria (PEM), son más específicas en valorar la fuerza de los músculos respiratorios27. Suelen realizarse mediante maniobras estáticas (sin flujo aéreo), mediante piezas bucales ocluibles y con un pequeño orificio, lo que previene el cierre de la glotis y el uso de los músculos buccinadores. La PIM (generalmente determinada desde volumen residual [RV]) refleja la fuerza realizada por todos los músculos inspiratorios, mientras que la PEM (normalmente determinada desde capacidad pulmonar total [TLC]) expresa fundamentalmente la fuerza de los músculos espiratorios de la prensa abdominal27 (tabla 2). Como en toda maniobra voluntaria, es esencial la estimulación verbal del paciente y se recomienda conseguir 3 maniobras aceptables y con una variación inferior al 20%. Existen valores de referencia para población sana mediterránea30. Por otra parte, valores de presiones máximas inspiratorias superiores a 80cmH2O permiten excluir la presencia de disfunción muscular grave27.
Escala propuesta (John Moxham. Test of respiratory muscle strength. UptoDate 2013) para evaluar la colaboración y la cooperación del paciente cuando realiza las maniobras de presiones máximas de los músculos respiratorios generadas en boca (PIM y PEM)
| Grados | |
|---|---|
| A | Excelente esfuerzo y reproducibilidad (diferencia <5cmH2O entre maniobras) |
| B | Buen esfuerzo y reproducibilidad (diferencia 5-10cmH2O entre maniobras) |
| C | Regular esfuerzo y reproducibilidad (diferencia 10-20cmH2O entre maniobras) |
| D | Una sola maniobra buena |
| F | Maniobras malas y no reproducibles |
Se determina la presión nasal durante una inhalación máxima (SNIP)27,31,32. Esta es una maniobra natural y dinámica que se realiza con el sujeto en sedestación y ocluyendo un orificio nasal. Suele realizarse desde capacidad residual funcional27,31,32, realizándose un mínimo de 10 maniobras y seleccionando el valor más elevado. Valores superiores a −70cm H2O (hombres) o −60cm H2O (mujeres) excluyen disfunción muscular inspiratoria27.
Pruebas invasivasLa determinación de la presión esofágica mediante la colocación de una sonda de presión a nivel del tercio medio del esófago durante la inhalación forzada (sniffPesmax) es una buena expresión de la presión pleural generada por la activación de los músculos inspiratorios 27,33. Valores de sniffPesmax superiores a −80cm H2O (hombres) o −70cm H2O (mujeres) excluyen disfunción muscular inspiratoria27.
También es posible determinar la fuerza diafragmática o presión transdiafragmática (Pdi), mediante la colocación de 2 sondas conectadas a transductores de presión (una en esófago y la otra en cavidad gástrica), obteniéndose la diferencia entre la presión gástrica y la esofágica27. Valores de sniffPdi inferiores a 75cmH2O en hombres o 53cm H2O en mujeres implican disfunción diafragmática34.
Los diversos estudios demuestran consistentemente que las pruebas de maniobras voluntarias de evaluación de la función muscular respiratoria son útiles y ofrecen mediciones confiables y comparables en el tiempo y entre individuos. Evidencia GRADE 1A.
Pruebas involuntarias de medición de la fuerza de los músculos respiratorios (tabla 1)Con el fin de evitar falsos positivos se han desarrollado técnicas de estimulación externa mediante estimuladores del nervio frénico que generan campos eléctricos o magnéticos (Pdi twitch) con valores de normalidad que corresponden a un 20-30% de la sniffPdi27,34.
Los diversos estudios demuestran consistentemente que las pruebas de maniobras involuntarias de evaluación de la función muscular respiratoria son útiles y ofrecen mediciones confiables y comparables en el tiempo y entre individuos. Evidencia GRADE 1A.
Evaluación de la resistencia de los músculos respiratorios (tabla 1)El producto presión-tiempo se calcula realizando la integración de la presión respiratoria medida en boca, esófago o Pdi, con respecto al tiempo (cmH2O/min)27. En cuanto a la ventilación máxima sostenible (MSV), expresada con respecto a la ventilación voluntaria máxima (VVM), se considera normal entre 60-80% de la VVM27. La MSV refleja la resistencia de los músculos respiratorios, así como la función de otros elementos de la caja torácica35. Más específicas son las pruebas con cargas umbral, que pueden ser inspiratorias o espiratorias. Existen 2 tipos: las incrementales, que proporcionan la presión máxima sostenible (PSIM y PSEM, según sea inspiratoria o espiratoria), y las de carga submáxima constante (porcentajes de la PSIM o la PIM para inspiratorios y de la PSEM o la PEM para espiratorios)36-39.
Los diversos estudios demuestran consistentemente que las pruebas de resistencia para la evaluación de la función muscular respiratoria son útiles y ofrecen mediciones confiables y comparables en el tiempo y entre individuos. Evidencia GRADE 1A.
Evaluación de los músculos periféricos: maniobras voluntarias e involuntariasEvaluación general de los músculos periféricos (fig. 3)Valoración de la masa muscularLas primeras aproximaciones se basan en sistemas de cálculo de compartimentos corporales, como el de Matiegka40, que considera el peso corporal como la suma de 4 componentes: O, peso esquelético; D, piel más tejido adiposo subcutáneo; M, músculo esquelético, y R, peso restante. El sistema de «antropometría de pliegue cutáneo» requiere de diversas medidas como la altura, la longitud y el ancho de la extremidad, pliegues y área de superficie corporal calculada, pero generalmente resulta en una sobreestimación de la masa libre de grasa en comparación con otros métodos41. La tecnología ha permitido el desarrollo de sistemas complejos o incluso invasivos, como el espacio de dilución de deuterio41, gold standard limitado a centros de investigación, pero que han permitido validar una serie de medidas de uso más común.
Análisis de bioimpedancia o impedancia bioeléctricaSe basa en la mayor conductividad de una corriente eléctrica a través de la masa libre de grasa, asimilable a la masa muscular, en comparación con la masa grasa42.
Absorciometría de rayos XLa absorciometría de rayos X (DEXA) es una técnica de imagen que permite estimar la masa muscular en regiones esqueléticas y en todo el cuerpo, y proporciona además la cuantificación del tejido magro, grasa y densidad mineral ósea43.
Los diversos estudios demuestran consistentemente que las diversas pruebas de cuantificación de la masa muscular en los pacientes EPOC son útiles y ofrecen mediciones confiables y comparables en el tiempo y entre individuos. Evidencia GRADE 1A.
Técnicas de estudio local de la masa muscularAunque la medición de la circunferencia del muslo es simple y barata, no es una buena medida de la masa muscular local44. Como alternativas se emplean la tomografía computarizada44, la resonancia magnética45 y la ecografía46, sobre todo para medir el tamaño del cuádriceps. En la EPOC, la cantidad de masa muscular local medida por estas técnicas se correlaciona con parámetros diversos como la fuerza muscular47 y la mortalidad44. La biopsia muscular es una técnica morfológica que informa de las propiedades estructurales y bioquímicas de los músculos48, pero tiene un lugar esencialmente limitado a la investigación por su carácter invasivo, incluso cuando se emplean agujas finas para microbiopsia47.
Los numerosos estudios demuestran consistentemente que la obtención de un fragmento de músculo (biopsia) de los pacientes EPOC es de gran utilidad y ofrece mediciones confiables y comparables en el tiempo y entre individuos. Evidencia GRADE 1A.
Actividad físicaPuede ser medida mediante cuestionarios como, más fiablemente, a través de acelerómetros que registran las actividades realizadas por un sujeto en un periodo prolongado49.
Pruebas de esfuerzoTanto la prueba de marcha como la ergometría son comentadas más ampliamente en otra sección específica de esta normativa.
ElectromiografíaLa electromiografía consiste en registrar la actividad eléctrica procedente de los músculos en reposo y durante la contracción, tanto voluntaria como estimulada externamente50-53 (ver más adelante).
Los diversos estudios demuestran consistentemente que la actividad física, la capacidad de ejercicio y la electromiografía son de gran utilidad para valorar la función muscular de los pacientes EPOC y ofrecen mediciones confiables y comparables en el tiempo y entre individuos. Evidencia GRADE 1A.
Pruebas de función de músculos periféricosManiobras voluntariasDinamometría de prensión de mano (handgrip)Es una medida sencilla, llevada a cabo con diferentes dinamómetros y que es ampliamente utilizada, con valor pronóstico en la EPOC54. Existen valores de referencia para diversas poblaciones55,56.
Contracción isométrica máxima del cuádriceps femoralSe realiza clásicamente en postura sentada, con caderas y rodillas siempre flexionadas a 90°, y mediante la extensión del cuádriceps con la pierna fijada por el tobillo, con conexión a un dinamómetro57. Existen valores de referencia58.
Prueba de tiempo de resistencia al 10% de la contracción isométrica máxima del cuádriceps femoralEs una prueba de resistencia59. Se fundamenta en la demostración de una claudicación tras un ejercicio en ciclos de contracción con una carga equivalente al 10% de la contracción isométrica máxima del cuádriceps femoral (ciclos de 2s de contracción con 3s de relajación del cuádriceps). Otras maniobras proporcionan una medida del par de fuerzas (torque) en Nm (Newton×metro) y se adecuan más específicamente a la medición de la resistencia60.
Los diversos estudios demuestran consistentemente que las pruebas de evaluación de la función de contracción y masa muscular en los pacientes EPOC son de gran utilidad y ofrecen mediciones confiables y comparables en el tiempo y entre individuos. Evidencia GRADE 1A.
Maniobras no voluntariasTwitch supramáximo del cuádriceps femoralLa técnica se basa en la estimulación eléctrica o magnética del nervio femoral en una estímulo único, o twitch, con medición de la fuerza generada tras la activación del cuádriceps61,62.
Los diversos estudios demuestran consistentemente que las pruebas de maniobras no voluntarias para la evaluación de la función muscular en los pacientes EPOC son de gran utilidad y ofrecen mediciones confiables y comparables en el tiempo y entre individuos, si bien su utilización no está extendida en la clínica habitual. Evidencia GRADE 1B.
Evaluación de la capacidad de esfuerzo: prueba de marcha de 6 minutosLa prueba de marcha de 6min es un protocolo simple de ejercicio que consiste en la medición de la distancia caminada de forma rápida por el paciente en una superficie dura y plana durante un período de 6min63.
Entre las diferentes pruebas de campo (escaleras, Bruce, marcha de 12min, marcha incremental, etc.)63-65, la prueba de marcha de 6min es la más popular, siendo en la actualidad el protocolo simple de ejercicio de referencia en la EPOC y otras enfermedades66-72. Tiene un buen nivel de estandarización63,73,74, con una reproducibilidad razonable75, y es muy útil para la evaluación del estado funcional de los pacientes, así como para medir los efectos de diferentes intervenciones en una gran variedad de enfermedades crónicas76-81.
La prueba de marcha de 6min corresponde a un ejercicio submáximo sostenible de alta intensidad82 que nos permite evaluar de forma global e integrada las diferentes funciones (cardíaca, respiratoria, transporte periférico de oxígeno, bioenergética muscular e integración neuromuscular) que determinan la capacidad aeróbica del paciente. Algunos estudios82,83 sugieren que la intensidad de ejercicio durante la prueba corresponde a la carga máxima sostenible en el tiempo (carga crítica)84 por el paciente. Ello explicaría su elevado valor predictivo de la mortalidad76,79,80 y su valioso papel en el proceso de toma de decisiones clínicas75,78,81.
IndicacionesEvaluación del estado funcional de pacientes con diferentes patologías crónicas como la EPOC, el asma, la obesidad, las enfermedades intersticiales pulmonares, la hipertensión pulmonar y enfermedades cardiovasculares diversas66-72, y la medición del efecto de intervenciones como entrenamiento, trasplante pulmonar, cirugía de resección de parénquima pulmonar e intervenciones farmacológicas en la hipertensión pulmonar, en la EPOC y en la insuficiencia cardíaca77,78. Aunque se trata de un protocolo de ejercicio muy seguro, dado que el mismo paciente determina la velocidad de la marcha, la prueba no debe efectuarse en pacientes con angina inestable, infarto de miocardio reciente (un mes), taquicardia con frecuencia superior a 120lat/min o situación de pico hipertensivo. Las medidas de seguridad y el entrenamiento de los profesionales son los propios de cualquier prueba de ejercicio63.
Medición de variablesLas variables son: a)distancia caminada expresada en metros; b)frecuencia cardíaca y saturación de la oxihemoglobina con pulsioximetría al inicio y al final de la prueba, y c)síntomas, disnea (escala de Borg) y molestias en extremidades inferiores, al inicio y final de la marcha. La primera vez que el paciente efectúa la prueba de marcha es aconsejable repetirla una segunda vez, con un intervalo aproximado de una hora, y escoger la que tiene una distancia recorrida mayor. Si el paciente requiere oxigenoterapia, la prueba se efectuará con el régimen de oxígeno prescrito.
Interpretación de resultadosPara la comparación de los resultados obtenidos antes y después de una determinada intervención es muy importante la identificación de la diferencia mínima con significación clínica expresada en metros, establecida en 25-30m después de una intervención66,69,70,85.
Aunque los resultados en términos de distancia recorrida suelen interpretarse en forma de valores absolutos (metros), también se utilizan valores de referencia, como los de Enright et al.86. En resumen, la prueba de marcha de 6min es altamente recomendable en la clínica como prueba de ejercicio simple para la valoración del estado funcional y del efecto de determinadas intervenciones en pacientes con enfermedades respiratorias y cardíacas crónicas. La simplicidad, la seguridad, la reproducibilidad y el elevado valor predictivo de la prueba hacen que sea el protocolo simple de referencia para el estudio de la capacidad aérobica en la clínica.
Los diversos estudios demuestran consistentemente que la prueba de marcha de 6min es de gran utilidad y ofrece mediciones muy confiables y comparables en el tiempo y entre individuos. Es de gran beneficio en la clínica habitual y en estudios. Evidencia GRADE 1A.
Evaluación de la capacidad de esfuerzo: cicloergometríaPruebas de esfuerzo incrementalesPermiten la evaluación tanto de la respuesta submáxima como de la respuesta máxima, y con frecuencia son capaces de identificar los mecanismos que subyacen a la disminución de la capacidad de ejercicio87-90. También permiten adecuar las intervenciones sobre la intolerancia al esfuerzo al origen de la limitación89-98 y descartar otros procesos médicos que pudieran suponer un riesgo, como el entrenamiento físico, aumentando la seguridad87,99.
El procedimiento está bien estandarizado64,87. Se usa con más frecuencia el cicloergómetro porque es barato, compacto, la potencia que suministra es conocida con precisión y no requiere práctica en la inmensa mayoría de los pacientes64,87,100.
VariablesLa mayoría de los softwares actuales son capaces de generar numerosas variables, aunque las más comúnmente utilizadas en estudios clínicos son el consumo máximo de oxígeno (O2max) y la carga máxima (WRmax), ambos limitados por síntomas. El O2max es una variable notablemente reproducible cuyos coeficientes de variación oscilan entre el 3 y el 7% cuando se alcanzan los criterios de esfuerzo máximo101-103. Se han obtenido mediciones consistentes en estudios clínicos multicéntricos cuando se establecen controles de calidad adecuados104,105 y, al menos en pacientes cardiacos, la mejoría del O2max tras intervenciones se traduce en mejorías de su supervivencia106. El O2max es sensible a intervenciones tanto farmacológicas como no farmacológicas, y en particular al entrenamiento muscular11,107-111.
La carga máxima (WRmax) tiene la ventaja sobre el O2max que puede determinarse sin disponer de un carro metabólico. Si bien se deberá tener en cuenta que, a diferencia del O2max, la WRmax depende de la velocidad del protocolo incremental (ΔWR/Δt) previo, y por tanto no se pueden hacer equivalencias con el O2max, al margen de que el protocolo utilizado debe ser exactamente igual antes y después de la intervención o exposición112.
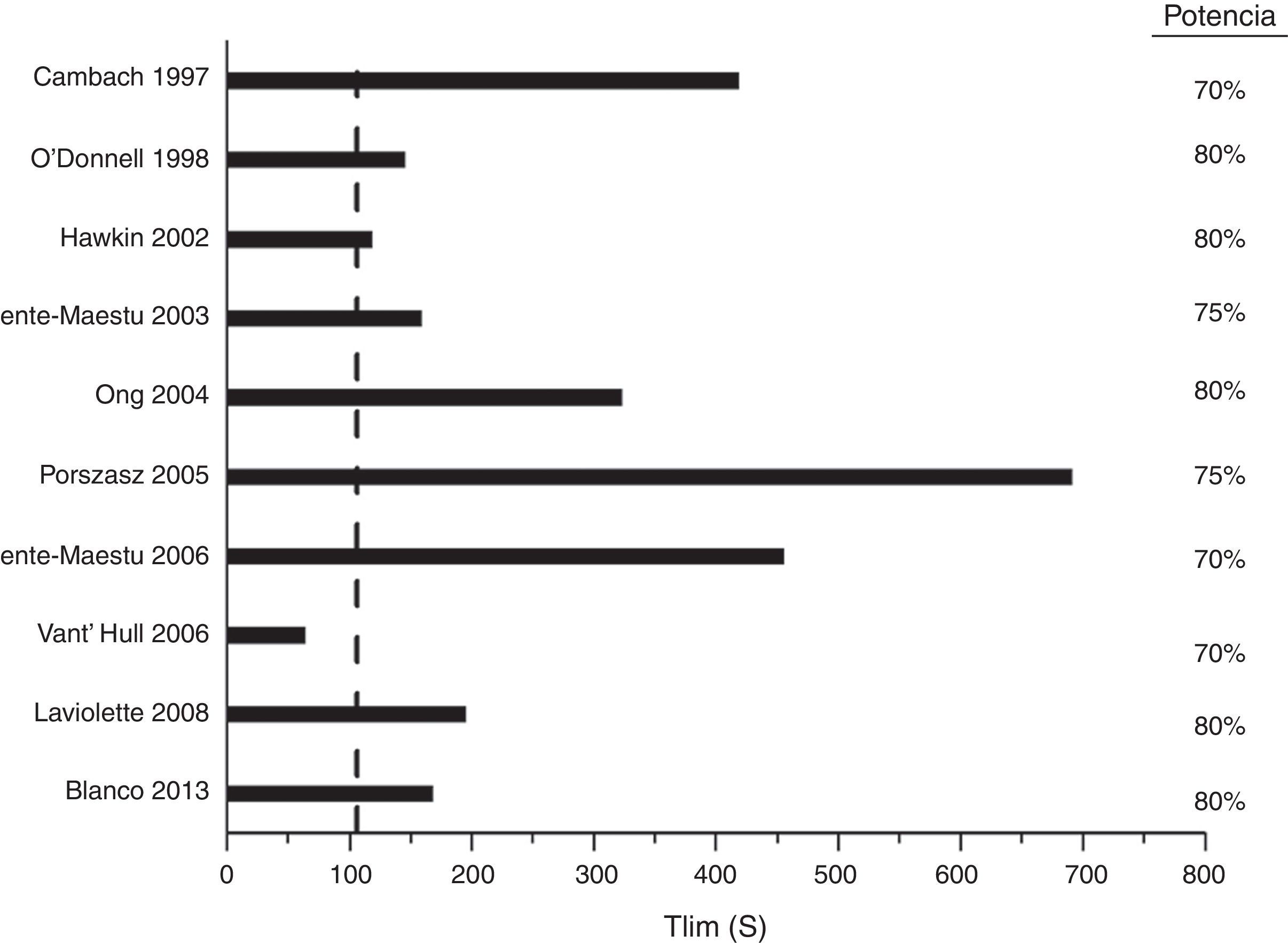
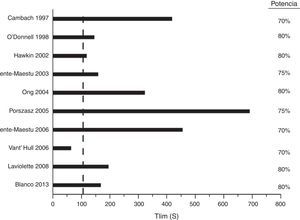
Pruebas constantes de intensidad altaAunque se pueden hacer pruebas constantes de intensidad moderada para caracterizar la cinética de la respuesta del sistema de transporte de oxígeno, dichas pruebas requieren un análisis complejo, por lo que su uso se reduce a estudios de investigación. Por el contrario, las pruebas a una potencia constante de intensidad alta se han utilizado profusamente en estudios para evaluar intervenciones dirigidas a los músculos. La variable que define la tolerancia al ejercicio es el tiempo transcurrido hasta que el paciente no puede seguir (tiempo límite [Tlim], expresado en segundos). En ensayos multicéntricos se ha demostrado que el Tlim es reproducible105,113 y consistente105 (fig. 4). La diferencia clínicamente significativa para esta pruebas es del orden de 100s (intervalo de confianza del 95%: 50-150s)113.
Selección de ensayos clínicos controlados que han utilizado pruebas a una potencia constante de intensidad alta para medir el efecto de intervenciones sobre los músculos de las extremidades inferiores.Potencia: intensidad a la que se hizo la prueba como porcentaje de la WRmax. Línea vertical: mínima diferencia clínicamente relevante.
Los diversos estudios demuestran consistentemente que la cicloergometría es de gran utilidad y ofrece mediciones muy confiables y comparables en el tiempo y entre individuos. Es de gran beneficio en la clínica habitual y en estudios. Evidencia GRADE 1A.
Entrenamiento muscular en la disfunción muscularSe ha demostrado ampliamente que el entrenamiento muscular, componente fundamental de los programas de rehabilitación respiratoria (RR), es eficaz para mejorar la tolerancia al ejercicio, la fuerza muscular, la disnea, la fatiga y la calidad de vida, siendo por ello un intervención terapéutica primordial para el abordaje de la disfunción muscular de los pacientes con EPOC2,114.
En los pacientes con enfermedad respiratoria crónica, el entrenamiento muscular general debe estar dirigido tanto a mejorar la capacidad aeróbica como la disfunción muscular característica de la enfermedad. La elección del tipo de entrenamiento estará condicionada por las necesidades del paciente y los objetivos planteados, pero también en gran medida por los recursos de que disponga el centro de rehabilitación115,116.
Los diversos estudios observacionales y ensayos clínicos demuestran consistentemente que el entrenamiento muscular es el mejor tratamiento para la disfunción muscular de los pacientes EPOC. Es beneficioso en la clínica habitual y en estudios. Evidencia GRADE 1A.
Tipos de entrenamientosEntrenamiento aeróbico o de resistencia (del inglés endurance training)Es la modalidad de ejercicio más utilizada en RR, existiendo la máxima evidencia para su recomendación (1A)2,114,117,118. El ejercicio aeróbico es un esfuerzo submáximo que implica a grandes masas musculares y se mantiene durante un tiempo prolongado. En pacientes con EPOC el entrenamiento físico tipo aeróbico no solo consigue una mejor adaptación cardiovascular sino que también mejora la función de la musculatura periférica. Esto se traduce en un aumento de la resistencia muscular, con fenómenos adaptativos a nivel de la bioenergética del músculo cuádriceps119,120 y de la estructura121.
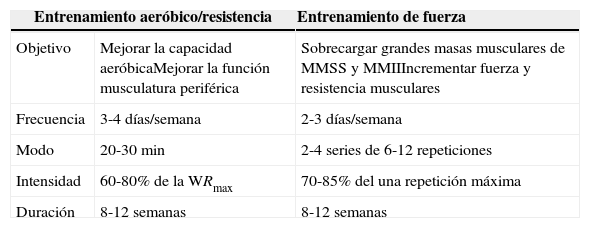
El entrenamiento con cicloergómetro, o en tapiz rodante, es el ejercicio aeróbico más utilizado en la RR, sobre todo en los programas de régimen ambulatorio y ámbito hospitalario. La intensidad del entrenamiento es muy importante en la prescripción del ejercicio terapéutico. Se recomienda una intensidad de trabajo que oscila entre el 60 y el 80% de la capacidad de esfuerzo máxima, evaluada previamente mediante una prueba de esfuerzo cardiopulmonar, un mínimo de 8 semanas118 para conseguir un beneficio sustancial, y 12 semanas como duración óptima114 (tabla 3). Programas de ejercicio más prolongados pueden conseguir efectos mayores y más duraderos sobre todo en los índices de calidad de vida122.
Recomendaciones prácticas para el entrenamiento aeróbico y el entrenamiento de fuerza en la enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica
| Entrenamiento aeróbico/resistencia | Entrenamiento de fuerza | |
|---|---|---|
| Objetivo | Mejorar la capacidad aeróbicaMejorar la función musculatura periférica | Sobrecargar grandes masas musculares de MMSS y MMIIIncrementar fuerza y resistencia musculares |
| Frecuencia | 3-4 días/semana | 2-3 días/semana |
| Modo | 20-30 min | 2-4 series de 6-12 repeticiones |
| Intensidad | 60-80% de la WRmax | 70-85% del una repetición máxima |
| Duración | 8-12 semanas | 8-12 semanas |
MMII: músculos de las extremidades inferiores; MMSS: músculos de las extremidades superiores; WRmax: carga máxima.
Los diversos estudios demuestran consistentemente que el entrenamiento muscular aeróbico de resistencia es uno de los mejores tratamientos para la disfunción muscular y el restablecimiento de la capacidad de ejercicio de los pacientes EPOC. Es beneficioso en la clínica habitual y en estudios. Evidencia GRADE 1A.
Entrenamiento interválicoSe trata de una modificación del entrenamiento aeróbico estándar en el que periodos cortos (de uno o 2min de duración) de ejercicio de alta intensidad (80-120% de la capacidad máxima) se alternan de forma regular con periodos de igual duración de descanso o de trabajo a menor intensidad. De este modo, los pacientes alcanzan niveles altos de esfuerzo pero con menor disnea y fatiga, obteniéndose beneficios equivalentes a los del entrenamiento aeróbico clásico121,123,124.
Los diversos estudios demuestran consistentemente que el entrenamiento interválico es uno de los mejores tratamientos para la disfunción muscular y el restablecimiento de la capacidad de ejercicio de los pacientes EPOC más graves. Es beneficioso en la clínica habitual y en estudios. Evidencia GRADE 1A.
Entrenamiento tipo fuerzaSiguiendo el «principio de especificidad», un entrenamiento de fortalecimiento muscular es potencialmente más capaz de aumentar la fuerza y la masa de la musculatura ejercitada que el entrenamiento aeróbico clásico125. La evidencia disponible apoya el uso del entrenamiento de fuerza en combinación con el entrenamiento general aeróbico (1A), ya que así se consiguen incrementos adicionales en la fuerza muscular periférica114,118. Para su aplicación en RR, habitualmente se recurre a los ejercicios de levantamiento de pesas para músculos de las extremidades inferiores y músculos de las extremidades superiores, realizados en aparatos gimnásticos con cargas elevadas, equivalentes al 70-85% del peso máximo que se puede movilizar en una única maniobra previa (o prueba de una repetición máxima), con pocas repeticiones118, en 2-3 sesiones por semana, durante 8-12semanas114,118.
Los diversos estudios demuestran consistentemente que el entrenamiento muscular de fuerza es uno de los mejores tratamientos para la disfunción muscular y el restablecimiento de la capacidad de ejercicio de los pacientes EPOC más graves. Es beneficioso en la clínica habitual y en estudios. Evidencia GRADE 1A.
Otras modalidades de entrenamientoFormas alternativas muy prometedoras de entrenamiento muscular periférico en los programas de RR son la estimulación eléctrica transcutánea2,126,127 y la estimulación electromagnética128, que es mejor tolerada pero menos estudiada.
Entrenamiento de músculos respiratoriosEn pacientes con EPOC se ha demostrado que el entrenamiento muscular inspiratorio mejora la fuerza y la resistencia musculares, con beneficios en la disnea, en la capacidad funcional y en la calidad de vida129. El entrenamiento específico de los músculos espiratorios mediante ejercicios de prensa abdominal es de dudosa eficacia. En general, el entrenamiento muscular inspiratorio debe realizarse 2 veces al día, a una intensidad de al menos el 30% de la PIM y en sesiones de unos 15min de duración118. Está indicado fundamentalmente en pacientes con disfunción muscular respiratoria.
Los diversos estudios demuestran consistentemente que el entrenamiento de los músculos respiratorios puede ser beneficioso en pacientes EPOC con importante disfunción muscular respiratoria, en la clínica habitual y en estudios. Evidencia GRADE 1B.
Otros tratamientos para la disfunción muscular no basados en el entrenamientoSuplementos nutricionales y tratamiento hormonalLas alteraciones nutricionales en pacientes con enfermedad respiratoria grave se cifran entre el 20 y el 40% y su génesis reviste un carácter multifactorial: desequilibrio entre el aporte y el gasto energético, la hipoxemia y el componente inflamatorio sistémico que frecuentemente acompaña a la enfermedad130-132. La utilización de suplementos nutricionales de alto valor energético en estos enfermos (esteroides anabolizantes y hormona de crecimiento, antioxidantes y otras moléculas proteicas) de alto valor energético en estos enfermos ha arrojado resultados contradictorios en la ganancia de peso y, sobre todo, en cuanto a su impacto en la recuperación funcional.
Suplementos nutricionalesEl empleo de suplementos nutricionales en el manejo de los pacientes con EPOC es habitual, pero existe todavía escasa evidencia a su favor. Mientras que algunos autores han comunicado que se consiguen incrementos de peso y de masa magra, así como mejoras en la tolerancia al ejercicio, otros estudios no apoyan estos datos. En la revisión Cochrane más reciente133 se incluye un metaanálisis de 17 ensayos clínicos aleatorizados134-148, con escasa evidencia en los pacientes que recibían suplementos nutricionales en cuanto a mejoría en el peso, masa magra, fuerza muscular respiratoria y distancia caminada durante la prueba de 6min, que se puso de manifiesto fundamentalmente en los pacientes malnutridos.
Los estudios no demuestran consistentemente que los beneficios superen a los riesgos en la administración de los tratamientos. Es de esperar que futuras investigaciones de mayor calidad aún puedan aportar mayor conocimiento y ayuden a implementar estos tratamientos en la clínica diaria en el manejo de pacientes EPOC, de ponerse de manifiesto resultados más confiables que los actuales. Evidencia GRADE 2B.
Esteroides anabolizantesHasta un 40% de los pacientes con EPOC muestran androgenopenia, que puede asociarse a pérdida de masa muscular149. La administración de esteroides anabolizantes se ha asociado a ganancia de peso y de masa muscular, hecho que soporta su utilización como adyuvantes en programas de rehabilitación. Sin embargo, los resultados no están suficientemente contrastados y, de hecho, las recomendaciones de la Sociedad Europea Respiratoria (ERS) y la Sociedad Torácica Americana (ATS) sobre rehabilitación no los aconsejan114. En diversos estudios publicados se demostró que a pesar del incremento de peso y masa magra, no se obtuvieron mejorías en los parámetros de función pulmonar, tolerancia al ejercicio ni función muscular respiratoria (PIM), o periférica (fuerza de contracción de la mano)143,150-155. Por otra parte, el metaanálisis incluye no solo tratamiento con derivados androgénicos sino también un estudio sobre la hormona de crecimiento y un estudio con grelina (secretagoga de la anterior), así como estudios que asocian o no entrenamiento, sin haberse realizado un análisis por subgrupos. Todos estos factores limitan la interpretación del mencionado metaanálisis. En realidad, la combinación de suplementos nutricionales o andrógenos con entrenamiento muscular sí ha puesto de manifiesto un incremento en el peso, la masa magra, la PIM, la fuerza del cuádriceps, el trabajo máximo y el tiempo de resistencia al ejercicio156.
Los estudios no demuestran consistentemente que los beneficios superen a los riesgos en la administración de los tratamientos. Es de esperar que futuras investigaciones de mayor calidad aun puedan aportar mayor conocimiento y ayuden a implementar estos tratamientos en la clínica diaria en el manejo de pacientes EPOC, de ponerse de manifiesto resultados más confiables que los actuales. Evidencia GRADE 2B.
Hormona de crecimiento y grelinaEl uso de hormona de crecimiento humana recombinante también se ha estudiado en pacientes con EPOC y desnutrición, en el contexto de programas de rehabilitación, con resultados escasamente concluyentes150,157. Más recientemente se ha probado la utilización de grelina, en pacientes con EPOC y desnutrición, también incluidos en programas de rehabilitación. La grelina es una hormona polipeptídica que actúa fijándose sobre los receptores hipotalámicos estimulantes de hormona de crecimiento, incrementando su liberación. Además estimula también la liberación de factores orexígenos, que aumentan del apetito158. Paradójicamente, los pacientes con EPOC y desnutrición pueden tener elevados los niveles de grelina159, y los resultados publicados hasta la fecha con la administración exógena de esta sustancia son escasamente concluyentes160-162.
Los estudios no demuestran consistentemente que los beneficios superen a los riesgos en la administración de los tratamientos. Es de esperar que futuras investigaciones de elevada calidad aun puedan aportar mayor conocimiento y ayuden a implementar estos tratamientos en la clínica diaria en el manejo de pacientes EPOC, de ponerse de manifiesto resultados mucho más confiables que los actuales. Evidencia GRADE 2C.
Otros nutrientesOtros productos analizados en relación con su capacidad de mejorar la función muscular y física de los pacientes con EPOC incluyen antioxidantes, vitaminas159 y moléculas de alta capacidad energética, pero en general se trata de estudios aislados y no controlados, o ensayos con escaso número de pacientes, difíciles de reproducir163,164.
Los estudios no demuestran consistentemente que los beneficios superen a los riesgos en la administración de los tratamientos. Es de esperar que futuras investigaciones de elevada calidad aun puedan aportar mayor conocimiento y ayuden a implementar estos tratamientos en la clínica diaria en el manejo de pacientes EPOC, de ponerse de manifiesto resultados mucho más confiables que los actuales. Evidencia GRADE 2C.
Tratamientos no farmacológicos: ventilación mecánica no invasiva y helioxEs un hecho conocido que la ventilación mecánica no invasiva (VMNI) consigue el descanso de los músculos respiratorios, lo que explica la mejoría de su función, puesta de manifiesto mediante un incremento en la PIM, la Pdimax y el índice tensión/tiempo. Aunque escasos, algunos estudios han asociado el uso de VMNI a una mejor función de los músculos periféricos, puesta de manifiesto mediante un incremento en la fuerza y resistencia del cuádriceps165, probablemente como consecuencia de un mayor aporte de oxígeno a los músculos periféricos, fruto de la reducción en el trabajo respiratorio166. Este mismo mecanismo se ha invocado para explicar el efecto de la respiración con heliox (mezcla de helio y oxígeno) sobre la función de los músculos periféricos. En una revisión Cochrane reciente, basada en un metaanálisis de 6 ensayos clínicos que evalúan los resultados de la VMNI durante un programa de ejercicio físico, se concluyó que las ligeras diferencias en capacidad de ejercicio y tolerancia al mismo son poco consistentes. En línea con las últimas recomendaciones de consenso establecidas por la ERS y ATS, no se recomienda la utilización de VMNI durante el entrenamiento muscular114, que quedaría reservada a pacientes hipercápnicos en programas de VMNI nocturna.
Los estudios no demuestran consistentemente que los beneficios superen a los riesgos en la administración de los tratamientos. Si bien futuras investigaciones aun puedan aportar mayor conocimiento y ayudar a implementar estos tratamientos en la clínica diaria en el manejo de pacientes EPOC. Evidencia GRADE 2A.
ConclusionesEn resumen, una buena función de músculos respiratorios y de las extremidades es esencial para mantener la vida y un nivel aceptable de calidad de vida. Dicha función se ve afectada en numerosas enfermedades respiratorias, pudiendo condicionar problemas tanto para la vida social del enfermo como para sostener un nivel adecuado de ventilación. La función muscular puede y debe ser valorada en estos pacientes, con el fin de aplicar las medidas terapéuticas adecuadas. A la luz de la evidencia actual, el entrenamiento, con o sin suplementos nutricionales, es sin lugar a dudas la mejor estrategia terapéutica para incrementar la masa y la función musculares y la calidad de vida de los pacientes EPOC.
Los autores agradecen el soporte recibido por Ester Puig-Vilanova y Anael Barberán-García por su inestimable contribución en la revisión bibliográfica e incorporación de las referencias. También agradecen la colaboración de Anna Salazar, María Cortés-Badia y Paula Bassagañas-Òdena en la confección del listado de abreviaturas y de referencias en el documento.