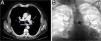
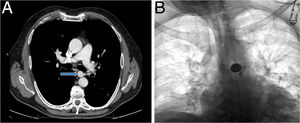
A 63-year-old man presented in the emergency room with self-limiting bloody sputum. As the patient had had prior episodes of hemoptysis, he was admitted to the hospital. Chest CT showed bilateral bronchiectasis and bronchial artery hypertrophy (up to 4.5mm in diameter), particularly in the left side, where a saccular aneurysmal dilation was visualized in the origin of one of the arteries, measuring 16×14mm in the axial plane, with a narrow neck connecting it to the anterior wall of the aorta (Fig. 1). Selective angiogram of the left bronchial artery was performed via the femoral route, and the distal bed was embolized with polyvinyl alcohol particles (700–1000 and 1000–1200μm), with good morphological outcome; the segment of the bronchial artery distal to the aneurysm and the aneurysmal sac was then embolized with coils, achieving complete exclusion, without complications (Fig. 1B).
Bronchial artery aneurysms are rare (1% of bronchial angiograms).1 They can be congenital (associated with pulmonary sequestration or agenesis) or acquired (associated with chronic pulmonary inflammation due to infections such as tuberculosis, bronchiectasis, tumors, or atherosclerosis).1 They must be treated, regardless of symptoms, given the high risk of life-threatening bleeding.1 The treatment of choice is endovascular, using local transcatheter embolization.2 If this procedure is contraindicated (allergy to iodinated contrast agents), the next option is surgery by ligation or resection.
Please cite this article as: Cerezo Lajas A, Rodríguez Guzmán MC, de Miguel Díez J. Aneurisma de arteria bronquial izquierda. Arch Bronconeumol. 2019;55:215.