The origin of systemic inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients remains to be defined, but one of the most widely accepted hypothesis is the ‘spill over’ of inflammatory mediators from the lung to the circulation.
ObjectiveTo evaluate the relationship between pulmonary and systemic inflammation in COPD quantifying several inflammatory markers in sputum and serum determined simultaneously.
MethodologyCorrelations between various inflammatory variables (TNFα, IL6, IL8) in sputum and serum were evaluated in 133 patients from the PAC-COPD cohort study. A secondary objective was the evaluation of relationships between inflammatory variables and lung function.
ResultsInflammatory markers were clearly higher in sputum than in serum. No significant correlation was found (absolute value, r=0.03–0.24) between inflammatory markers in blood and in sputum. There were no significant associations identified between those markers and lung function variables, such as FEV1, DLCO and PaO2 neither.
ConclusionsWe found no correlation between pulmonary and systemic inflammation in patients with stable COPD, suggesting different pathogenic mechanisms.
El origen de la inflamación sistémica en pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica (EPOC) es poco conocido, y una de las hipótesis más aceptadas es el paso de la inflamación del pulmón a la sangre (spill-over).
ObjetivoEvaluar la relación entre la inflamación pulmonar y sistémica en la EPOC mediante la cuantificación de diversos marcadores inflamatorios en esputo y suero obtenidos en el mismo individuo de forma simultánea.
MetodologíaDe 133 pacientes de la cohorte PAC-EPOC se evaluaron las relaciones entre diferentes variables inflamatorias (TNFα, IL-6, IL-8) en suero y esputo. Como objetivo secundario se evaluaron las relaciones de las variables inflamatorias de suero con la función pulmonar.
ResultadosLos valores de los marcadores inflamatorios fueron claramente superiores en esputo que en suero. No se hallaron correlaciones relevantes (en valor absoluto, r=0,03–0,24) entre los marcadores inflamatorios en sangre y en esputo. Tampoco se identificaron asociaciones significativas entre dichos marcadores, con variables de función pulmonar como el FEV1, DLCO y la PaO2.
ConclusionesEn pacientes con EPOC estable no existe correlación entre la inflamación pulmonar y sistémica, lo que sugiere mecanismos patogénicos diferentes.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is associated with pulmonary and systemic inflammation.1–3 Pulmonary inflammation appears to be more common in patients with greater airflow limitation, although it should be pointed out that current data are based on cross-sectional analyses,4 so no cause–effect relationship can be established. While systemic inflammation does not occur in all COPD patients, it is associated with higher mortality and exacerbation rates in patients in whom it persists over time.1
The origin of systemic inflammation in COPD remains to be defined, but one of the most widely accepted hypothesis is the ‘spill-over’ of inflammatory mediators from the lung to the blood, suggesting an association between these inflammatory processes. However, the relationship between pulmonary and systemic inflammation in COPD continues to be a topic for debate.5–7 Studies published to date have several limitations, such as relatively small sample sizes,6,8,9 or lack of simultaneous quantification (in the same patient) of the same inflammatory markers in both pulmonary and systemic compartments.10
The aim of this study was to address these limitations and to evaluate possible relationships between pulmonary and systemic inflammation in COPD, by quantifying inflammatory markers in sputum and serum samples obtained simultaneously from the same individual, in a large sample of COPD patients (n=133) from the PAC-COPD study cohort.11,12 Secondary objectives included the exploration of potential associations between systemic inflammation and lung function variables possibly related with pulmonary inflammation, such as forced expiratory volume in 1s (FEV1), diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO) and partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood (PaO2).
MethodPopulation and Ethical AspectsThe PAC-COPD study included 342 patients hospitalized for a first COPD exacerbation in 9 hospitals in Spain between January 2004 and March 2005.11,12 Patients were followed up for 3 months after hospital discharge (maximum deviation of 1 week). They were in a clinically stable phase (8 weeks without new exacerbations or changes in medication) and followed up in outpatient clinics for 3 years.12 The COPD diagnosis was established when the patient was clinically stable, in accordance with ATS/ERS recommendations.13 Patients younger than 45 years of age, with cancer, post-tuberculous sequelae, pneumonectomy and/or pnemoconiosis were excluded. In total, 113 patients (39% of the total cohort) with simultaneously obtained samples evaluable for pulmonary and systemic inflammation took part. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of all participating hospitals, and all patients signed informed consent forms.
Clinical and Functional DeterminationsAs described above,11,12 clinical data and smoking history were obtained from validated questionnaires. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as the individual's weight divided by the square of their height in meters.11,12 Forced spirometry with bronchodilator challenge, lung volumes, DLCO and blood gases were quantified using standard methodologies.14–16 Reference values for spirometry, lung volumes and DLCO correspond to a Mediterranean population.17,18
Pulmonary InflammationWhenever possible, a spontaneous sputum sample was obtained at least 60min after the lung function tests (225 patients). If the patient could not expectorate spontaneously, a sputum sample was obtained by induction with saline serum, according to the conventional method.19 Of the patients who provided a sputum sample (n=255), 133 had <20% squamous cells and were included in the analysis.20
Concentrations of interleukin 6 (IL-6), IL-8 and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) (cytokine bead array system, BD Biosciences, San Diego, CA, US) were quantified in sputum supernatant. The lower limits of quantification (LLQ) of IL-6, IL-8 and TNFα were 2.5, 3.6 and 3.7pg/ml, respectively. According to previous recommendations, patients with values below these levels were assigned a nominal level of half of the LLQ in order to avoid a downward bias.1 All determinations were performed in duplicate in the central laboratory of the Hospital Universitari Son Espases (Palma de Mallorca, Spain). Since the coefficient of variation was <10% in all cases, the mean of 2 determinations was used for the analysis.
Sputum samples were also cultured according to conventional methods.21 The bacterial load was quantified by colony-forming units (CFU)/milliliter. Cultures were considered positive for colonization if minimum growth of 100CFU/ml was found for Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacteriaceae and/or Staphylococcus aureus.22 For patients with mixed microbial cultures, the potentially pathogenic microorganism (PPM) with the highest bacterial load was selected for the analysis.
Systemic InflammationOn the same day of sputum collection, a venous blood sample (20ml) was collected in an EDTA tube by peripheral venipuncture between 8.00am and 9.00am, after a fast of at least 6h; active smokers were also asked to abstain from smoking for 6h before the biological samples were obtained. The blood sample was immediately centrifuged for 10min at 2000rpm, and the resulting serum was stored at −80°C until analysis.
C-reactive protein (CRP) levels were determined in duplicate using high sensitivity nephelometry, with an LLQ of 0.175mg/l (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Products GMBH, Marburg, Germany). IL-6, IL-8 and TNFα serum levels were determined (in duplicate) by high sensitivity ELISA (Biosource, Camarillo, CA, USA), with LLQs of 0.03, 0.10 and 0.13pg/ml, respectively. As mentioned above for sputum samples, to avoid a downward bias, a nominal level of half of the LLQ value was assigned to patients with values below the LLQ.1 All analyses were performed in a central facility in the Hospital Universitari Son Espases (Palma de Mallorca, Spain). Since the coefficient of variation was <10% in all cases, the mean of 2 determinations was used for the data analysis.
Statistical AnalysisThe sample size for the PAC-COPD study (n=342) was determined by its primary objectives12; for this study, data could be used from 133 patients. Before any analyses were performed, we calculated the sample size needed to determine a statistically significant correlation of 0.35 between inflammatory markers in serum and in the airway,6 and a correlation of 0.29 between inflammatory markers and FEV1,8 using the GRANMO 7.12 program.23 With an alpha risk of 0.05 and a beta risk of 0.2 in a two-tailed comparison, the number of patients required was 62 and 92, respectively; in both objectives, the number of patients available exceeded the number required. Normal distribution of the variables was calculated using the Kolgomorov–Smirnov test. Results are shown as mean (standard deviation) for normally distributed variables, or median (25–75th percentile) otherwise. Qualitative variables are given as percentages. To compare the values of 2 groups, the Student t test was used for normally distributed variables and the Mann–Whitney or Wilcoxon for variables with non-normal distribution. Differences between qualitative variables were evaluated using the Chi-squared test. The relationship between variables of pulmonary and systemic inflammation was estimated using Spearman's rank correlation coefficients. A correlation was considered very low, low, moderate or high if the correlation coefficient had an absolute value of <0.25, 0.25–0.50, 0.51–0.75, or >0.75, respectively.24 A P-value of <.05 was considered significant, except in the case of multiple comparisons/correlations, for which the above-mentioned P-value was modified according to the Bonferroni correction. The statistical analysis was conducted using the SPSS program (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
ResultsClinical and Functional Characteristics of PatientsOf the initial cohort (342 patients), one third of patients could not provide sputum samples, as they could not expectorate, so a total of 225 patients with sputum samples were initially evaluated. These patients were (P<.05) younger (66 vs 69 years), had less exposure to tobacco smoke (58 vs 69 pack-years), greater airflow limitation (FEV1 49% vs 54% predicted) and lower DLCO (60% vs 67% predicted). Only 133 of these 225 patients had evaluable sputum samples. The clinical characteristics of these patients were similar to those who did not have evaluable sputum, except for lower FEV1 (52% vs 57%, P<.05). Of the 133 patients with evaluable sputums, 76 individuals provided spontaneous samples and 57 provided induced sputum; no clinical or biological differences were found between the 2 groups (data not shown).
Table 1 shows the main anthropometric, clinical and functional data of the patients included in the study.
Clinical and Functional Data of Patients Included in the Analysis.
| Patients (n=133) | |
|---|---|
| Age (years), mean±SD | 69±9 |
| Men, n (%) | 124 (93%) |
| Tobacco exposure (pack-years), mean±SD | 71±42 |
| BMI, kg/m2, mean±SD | 28±5 |
| FEV1 (% predicted), mean±SD | 52±16 |
| FEV1/FVC (% predicted), mean±SD | 53±12 |
| DLCO (% predicted), mean±SD | 66±21 |
| PaO2 (mmHg), mean±SD | 72±9 |
| PaCO2 (mmHg), mean±SD | 41±5 |
BMI, body mass index; DLCO, diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1s; FEV1/FVC (%), ratio between forced expiratory volume in 1s and forced vital capacity; PaCO2, partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood; PaO2, partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood.
Thirty-nine (29%) of the 133 patients with evaluable sputum samples were colonized with PPMs. The most commonly isolated PPM was H. influenzae (n=22, 19%).
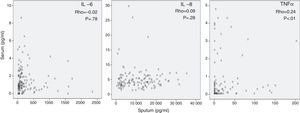
Inflammatory MarkersTable 2 shows inflammatory biomarker levels in sputum and blood (consistently higher in sputum). Median CRP was 4.1 [1.9–7]mg/l. Practically no relationship was found between IL-6, IL-8 and TNFα values measured simultaneously in serum and sputum in the same patient (Fig. 1). One isolated, low correlation with outliers and wide dispersion was seen between TNFα in sputum and in blood (r=0.24, P<.01).
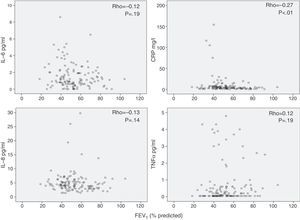
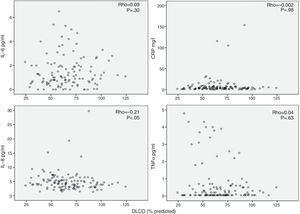
Moreover, we found that inflammatory markers in serum were unrelated with FEV1 (Fig. 2), DLCO (Fig. 3), PaO2 or age (data not shown) – some isolated correlations were found but like the parameters mentioned above, these were low and not statistically significant. Previously published results of associations between systemic inflammation and bronchial colonization showed only 1 isolated association between CRP and bronchial colonization.20
The main observation of this study is the lack of correlation between different inflammatory markers determined simultaneously in blood and sputum in the same stable COPD patient. Nor were any significant associations found between these markers and lung function variables, such as FEV1, DLCO and PaO2, or with age.
Previous StudiesVarious studies have previously evaluated the relationships between pulmonary and systemic inflammation in COPD patients. However, they have certain methodological limitations, such as correlating different markers in the pulmonary and systemic compartments,10 or evaluating the relationships between systemic inflammation and lung function variables, assuming that the latter reflect pulmonary inflammation.25,26 Moreover, studies which compare the same markers in blood and in the lung have small sample sizes (<30 patients).6,8,9 Our study compares the same markers in serum and in sputum in a much larger sample (133 patients) than reported in previous studies, and moreover, our patients are better characterized than previous series.11,12
Interpretation of ResultsIt has been suggested that systemic inflammation in COPD patients is caused by the spill-over of inflammatory cells and/or proteins from the lung to the blood.7 This hypothesis is based on previous observations in experimental animal models27 and in humans28 indicating that the passage of pulmonary proteins to the systemic circulation was possible. Our results do not support the spill-over theory, because we observed no significant relationship between pulmonary and systemic inflammatory markers determined simultaneously in the same patient (Fig. 1). In contrast, our observations suggest that the inflammatory response in these 2 biological compartments in stable COPD patients have different regulatory mechanisms. The lack of significant correlations between systemic inflammation and lung function variables (Figs. 2 and 3) supports this interpretation, and is in line with several previous studies.2,29–31 Similarly, bronchial colonization, which is associated with a marked local inflammatory response,20 was not associated with a parallel systemic increase in the same markers in our patients. However, it was associated in some isolated cases of higher CRP levels in blood in colonized patients,20 but at a lower magnitude than observed during disease exacerbations.6 In all, these observations suggest that systemic inflammation is characteristic of an independent COPD phenotype, the origin and consequences of which will have to be defined in future studies.
Finally, it should be noted that the relationship between systemic inflammatory markers and age is controversial29; in this study, we observed no such correlation.
Potential Clinical ImplicationsIf, as our results suggest, systemic inflammation is a feature of an independent COPD phenotype, and its presence is associated with increased exacerbations and higher mortality,1 randomized clinical trials will be needed to evaluate different therapeutic alternatives in this type of patient. An interesting approach in this respect is the pilot study of McDonald et al.,32 who used a CRP value to guide initiation of statin treatment; patients treated showed a significant reduction in CRP.
Strengths and LimitationsObvious strengths of our study include the sample size (n=133), which is far larger than that of previous studies,8,9 the complete clinical characterization of the study patients (lung function, nutritional status, microbiology, comorbidities, etc.), and in particular, the fact that the various inflammatory markers were determined simultaneously in serum and sputum. As with any study, there are also limitations, the most relevant of which are: (1) inflammation determined in sputum may not be identical to that present in pulmonary tissue. (2) no sputum was obtained from 117 patients in the initial cohort of 342 patients (34%); these patients were younger (66 vs 69 years), heavier smokers (58 vs 69 pack-years), and had worse lung function (FEV1 49% vs 54%). This may be explained by the greater smoking burden, which may increase expectoration,33 or perhaps these patients may constitute another phenotype per se. Although differences in age were statistically significant, absolute values (3 years) were clinically irrelevant. (3) Evaluable sputum was obtained from only 133 of the 225 patients who produced samples. When patients with evaluable sputum were compared with the rest of the patients who managed to expectorate, differences were found only in FEV1 (52% vs 57%, P<.05). This phenomenon has already been described in other studies, which showed a direct correlation between evaluable sputum and the degree of airflow obstruction.34 The percentage of evaluable sputum among the entire cohort (133/342; 39%) was similar to that of other series.35,36 (4) The microbiological data have been published in a separate paper,20 but the objectives of this study are different, as are most of the results, too. These microbiological data have been added to throw more light on relationships between colonization/infection and pulmonary inflammation. (5) Most patients were men, so our results cannot be directly extrapolated to women, since the disease manifests differently in men and women.37
ConclusionsPatients with stable COPD show no correlation between pulmonary and systemic inflammation, suggesting that spill-over is an unlikely hypothesis, and that other, independent pathogenic mechanisms are responsible for inflammation in both compartments.
FundingFunded in part by: Health Research Fund (PI020541, PI052082, PI052486, 11/02029, 14/00713), Spanish Ministry of Health; Technological Evaluation and Medical Research Agency (AATRM 035/20/02), Government of Catalonia; Spanish Society of Pulmonology and Thoracic Surgery (SEPAR 2002/137, SEPAR 2013); Catalan Pulmonology Foundation (FUCAP 2003 Beca Marià Ravà); RESPIRA Network (RTIC C03/11); RCESP Network (RTIC C03/09); La Marató Foundation, TV3 (No. 041110); DURSI (2005SGR00392), and an educational grant from Novartis Farmacéutica. CIBERESP and CIBERES are funded by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Spanish Ministry of Health. General Department of Research and Technological Development of the Ministry of Innovation, Department of the Interior and Justice of the Autonomous Community of the Balearic Islands and FEDER Funds (Competitive groups) (PRE-R-22528-2011).
AuthorshipBelén Núñez: patient recruitment, sample collection, analysis of inflammation in sputum and blood, statistical analysis, discussion of results, drafting the manuscript.
Jaume Sauleda: drafting the FIS project proposal (PI052082), recruitment, statistical analysis, discussion of results, drafting the manuscript.
Judith García-Aymerich: drafting the cohort study proposal, statistical analysis, discussion, drafting the manuscript.
Aina Noguera: analysis of inflammation in blood and sputum, discussion, drafting the manuscript.
Eduard Monsó: sputum collection and processing, discussion, drafting the manuscript.
Federico Gómez: recruitment, sputum collection and processing, discussion, drafting the manuscript.
Esther Barreiro: recruitment, sample collection, discussion, drafting the manuscript.
Alicia Marín: recruitment, sputum collection and processing, discussion, drafting the manuscript.
Josep María Antó: drafting the cohort study proposal, discussion, drafting the manuscript.
Alvar Agustí: drafting the FIS project proposal (PI052082), statistical analysis, discussion of results, drafting the statistical analysis manuscript, discussion, drafting the manuscript.
Conflict of InterestsThe authors state that they have no conflict of interests.
We would like to the study participants for their willingness to contribute to biomedical research. We also thank Meritxell López (E.I.), Angel Ríos (E.I.), Josep Lluis Valera (E.I.), Sara Barea (E.I.) and Dr. Cristina Villena for her technical assistance during this study.
Members of the Phenotype Characterization and Evolution of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (PAC-COPD) Study Group
Centro de Investigación en Epidemiología Ambiental (CREAL), Institut Municipal d’Investigació Mèdica (IMIM), Barcelona: Josep M. Antó (investigador principal), Judith Garcia-Aymerich (coordinadora de proyecto), Marta Benet, Jordi de Batlle.
Hospital del Mar-IMIM, Barcelona: Joaquim Gea (coordinadordel centro), Eva Balcells, Àngel Gayete, Mauricio Orozco-Levi.
Hospital Clínic-Institut d’Investigacions Biomèdiques August Pii Sunyer (IDIBAPS), Barcelona: Joan Albert Barberà (coordinadordel centro), Federico P. Gómez, Carles Paré, Josep Roca, Robert Rodríguez-Roisin.
Hospital General Universitari Vall d’Hebron, Barcelona: Jaume Ferrer (coordinador del centro), Esther Pallissa, Esther Rodríguez.
Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau, Barcelona: Pere Casan (coordinador del centro), Rosa Güell, Ana Giménez.
Hospital Universitari Germans Trias i Pujol, Badalona: Eduard Monsó (coordinador del centro), Alicia Marín, Josep Morera.
Hospital Universitario de Bellvitge, l’Hospitalet de Llobregat: Eva Farrero (coordinador del centro), Joan Escarrabill.
Hospital de Sabadell, Corporació Parc Taulí, Institut Universitari Parc Taulí (Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona), Sabadell: Antoni Ferrer (coordinador del centro).
Hospital Universitari Son Dureta, Palma de Mallorca: Jaume Sauleda (coordinador del centro), Àlvar G.N. Agustí, Bernat Togores.
Hospital de Cruces, Barakaldo: Juan Bautista Gáldiz (coordinadordel centro), Lorena López. Hospital General Universitari, Valencia: José Belda.
Please cite this article as: Núñez B, Sauleda J, Garcia-Aymerich J, Noguera A, Monsó E, Gómez F, et al. Ausencia de correlación entre marcadores de inflamación pulmonar y sistémica en pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica: un análisis bi-compartimental simultáneo. Arch Bronconeumol. 2016;52:361–367.
Members of the Phenotype Characterization and Evolution of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (PAC-COPD) Study Group are listed in Appendix A.