La calidad de vida relacionada con la salud es una importante medida de resultado utilizada en la monitorización del control del asma. La autoeficacia es un determinante de las conductas de automanejo, por lo que puede contribuir a la mejora del control del asma y de la calidad de vida. Nuestro objetivo es analizar la relación entre la autoeficacia y la calidad de vida de niños con asma y la de sus cuidadores.
MétodosEn un total de 176 pacientes entre 6-14 años con asma se ha determinado el nivel de autoeficacia identificando tres grupos (niveles bajo, medio y alto). Cada niño y su cuidador principal completan PAQLQ y PACQLQ, respectivamente.
ResultadosPAQLQ rang=(1-7): 5,61±1,11; PACQLQ rang=(1-7): 5,42±1,35; autoeficacia rang=(0-60): nivel bajo 28,44±4,58; nivel medio 37,41±1,7 y nivel alto 47,50±5,5. Diferencias significativas en calidad de vida según niveles de autoeficacia bajo-medio vs. alto. Dominios específicos relacionados: PAQLQ emociones y PAQLQ síntomas con autoeficacia en las habilidades para resolver problemas relacionados con el asma y autoeficacia para el tratamiento. PACQLQ emociones con autoeficacia en las habilidades para resolver problemas relacionados con el asma.
ConclusionesUn alto nivel de autoeficacia se asocia a una mejor calidad de vida de los niños y sus cuidadores. Basándonos en estos resultados, la medida de la autoeficacia podría ser incorporada en la evaluación de las intervenciones educativas en automanejo cuyo objetivo final es alcanzar la calidad de vida diana del paciente y su familia.
Health-related quality of life is an important outcome measurement in the monitoring of asthma control. Self-efficacy is a determinant of self-management behaviors that can contribute to the improvement of asthma control and quality of life. Our objective was to analyze the relationship between self-efficacy and quality of life in children with asthma and their caregivers.
MethodsWe included 176 patients aged 6-14 years with asthma, and determined their level of self-efficacy according to three groups (low, medium and high levels). Each child and their main caregiver completed the PAQLQ and PACQLQ questionnaires, respectively.
ResultsPAQLQ range=1-7: 5.61±1.11; PACQLQ range=1-7: 5.42±1.35; self-efficacy range=0-60: low level 28.44±4.58; average level 37.41±1.7, and high level 47.50±5.5. Significant differences were observed in quality of life according to low-medium vs. high levels of self-efficacy. Specific related domains: PAQLQ emotions and PAQLQ symptoms with self-efficacy in problem-solving skills related to asthma and treatment self-efficacy; PACQLQ emotions with self-efficacy in problem-solving skills related to asthma.
ConclusionsA high level of self-efficacy is associated with a better quality of life for children and their caregivers. Based on these results, the measurement of self-efficacy could be incorporated in the assessment of educational interventions in self-management targeted at the quality of life of the patient and his or her family.
El automanejo está considerado un enfoque efectivo para alcanzar y mantener el control del asma, principal objetivo del tratamiento1. Esta aproximación requiere de un individuo empoderado, donde sus necesidades y percepciones cobran una gran relevancia. De ahí que las clásicas medidas clínicas de resultado se hayan complementado con otras centradas en el paciente (Patient-Reported Outcomes Measures [PROM] por sus siglas en inglés), adquiriendo en los últimos años un creciente desarrollo en la edad pediátrica2.
La calidad de vida relacionada con la salud es una importante PROM que mantiene una estrecha relación con el grado de control del asma3–5, por lo que su valoración es utilizada como un elemento clave en la monitorización del mismo6.
Distintos estudios han puesto de manifiesto que la calidad de vida está determinada por múltiples factores, aunque los resultados se muestran menos sólidos cuando se utilizan criterios objetivos7–9, que cuando se tienen en cuenta parámetros subjetivos10,11. Entre estos últimos, podemos destacar a la autoeficacia que es definida como las creencias que una persona posee acerca de su capacidad para desempeñar exitosamente una conducta.
La autoeficacia desempeña un papel fundamental en el automanejo del asma12 y ha sido incluida como un componente básico en intervenciones educativas dirigidas a conseguir la calidad de vida diana del paciente13. Estudios realizados en adultos han encontrado asociaciones entre la autoeficacia y la calidad de vida de los pacientes14–16. En población pediátrica, la autoeficacia parental también ha sido relacionada con la calidad de vida de los niños y otros indicadores de morbilidad17,18.
Sin embargo, a pesar de la importancia que parece mostrar la autoeficacia en la calidad de vida, aún no disponemos de datos que examinen esta relación desde la perspectiva del niño.
Por todo ello, el objetivo del presente estudio es analizar la calidad de vida de niños y cuidadores según el nivel de autoeficacia que los niños poseen para el manejo de su asma.
MétodosEstudio descriptivo transversal realizado en un hospital universitario y centros de atención primaria de referencia, en la zona del Mar Menor, en el sureste de España.
Se incluyó a todos los pacientes pediátricos en régimen ambulatorio y sus respectivos cuidadores que cumplían con los siguientes criterios: a) niños entre 6 y 14 años; b) diagnóstico médico de asma; c) buena capacidad de lectoescritura del español; d) consentimiento por escrito.
El período de estudio fue de noviembre de 2010 hasta diciembre de 2011. El protocolo de investigación fue aprobado por los correspondientes comités éticos.
La autoeficacia se valoró mediante la versión adaptada y validada al español del Asthma Self-efficacy Scale19 (Anexo A, disponible en la versión electrónica). Esta escala evalúa las creencias de los niños acerca de su capacidad para llevar a cabo determinadas conductas de automanejo que son necesarias para un adecuado control del asma. Incluye 20 ítems de los cuales 19 se distribuyen en cuatro dimensiones: autoeficacia en las habilidades para resolver problemas relacionados con el asma (6 ítems), autoeficacia para el tratamiento (6 ítems), autoeficacia en la relación médico-paciente (4 ítems) y autoeficacia para resolver problemas interpersonales (3 ítems). Cada ítem es respondido en una escala tipo likert con cuatro opciones de respuesta donde 0=inseguro; 1=poco seguro; 2=seguro; 3=muy seguro. La puntuación final resulta de la suma de las respuestas en cada ítem, proporcionando una puntuación global y otra específica para cada una de las dimensiones.
Para la evaluación de la calidad de vida de los niños y sus cuidadores se utilizaron los cuestionarios Paediatric Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (PAQLQ)20–22 y Paediatric Asthma Caregiver's Quality of Life Questionnaire (PACQLQ)23, respectivamente (Anexo B y C, disponible en la versión electrónica). El PAQLQ se compone de 23 ítems estructurados en tres dominios: actividades (5 ítems), emociones (8 ítems) y síntomas (10 ítems). Para la dimensión de actividades se empleó la versión de ítems individualizados mediante la lista estandarizada de actividades21,22. El PACQLQ consta de 13 ítems que se configuran en dos dimensiones: emociones (9 ítems) y actividades (4 ítems). El resultado en ambos cuestionarios se expresa en forma de puntuación media que puede oscilar entre 1 (máxima limitación) y 7 puntos (ausencia de limitación).
Las pruebas cumplimentadas por los niños fueron recogidas mediante una entrevista personal realizada por un único evaluador previamente entrenado y una escala visual analógica. Con los cuidadores se empleó un formato autoadministrado.
La distribución de los datos indicó la utilización de pruebas no paramétricas. Mediante el test de Kruskal-Wallis se compararon las puntuaciones de la calidad de vida en tres grupos de pacientes (niveles bajo, medio y alto de autoeficacia) obtenidos mediante terciles. Para evaluar las posibles diferencias entre dos grupos se usó el test U de Mann-Whitney. El nivel de significación estadística se asumió en p-valor inferior a 0,05 en todas las pruebas.
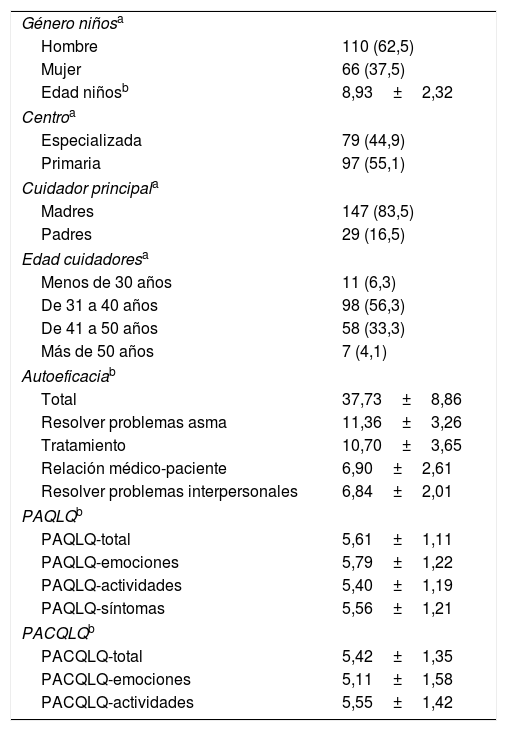
ResultadosSe identificó un total de 217 pacientes elegibles, aunque 41 fueron excluidos (35 no pudieron ser localizados, 4 rechazaron participar y 2 no poseían suficiente conocimiento del idioma). La muestra final estuvo compuesta por 176 niños y sus respectivos cuidadores. Las características de la muestra se pueden consultar en la tabla 1. Se observó una mayor proporción de pacientes varones (62,5%) y de madres (83,5%) como cuidador principal.
Características de la muestra
| Género niñosa | |
| Hombre | 110 (62,5) |
| Mujer | 66 (37,5) |
| Edad niñosb | 8,93±2,32 |
| Centroa | |
| Especializada | 79 (44,9) |
| Primaria | 97 (55,1) |
| Cuidador principala | |
| Madres | 147 (83,5) |
| Padres | 29 (16,5) |
| Edad cuidadoresa | |
| Menos de 30 años | 11 (6,3) |
| De 31 a 40 años | 98 (56,3) |
| De 41 a 50 años | 58 (33,3) |
| Más de 50 años | 7 (4,1) |
| Autoeficaciab | |
| Total | 37,73±8,86 |
| Resolver problemas asma | 11,36±3,26 |
| Tratamiento | 10,70±3,65 |
| Relación médico-paciente | 6,90±2,61 |
| Resolver problemas interpersonales | 6,84±2,01 |
| PAQLQb | |
| PAQLQ-total | 5,61±1,11 |
| PAQLQ-emociones | 5,79±1,22 |
| PAQLQ-actividades | 5,40±1,19 |
| PAQLQ-síntomas | 5,56±1,21 |
| PACQLQb | |
| PACQLQ-total | 5,42±1,35 |
| PACQLQ-emociones | 5,11±1,58 |
| PACQLQ-actividades | 5,55±1,42 |
Según los resultados en la escala de autoeficacia, solo el 37,9% de los niños declaró sentirse seguro/muy seguro con su capacidad para manejar el asma. En las dimensiones de la autoeficacia, el 48,9% se mostró seguro/muy seguro con sus habilidades para resolver problemas relacionados con el asma, el 42,7% en la autoeficacia para el tratamiento y el 39,2% en la relación médico-paciente, siendo la autoeficacia para la resolución de problemas interpersonales la dimensión en la que los niños se juzgaron como más competentes, con un 73,9% de los casos.
Respecto a la calidad de vida, se encontró que el 95,5% de los niños refería tener limitaciones como consecuencia de su asma con puntuaciones inferiores a 7 puntos según PAQLQ total, valor que indica ausencia de limitación. El porcentaje de afectados en las dimensiones PAQLQ actividades, emociones y síntomas fue del 87,5%, el 84,7% y del 92%, respectivamente. Las actividades de la lista que resultaron más limitadas fueron correr (92 elecciones) y jugar al fútbol (53 elecciones). La calidad de vida de los cuidadores también se mostró alterada con resultados inferiores a 7 puntos en el 86,4% de los casos según PACQLQ total, el 77,3% en PACQLQ actividades y el 82,4% en PACQLQ emociones.
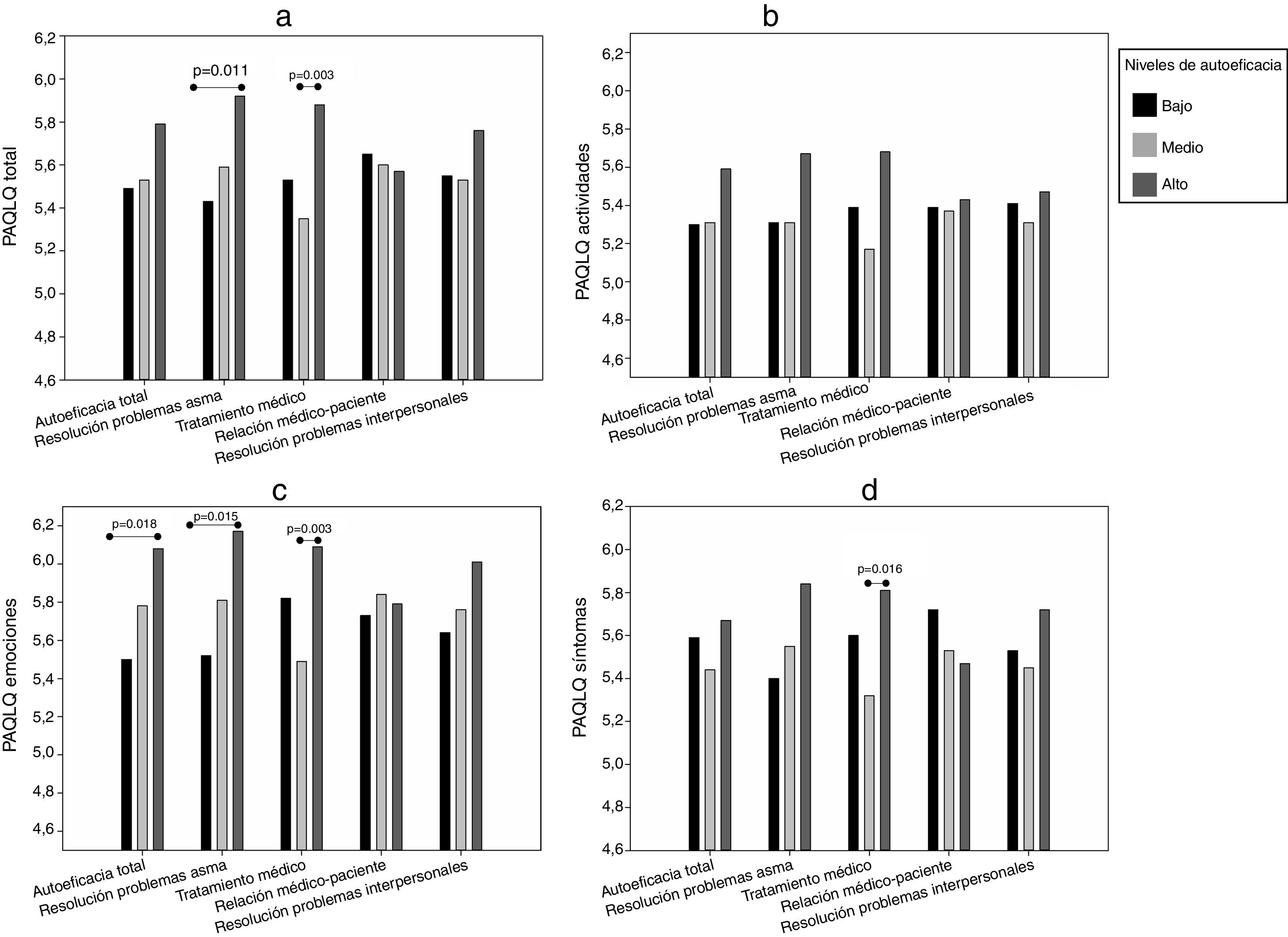
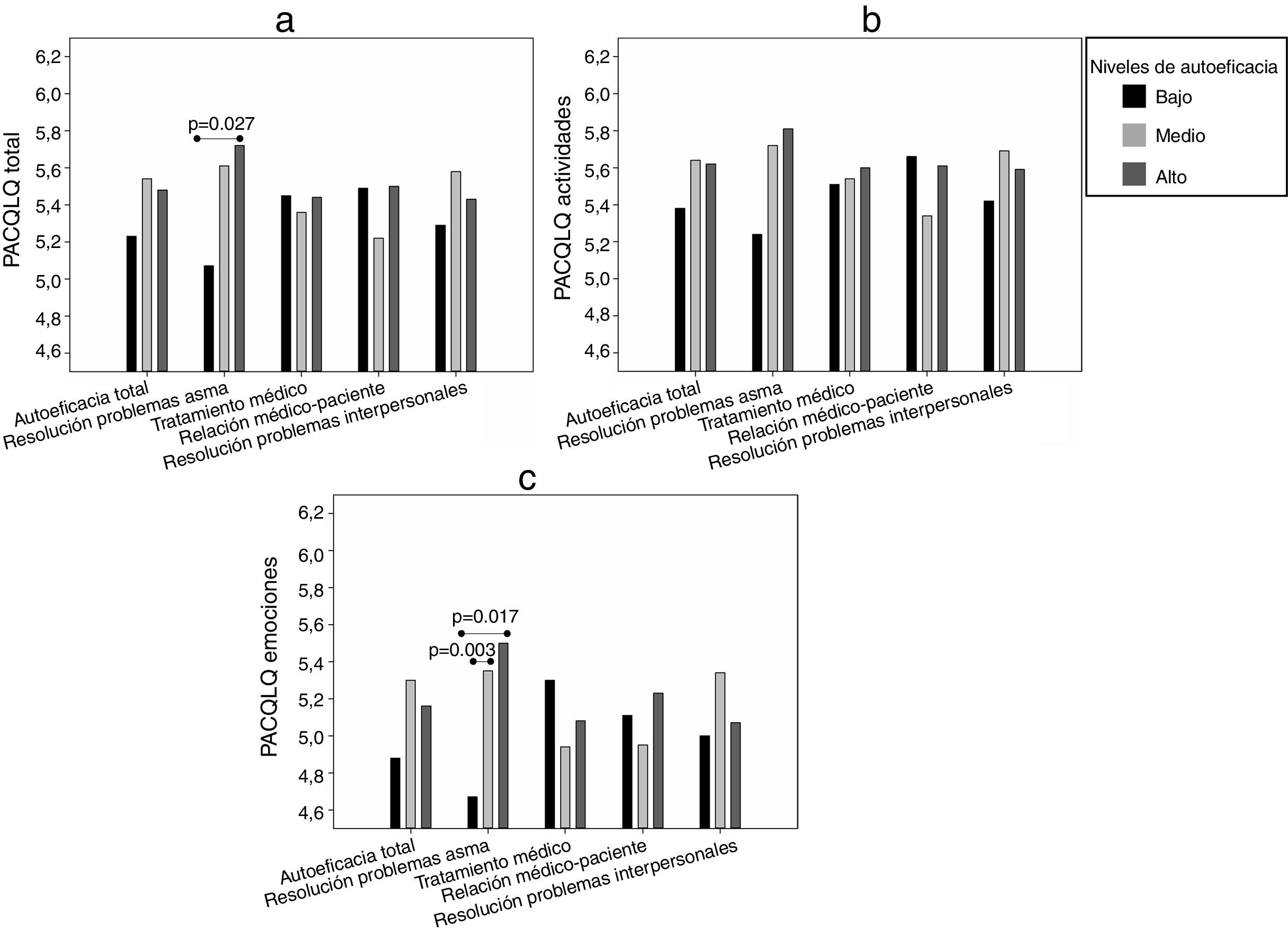
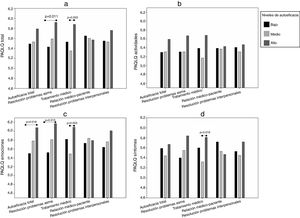
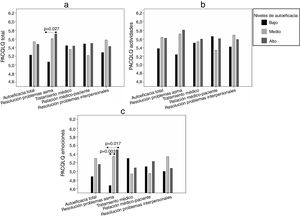
Para el análisis de la calidad de vida en relación con la autoeficacia se identificaron tres grupos de pacientes con distinto nivel de autoeficacia (bajo, medio y alto) para el total de la escala y sus dimensiones. En la tabla 2 se muestra la puntuación de corte que definió a cada grupo, su tamaño y puntuaciones medias. Se observó que, en la mayoría de las dimensiones, el grupo de alta autoeficacia presentaba puntuaciones medias más elevadas en su calidad de vida (fig. 1) y en la de sus cuidadores (fig. 2), aunque los resultados no fueron significativos para los análisis en el resto de dimensiones.
Nivel de autoeficacia: puntuación media y tamaño de los grupos según puntuación de corte
| Nivel de autoeficacia | Rango puntuación originala | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bajo | Medio | Alto | ||||||||
| Puntuaciónb | n | M ± DE | Puntuaciónb | n | M ± DE | Puntuaciónb | n | M ± DE | ||
| Total | ≤34 | 59 (33,5%) | 28,44±4,58 | ˃34 ≤40 | 59 (33,5%) | 37,41±1,7 | ˃40 | 58 (33%) | 47,50±5,5 | 0-60 |
| Resolver problemas asma | ≤10 | 72 (40,91%) | 8,25±1,83 | ˃10 ≤13 | 59 (33,52%) | 11,98±0,77 | ˃13 | 45 (25,57%) | 15,53±1,39 | 0-18 |
| Tratamiento | ≤9 | 64 (36,36%) | 6,92±2,13 | ˃9 ≤12 | 61 (34,66%) | 11,05±0,86 | ˃12 | 51 (28,98%) | 15,04±1,5 | 0-18 |
| Relación médico-paciente | ˂6 | 55 (31,25%) | 3,91±1,17 | ≥6 ˂8 | 52 (29,55%) | 6,56±0,50 | ≥8 | 63 (39,20%) | 9,54±1,37 | 0-12 |
| Resolver problemas interpersonales | ≤6 | 75 (42,61%) | 4,83±1,24 | ˃6 ≤8 | 48 (27,27%) | 7,60±0,49 | ˃8 | 53 (30,12%) | 9±0 | 0-9 |
En los niños, los resultados en PAQLQ total (fig. 1a) fueron significativos para las dimensiones de la autoeficacia en las habilidades para resolver problemas con el asma (p=0,044) y autoeficacia para el tratamiento (p=0,012). En cuanto a los dominios específicos del cuestionario, PAQLQ actividades (fig. 1b) no mostró relación con la autoeficacia, aunque esta resultó casi significativa con la dimensión de la autoeficacia para el tratamiento (p=0,053). El PAQLQ emociones (fig. 1c) fue el dominio más relacionado con el nivel de autoeficacia en las dimensiones de habilidades para resolver problemas con el asma (p=0,013) y tratamiento (p=0,008), así como con la autoeficacia total (p=0,042); en la autoeficacia para resolver problemas interpersonales los análisis parecían indicar algún tipo de relación, pero esta resultó ser estadísticamente no significativa (p=0,060). Los resultados para PAQLQ síntomas (fig. 1d) también mostraron una relación significativa con la autoeficacia para el tratamiento (p=0,049).
Al comparar la calidad de vida (PAQLQ total y PAQLQ emociones) según el nivel de autoeficacia en las habilidades para resolver problemas relacionados con el asma y el nivel de autoeficacia total, se encontraron diferencias significativas entre los niveles bajo y alto (fig. 1a y 1c); mientras que en los dominios de calidad de vida asociados a la autoeficacia para el tratamiento, las diferencias se hallaron entre los niveles medio y alto (fig. 1a, 1c y 1d).
Para los cuidadores, los resultados en PACQLQ total (fig. 2a) indicaron una asociación significativa con la dimensión de la autoeficacia en las habilidades para resolver problemas relacionados con el asma (p=0,046). El dominio de actividades (fig. 2b) no mostró resultados significativos con la autoeficacia, aunque sí fueron encontrados entre PACQLQ emociones (fig. 2c) y la autoeficacia en las habilidades para resolver problemas relacionados con el asma (p=0,026).
Al analizar las medias de PACQLQ total según el nivel de autoeficacia en las habilidades para resolver problemas relacionados con el asma (fig. 2a), se encontraron diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre los niveles bajo y alto. En PACQLQ emociones las diferencias en la calidad de vida fueron significativas al comparar el nivel bajo con los niveles medio y alto (fig. 2c).
DiscusiónEl asma tiene un gran impacto en la calidad de vida provocando limitaciones en torno al 90% de los niños y cuidadores de nuestro estudio. Este elevado porcentaje puede ser un indicador de asma no controlado en aquellos casos que presentan puntaciones inferiores a 6,2 en PAQLQ, punto de corte establecido por Nordlund et al.24, capaz de discriminar la falta de control del asma a través de la calidad de vida. En nuestra muestra, esta puntuación se presenta en el 63,1% de los niños (46,6% nivel bajo-medio de autoeficacia vs. 16,5% nivel alto; p=0,0001; datos no mostrados). También la gravedad es un elemento que puede explicar este impacto del asma, sobre todo en los cuidadores, ya que cuanto mayor es la gravedad, peor es la calidad de vida de estos7.
Sin embargo, la calidad de vida está multideterminada y como ponen de manifiesto los resultados de este estudio, la autoeficacia desempeña un papel relevante.
Aunque no es frecuente encontrar una elevada autoeficacia en niños con asma25–27, en nuestro estudio cerca del 40% de los pacientes declaran sentirse seguros o muy seguros con su capacidad para manejar el asma. La autoeficacia no es un proceso único y estable, sino un mecanismo en el que se pueden identificar distintos niveles y dominios19. Este carácter específico también se ha encontrado en nuestro estudio, ya que solo dos de sus dimensiones se muestran asociadas con la calidad de vida.
En el caso de los niños, la dimensión PAQLQ actividades es la que presenta un mayor deterioro, mostrando resultados congruentes con los obtenidos por otros autores21,22,24,28,29.
Entre las actividades que componen la lista estandarizada, las que resultan más limitadas para la mayoría de nuestros niños, como correr y jugar a fútbol, también son similares a las encontradas en la literatura30. Este deterioro puede deberse a una falta de control del asma, ya que la presencia de síntomas y exacerbaciones frecuentes perjudica que los niños puedan realizar con normalidad actividades como asistir a la escuela, practicar deporte o dormir4,31. Además, las creencias erróneas sobre el ejercicio físico en niños con asma pueden hacer que muchos cuidadores sean sobreprotectores y opten por restringir la práctica de una actividad e incluso que los propios menores se abstengan de realizarla32. Aunque aquellos niños con un alto nivel de autoeficacia para el tratamiento tienen menos limitaciones, no se han encontrado diferencias significativas con los otros grupos.
Los mejores resultados se han obtenido en PAQLQ emociones, dominio que se ha mostrado claramente relacionado con la autoeficacia. Estar muy seguro en las habilidades para resolver problemas relacionados con el asma, como saber si una crisis puede empeorar o alejarse de elementos desencadenantes, tiene un efecto positivo sobre el estado emocional, hecho que ya ha sido demostrado por estudios realizados en adultos33.
Un alto nivel de autoeficacia para el tratamiento también tiene un gran impacto en la calidad de vida de los niños. Los hallazgos para PAQLQ emociones y PAQLQ síntomas muestran que los niños con más autoeficacia son los que mejor calidad de vida tienen, aunque aquellos que se sienten inseguros con su capacidad para tomar decisiones acerca de la medicación y su administración, poseen una calidad de vida superior que los tienen en un nivel medio de autoeficacia. Estos resultados podrían deberse a características relacionadas con el desarrollo de la autoeficacia en este dominio, ya que una de sus principales fuentes es la experiencia. Inicialmente, las competencias del cuidado de niños con asma son asumidas por los cuidadores, para posteriormente ser transferidas al niño34. Es posible que los niños de nuestro estudio con una baja autoeficacia para el tratamiento todavía no hayan tenido oportunidad de tomar decisiones en cuanto a su medicación, estando inseguros de sus capacidades para gestionarla, pero posiblemente seguros de que sus cuidadores son capaces de hacerlo, por lo que tienen una mayor calidad de vida emocional y un menor impacto de los síntomas; mientras que aquellos que tienen un nivel medio, se encuentran inmersos en el desarrollo de estas destrezas, afectando así a su bienestar.
Respecto a los cuidadores, los resultados obtenidos son similares a los encontrados en otras muestras7,11,35,36. En nuestro estudio, el dominio más limitado es PACQLQ emociones, aunque la autoeficacia en las habilidades para resolver problemas con el asma modula este impacto. En este sentido, la supervisión permanente del niño puede conducir a una falta de independencia para ambos con consecuencias negativas tanto para el desarrollo psicosocial del niño como para la calidad de vida del cuidador. Que los niños sientan seguridad en su capacidad para identificar y manejar situaciones problemáticas del asma, muchas de las cuales se pueden dar en momentos en los que no van a estar presentes los cuidadores, puede hacer que estos se sientan menos preocupados y/o frustrados.
Siendo el primer estudio publicado en nuestro medio que examina la relación entre la autoeficacia y la calidad de vida en población pediátrica con asma, la originalidad de este radica en considerar este análisis desde la perspectiva del niño, evaluando el impacto de su propia autoeficacia. Asimismo, la muestra del estudio compuesta por niños y cuidadores proporciona una imagen más completa de las repercusiones de la enfermedad y reafirma la capacidad de los niños para informar sobre su propia salud37–39.
Nuestros hallazgos subrayan la importancia de la autoeficacia en el automanejo del asma, con importantes aplicaciones en términos de investigación y práctica clínica. La medición de la autoeficacia permite detectar a aquellos pacientes en riesgo que precisen de una intervención para mejorar su calidad de vida, por lo que se propone incorporar a la autoeficacia como un componente más de las intervenciones educativas destinadas a alcanzar la calidad de vida diana del paciente y su familia.
A pesar de estas ventajas, nuestro estudio también cuenta con algunas limitaciones. Además de las dificultades asociadas al uso de PROM2,40, un posible sesgo podría ser la utilización del PAQLQ en niños de 6 años. Aunque algunos han encontrado problemas al utilizar el instrumento en menores de 7 años22,28, en nuestro estudio estos han podido quedar solventados por la administración de la prueba mediante un entrevistador experimentado y el uso de una escala visual analógica como apoyo en las respuestas. Asimismo, el diseño de tipo transversal empleado no permite establecer relaciones de causalidad entre las variables, por lo que se recomiendan futuros estudios longitudinales que incluyan otros determinantes de la calidad de vida que puedan afectar a la estabilidad de las relaciones encontradas.
No obstante, consideramos que el nivel de autoeficacia de los niños puede modular el impacto que el asma tiene en su calidad de vida y en la de sus cuidadores. Sentirse seguros de su capacidad para manejar el asma, facilita la percepción de bienestar y alivia la carga del cuidador lo que redunda en una mejor calidad de vida para ambos.
En conclusión, un alto nivel de autoeficacia se asocia a una mejor calidad de vida de los niños y sus cuidadores. Basándonos en estos resultados, la medida de la autoeficacia podría ser incorporada en la evaluación de las intervenciones educativas en automanejo.
Conflicto de interesesLos autores declaran no tener ningún conflicto de intereses.
Los autores agradecemos la ayuda del personal sanitario de la Unidad de Neumología Pediátrica del Hospital Universitario Los Arcos del Mar Menor y el interés de todos los niños y cuidadores en participar en este estudio.