La fibroelastosis pleuropulmonar (FEPP) es una entidad rara que ha sido recientemente incluida en el último consenso internacional multidisciplinar sobre neumonías intersticiales idiopáticas. Comparte rasgos clínicos con otras neumonías intersticiales crónicas (disnea de esfuerzo, tos seca, entre otros), y radiológicamente se caracteriza por afectación pleural y pulmonar de predominio en lóbulos superiores. Sus principales hallazgos histológicos incluyen fibrosis de la pleura visceral con prominente fibroelastosis subpleural y parenquimatosa. El conocimiento de sus características se basa en el creciente número de casos descritos en la literatura, por lo cual se desconocen varios aspectos sobre su etiología, patogénesis e historia natural. Aunque algunos casos han sido identificados como idiopáticos, la FEPP ha sido asociada como complicación tras el trasplante de médula ósea, trasplante pulmonar y tratamiento con quimioterapia, especialmente con agentes alquilantes. El neumotórax espontáneo o iatrogénico tras las pruebas invasivas para su diagnóstico es una complicación frecuentemente comunicada. La evolución descrita de la FEPP es variable, desde lentamente progresiva hasta casos con rápido deterioro clínico. No hay ningún tratamiento con evidencia de eficacia, y el trasplante pulmonar se erige como la única opción en aquellos pacientes que cumplan los criterios. El reconocimiento y difusión de las características de esta entidad son fundamentales para elevar el grado de sospecha clínica y permitir un adecuado manejo diagnóstico por parte del equipo multidisciplinar.
Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis (PPFE) is a rare disease that has been recently included in the updated consensus on idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. It shares some clinical features with other chronic interstitial pneumonias (dyspnea, dry cough), and is radiologically characterized by pleural and subpleural parenchymal fibrosis and elastosis, mainly in the upper lobes. The main histological findings include pleural fibrosis and prominent subpleural and parenchymal fibroelastosis. Its characterization is based on the increasing number of cases reported in the literature, so several aspects of the etiology, pathogenesis and natural history are still unknown. Although some cases have been described as idiopathic, PPFE has been reported as a complication after bone marrow transplantation, lung transplantation and chemotherapy, especially with alkylating agents.Spontaneous or iatrogenic pneumothorax is a frequently reported complication of invasive diagnostic tests for identifying PPFE. The disease course is variable, ranging from slow progression to rapid clinical deterioration. No treatment has shown evidence of efficacy, and lung transplantation remains the only option for patients who fulfill the diagnostic criteria for this option. Recognizing and disseminating the specific features of PPFE is essential to raise the level of clinical suspicion for this entity, and to implement appropriate multidisciplinary diagnostic management.
La fibroelastosis pleuropulmonar (FEPP) es una entidad clínico patológica incluida dentro del grupo de la neumonías intersticiales idiopáticas (NII) raras en la última clasificación de la American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society1. Existen series de casos descritos de fibrosis pulmonar en lóbulos superiores (enfermedad de Amitani) con características similares a la FEPP publicados a principios de la década de los 90, especialmente en la literatura no inglesa2,3. Sin embargo, su caracterización oficial fue realizada en 2004 por Frankel et al.4, quienes describieron los hallazgos clínicos radiológicos e histológicos en una serie de 5 pacientes y propusieron la FEPP como una entidad diferenciada dentro de las enfermedades pulmonares intersticiales difusas (EPID). Desde entonces han sido publicados aproximadamente un centenar de casos en la literatura que han permitido ampliar el conocimiento acerca de las particularidades de la enfermedad5–24. Esta se caracteriza por la afectación pleural y parenquimatosa de predominio en los lóbulos superiores, con fibrosis pleural y fibroelastosis subpleural. El neumotórax es una complicación frecuentemente descrita en estos pacientes, siendo en algunos casos la primera manifestación de la enfermedad2,8,21. Su etiología es desconocida, sin embargo existe un creciente interés científico por su identificación en pacientes trasplantados de médula ósea, de pulmón y tras tratamiento con quimioterapia. También se ha relacionado con infecciones pulmonares recurrentes, con trastornos inmunitarios, así como también han sido comunicados casos familiares7,11.
En la presente revisión se discutirán los aspectos más relevantes de FEPP, con énfasis en los criterios diagnósticos propuestos. Asimismo, se comentará brevemente las nuevas hipótesis fisiopatológicas que consideran que esta entidad puede ser la respuesta final a diferentes insultos pulmonares, y que puede constituir un nuevo fenotipo patológico dentro del espectro de ciertos trastornos, como la disfunción crónica del injerto pulmonar.
Características epidemiológicas y entidades asociadasSegún la información obtenida de los casos comunicados en la literatura, la edad de inicio de la FEPP comprende un amplio rango de edad. Es una entidad que afecta con mayor frecuencia a adultos jóvenes (tercera a cuarta década de la vida), con una media de edad de 57 años25,26. No existe un claro predominio de género.
El tabaquismo no parece ser un factor de riesgo para el desarrollo de esta enfermedad. En cambio, la exposición al asbesto o aluminio y antígenos aviares sí son antecedentes que se han recogido en algunas series2,7,11.
Una asociación descrita con frecuencia con la FEPP ha sido el antecedente de tratamiento oncológico previo con radioterapia y quimioterapia, especialmente con agentes alquilantes como la ciclofosfamida o la nitrosurea20,27,28. El intervalo de desarrollo de la FEPP posterior a la administración de estos tratamientos presenta gran variabilidad en los casos publicados, desde 6 meses hasta los 16 años28.
Varias series han descrito la FEPP como complicación tras el trasplante de médula ósea y el trasplante de pulmón8,10,11,13,16,23,24. En algunos de estos casos se ha comunicado la coexistencia de focos de bronquiolitis obliterante (BO) o de daño alveolar difuso. Algunos autores postulan que esta última lesión puede preceder a la FEPP10,24,26. También se ha especulado que la FEPP puede formar parte del espectro de manifestaciones del rechazo crónico pulmonar como un fenotipo restrictivo, funcional e histológicamente diferente al clásico síndrome de BO. Este último se caracteriza por por un descenso irreversible en el volumen espiratorio en el primer segundo (FEV1) y obliteración fibrótica de la pequeña vía aérea de los pulmones trasplantados. Cuando el rechazo se acompaña de los cambios histológicos de la FEPP, además de la caída del FEV1 se presenta una disminución de la capacidad vital forzada (FVC) y de la capacidad pulmonar total (CPT), siendo de peor pronóstico que el síndrome de BO10,24,26.
Esta asociación también implica un potencial trasfondo autoinmune en su patogénesis. Títulos altos de anticuerpos antinucleares y de factor reumatoide se han observado en algunas series4,11, así como la coexistencia de enfermedades autoinmunes como la espondilitis anquilopoyética o colitis ulcerosa, entre otras3.
Pacientes con historia familiar de EPID han sido publicados tanto en la serie de Frankel et al.4 como en la realizada por Reddy et al.11. El antecedente en algunos casos de infecciones respiratorias recurrentes previas al diagnóstico de la FEPP ha llevado a plantear la hipótesis de que la inflamación repetida puede ser otro factor que predisponga a su desarrollo11–13. El resumen de las entidades asociadas a la FEPP se muestra en la tabla 1.
Entidades asociadas a FEPP
| FEPP idiopática |
| Trasplante médula ósea |
| Quimioterapia |
| Trasplante pulmonar |
| Radioterapia |
| Infecciones de tracto respiratorio: bronquitis a repetición, Aspergillus, MAI |
| Enfermedades autoinmunes: EA, colitis ulcerosa, psoriasis, AR |
| Exposición laboral: asbesto, aluminio |
| Neumonitis por hipersensibilidad |
| FEPP familiar |
AR: artritis reumatoide; EA: espondilitis anquilopoyética; FEPP: fibroelastosis pleuropulmonar; MAI: Mycobacterium avium intracelular.
Modificada de: Watanabe3.
La presentación más habitual es la disnea de esfuerzo y la tos seca de aparición insidiosa. La pérdida de peso también es un síntoma frecuentemente referido.
La presencia de dolor pleurítico puede ser secundaria a un neumotórax espontáneo y puede ser el primer síntoma en algunos pacientes. Se puede decir que el neumotórax es una complicación característica en la historia natural de la FEPP. Esta alteración puede ser secundaria a los cambios parenquimatosos, como los quistes en los ápices fibrosos, la reacción pleural alterada por el estrés friccional o la hipovascularización en la zona afectada26,28. La reabsorción espontánea del neumotórax es infrecuente en la FEPP, además, la fuga persistente tras su tratamiento y una reexpansión lenta del pulmón afectado es un hecho común8,21,28. El neumotórax iatrogénico también puede presentarse tras la biopsia quirúrgica.
Las acropaquias y los crepitantes secos en velcro son hallazgos mucho menos frecuentes en estos pacientes, comparados con los pacientes con otras NII como la fibrosis pulmonar idiopática (FPI)3.
La deformidad de la caja torácica o «tórax aplanado» (debida a una disminución entre el diámetro anteroposterior y el diámetro transverso del tórax) es un signo clínico común, y es un indicador de progresión de la enfermedad3,28–30. Existen diversas series asiáticas que describen un índice de masa corporal bajo o en el límite inferior de la normalidad, característica que denominan slender stature3,9,12,29.
Características funcionalesEl patrón ventilatorio restrictivo es similar al de la FPI; se presenta con una relación FEV1/FVC aumentada y una disminución de la FVC y de la CPT. Sin embargo, también se observa un aumento de la relación entre el volumen residual (VR) y la CPT. Este rasgo funcional particular se deriva del colapso por la fibrosis de los lóbulos superiores, que puede conllevar a una hipersinsuflación compensatoria en los lóbulos inferiores3,9. La difusión alveolar (DLco) se encuentra reducida y el cociente con el volumen alveolar (DLco/VA) puede estar normal o discretamente disminuido. La hipoxemia arterial y la hipercapnia aparecen conforme la enfermedad progresa. Watanabe et al.12 describieron una rápida caída anual de la FVC en 7 pacientes con una media de declive del 20%. La caída acelerada de la FVC también ha sido un hallazgo remarcable en otra serie asiática recientemente descrita de 12 pacientes29. Este dato parece indicar que la evolución de la FEPP tiene una mayor tendencia hacia la progresión rápida.
Características radiológicasLos hallazgos radiológicos de la FEPP pueden ser fundamentales en el diagnóstico de sospecha de esta entidad. En la radiografía de tórax el hallazgo más frecuente es el engrosamiento pleural irregular apical bilateral en la fase inicial de la enfermedad; este hallazgo puede observarse incidentalmente en pacientes aún asintomáticos3, y fácilmente pasa inadvertido al confundirse con casquetes apicales.
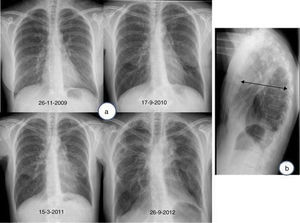
Posteriormente, aparece una retracción hiliar ascendente y elevación diafragmática que traduce una pérdida de volumen pulmonar a expensas de los lóbulos superiores (fig. 1 A). Un hallazgo característico de la FEPP es el «aplanamiento» de la caja torácica acorde al signo observado en la exploración clínica. Este hallazgo puede apreciarse en la proyección lateral, y se traduce por una marcada disminución del diámetro antero-posterior de la caja torácica3 (fig. 1B). A medida que progresa la enfermedad se pueden apreciar opacidades reticulares y nodulares subpleurales en los lóbulos superiores4. Estas alteraciones inicialmente respetan los otros lóbulos pulmonares. Durante la evolución pueden aparecer signos de fibrosis con pérdida de volumen pulmonar, aparición de bullas o quistes en los lóbulos superiores y, además, los cambios fibróticos pueden extenderse a los lóbulos adyacentes3,11.
a) Radiografía de tórax (proyección postero-anterior): Evolución de un caso de fibroelastosis pleuropulmonar, caracterizada por una pérdida progresiva de volumen pulmonar a expensas de los lóbulos superiores, con una retracción ascendente de ambos hilios, así como por engrosamientos pleurales biapicales. b) Radiografía de tórax (proyección lateral): aplanamiento de la caja torácica; obsérvese la disminución del diámetro anteroposterior de la caja torácica (flecha) en relación con el diámetro cráneo-caudal.
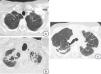
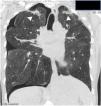
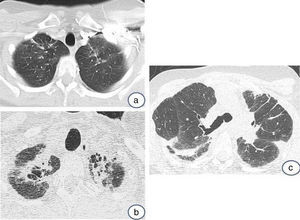
En la tomografía computarizada de alta resolución (TCAR) se observan engrosamientos pleurales prominentes, asociados a signos de fibrosis (bronquiectasias de tracción, distorsión de la arquitectura pulmonar, pérdida de volumen), reticulación, más marcada en los lóbulos superiores7,9,11 (fig. 2A). A medida que la enfermedad progresa las opacidades reticulares y los signos de fibrosis se extienden al resto de los campos pulmonares (fig. 2B). En contraste con los hallazgos mucho más pronunciados en los campos superiores y medios, los cambios radiológicos en las bases pulmonares son leves o mínimos, e incluso pueden encontrarse ausentes (fig. 2C).
Tomografía axial computarizada de alta resolución (TCAR):Evolución del caso anterior en un intervalo de 2 años y dos meses. En la imagen superior (a), únicamente aparecen unas muy discretas opacidades alargadas en ambos vértices pulmonares; en la imagen inferior (b), se observa perdida de volumen e infiltrados pleuro- parenquimatosos de aspecto fibrótico. En la figura 2c se muestra una imagen de TCAR en un corte a la altura de la carina traqueal. Se muestra distorsión de la arquitectura pulmonar, con presencia de engrosamientos pleurales y opacidades parenquimatosas alargadas por fibrosis (ventana pulmonar).
En la serie de 12 pacientes descritos por Reddy et al.11 los hallazgos de TCAR mostraron cambios de fibrosis en regiones alejadas de los engrosamientos pleuro-parenquimatosos, simulando un patrón de posible neumonía intersticial usual (NIU) o de neumonía intersticial no específica. Además, en los estudios radiológicos de seguimiento disponibles en 6 pacientes, 5 mostraron estabilidad o leve progresión de los cambios pleuro-parenquimatosos, mientras que en un paciente se observó marcada progresión de los signos de fibrosis.
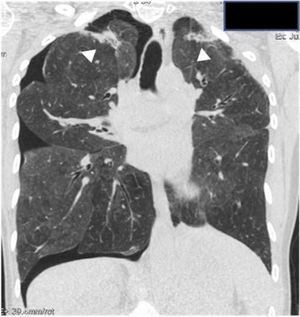
El neumotórax puede complicar el curso de la enfermedad y ser recurrente (fig. 3). Puede ser espontáneo o iatrogénico después de procedimientos intervencionistas o quirúrgicos, y de difícil tratamiento debido a la presencia de fístulas bronco-pleurales, probablemente secundarias a una capacidad limitada de curación del tejido pulmonar dañado6.
El diagnóstico radiológico diferencial se realiza con aquellas entidades que afectan predominantemente los lóbulos superiores, como la sarcoidosis en estadio avanzado con fibrosis, la fibrosis posradioterapia y el casquete apical. Esta última entidad afecta a pacientes ancianos con historia de tabaquismo y no suele presentar empeoramiento evolutivo ni funcional ni radiológico26. Por otra parte, los casquetes apicales están localizados en los vértices pulmonares, mientras que la FEPP, aunque de predominio en los campos superiores, tiene una distribución subpleural más difusa8.
Características histológicasLa similitud de las características histológicas y radiológicas descritas en los casos de FEPP han servido como base para proponer una serie de criterios para establecer un patrón «definitivo» y otro como «consistente» con FEPP11,24,26 (tabla 2).
Criterios diagnósticos de fibroelastosis pleuropulmonar (FEPP)
| Patrón definitivo | Patrón consistente | |
|---|---|---|
| Criterios radiológicos por TCAR | Engrosamiento pleural en lóbulos superiores, con ausencia o menor afectación de lóbulos inferiores | Engrosamiento pleural en lóbulos superiores, pero distribución de los cambios radiológicos no concentrado en lóbulos superiores o hallazgos típicos de otra EPID coexistente (en cualquier localización) |
| Criterios histopatológicos | Fibrosis de pleura visceral en lóbulos superiores con marcada y homogénea fibrosis intraalveolar con elastosis alveolar/septal (>80% de fibras elásticas) | Fibrosis intra-alveolar pero no asociada con fibrosis subpleural llamativa o no predominantemente debajo de la pleura o no en biopsia de lóbulos superiores |
| Parénquima preservado distal a la pleura | ||
| Presencia de infiltrado linfoplasmocitario desigual | ||
| Presencia de algunos focos fibrobásticos |
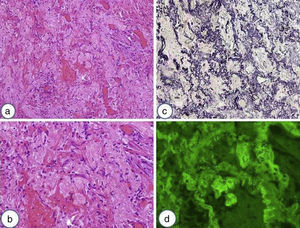
Los hallazgos histológicos más relevantes de la FEPP son la fibrosis de la pleura visceral y fibroelastosis subpleural y parenquimatosa. Esta se extiende a las paredes alveolares adyacentes, con deposición de colágeno, predominantemente en los lóbulos superiores (fig. 4). Sin embargo, hay casos descritos en donde el hallazgo del engrosamiento pleural está ausente11,17,28,29. La transición entre las lesiones y el parénquima normal suele ser abrupta. Pueden existir pocos focos fibroblásticos y una cantidad variable de infiltrado linfocitario. La elastosis no es un hallazgo histológico exclusivo de la FEPP, ya que lo pueden presentar otras NII. Sin embargo, en un estudio en el cual comparaban la cantidad de fibras elásticas entre un grupo de pacientes con FPI y otro con FEPP, se observó que estos últimos presentaban una cantidad significativamente más elevada de fibras elásticas19. Otra particularidad histológica descrita es que la FEPP puede coexistir con otros patrones de EPID (NIU, neumonía intersticial no específica, neumonitis por hipersensibilidad, inclusive con patrón de neumonía intersticial no clasificable) como se ha comentado previamente10,11,26,29. Recientemente, Oda et al.17 demostraron que los pacientes con FEPP y coexistencia de NIU presentaban peor supervivencia.
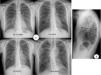
Biopsia quirúrgica de lóbulo superior derecho de una paciente mujer de 40 años con el diagnóstico de fibroelastosis pleuropulmonar. a) Las estructuras alveolares estan completamente obliteradas debido a la acumulación de material elastótico en la pared (tinción de hematoxilina-eosina). b) Se muestran estos cambios con mayor aumento y se observa la presencia de muy escaso infiltrado linfocitario. c) Mediante la tinción para fibras elásticas de Van Gieson se relata el contenido elastóstico de la pared y se observa que la luz alveolar está sustituida por tejido conectivo laxo. d) Mediante la autofluorescencia se puede apreciar la presencia de numerosas fibras elásticas en el mismo campo de la imagen 4b.
Como se ha comentado en apartados anteriores, la presencia concurrente de BO y de daño alveolar difuso reportada en algunos casos de pacientes trasplantados de pulmón hace pensar que la FEPP pueda manifestarse como una complicación tardía de la enfermedad de injerto contra huésped10,24,31–35.
No se ha descrito ningún patrón característico en el lavado broncoalveolar.
Pronóstico y tratamientoLos datos procedentes de los casos publicados acerca del pronóstico de la FEPP son heterogéneos: mientras que en algunos casos se describe una evolución lentamente progresiva, en otros existe rápido deterioro clínico2,11,25,29. Como en otras NII, el curso evolutivo depende en parte del momento en el que se realiza el diagnóstico. De aquí la importancia de difundir sus características para elevar el nivel de sospecha diagnóstica, sobre todo en los grupos de riesgo (por ejemplo en pacientes postrasplantados de pulmón, médula ósea o tratados previamente con quimioterapia). Ha de tenerse en cuenta por parte del equipo multidisciplinar la propensión de estos pacientes a realizar neumotórax. Algunos autores proponen que la familiarización con los hallazgos clínicos y radiológicos podrían evitar la necesidad de biopsia quirúrgica28. Sería intersante analizar la rentabilidad de otras técnicas diagnósticas como la criobiopsia, ya que potencialmente podría minimizar los riesgos y conseguir un adecuado diagnóstico histopatológico.
En la actualidad no existe ningún tratamiento que haya demostrado su eficacia en esta enfermedad. Los pacientes han sido tratados de forma empírica con corticoides, N-acetil cisteína y diversos inmunosupresores, sin evidencia clara de mejoría11,29. La oxigenoterapia está indicada en los casos que desarrollan insuficiencia respiratoria, mientras que el trasplante pulmonar es la opción en los pacientes que cumplan los criterios. Nuestro grupo ha comunicado recientemente un caso trasplantado satisfactoriamente con 24 meses de supervivencia hasta la actualidad (datos no publicados).
Son necesarios estudios multicéntricos, registros internacionales y estudios en modelos animales que puedan ayudar a un mejor conocimiento de la historia natural de la FEPP, de su etiopatogenia y de sus factores desencadenantes. Tal vez de esta forma comprenderíamos que no estamos ante una entidad tan infrecuente como se pensaba inicialmente, a la vez que se podrían establecer estrategias de diagnóstico precoz y opciones adecuadas para su tratamiento.
FinanciaciónKarina Portillo Carroz es beneficiaria de una beca ayuda para la investigación de la Sociedad Española de Neumología y Cirugía Torácica (2013) y de una beca EPID–futuro patrocinada por Roche (2013)
Conflicto de interesesLos autores declaran no tener ningún conflicto de intereses.
Lo autores quieren agradecer a los miembros del Grup d’Estudi Clínic Radiològic i Anatomopatològic de les Malalties Pulmonars Intersticials Difuses (CRAMPID) por su estímulo constante, y a la Dra. María Teresa Fernández Figueras por su valioso apoyo y por la cesión de las imágenes anatomopatológicas.