Home noninvasive ventilation (NIV), targeting a reduction of carbon dioxide with a combination of sufficient inspiratory support and backup-rate improves outcomes in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The aim of this systematic review with individual participant data (IPD) meta-analysis was to evaluate the effects of intensity of home NIV on respiratory outcomes in individuals with slowly progressive neuromuscular (NMD) or chest-wall disorders (CWD).
MethodsControlled, non-controlled and cohort studies indexed between January-2000 and December-2020 were sought from Medline, Embase and the Cochrane Central Register. Outcomes were diurnal PaCO2, PaO2, daily NIV usage, and interface type (PROSPERO-CRD 42021245121). NIV intensity was defined according to the Z-score of the product of pressure support (or tidal volume) and backup-rate.
Results16 eligible studies were identified; we obtained IPD for 7 studies (176 participants: 113-NMD; 63-CWD). The reduction in PaCO2 was greater with higher baseline PaCO2. NIV intensity per se was not associated with improved PaCO2 except in individuals with CWD and the most severe baseline hypercapnia. Similar results were found for PaO2. Daily NIV usage was associated with improvement in gas exchange but not with NIV intensity. No association between NIV intensity and interface type was found.
ConclusionFollowing home NIV initiation in NMD or CWD patients, no relationship was observed between NIV intensity and PaCO2, except in individuals with the most severe CWD. The amount of daily NIV usage, rather than intensity, is key to improving hypoventilation in this population during the first few months after introduction of therapy.
Treatment of chronic respiratory failure with long-term home noninvasive ventilation (NIV) to reduce symptom load and improve survival in patients with slowly progressive neuromuscular and chest wall disorders (NMD, CWD) is part of standard clinical practice.1,2 Guideline criteria for NIV initiation in stable restrictive lung disease is targeted toward relief of symptoms, which is achieved by treating nocturnal hypoventilation and chronic respiratory hypercapnia with home NIV.2–5 Targeted reduction of carbon dioxide is one of the main goals of NIV.6 This implies a combination of sufficient ventilatory support to treat alveolar hypoventilation, and sufficient usage of this treatment.
In chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a common indication for home NIV, the concept of “high-intensity” NIV has led to a paradigm shift over the past decade and is gaining growing consideration.7–11 High-intensity NIV can be defined as a strategy that consists of adjusting ventilator parameters with the specific goal of reducing transcutaneous carbon dioxide (TcCO2) and arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) by setting sufficient levels of pressure support (PS) (or tidal volume, VT) and back-up respiratory rate (BURR).12–15 Current clinical practice guidelines clearly state that NIV should be set with the aim of reducing or normalising PaCO2 levels in individuals with COPD.10,11
However, data suggest that NIV may not always effectively improve PaCO2 levels and reverse hypoventilation-related symptoms.16–18 For instance, 12–40% of individuals with NMD have residual hypercapnia under NIV; furthermore, residual hypercapnia is associated with negative outcomes.19 Despite these findings, the concept of using higher levels of NIV intensity in individuals with NMD and CWD has never really been discussed and deserves to be evaluated.20
Our aim was to determine the extent to which, during the initial period of NIV initiation, the intensity of NIV parameters influences PaCO2 levels in individuals with chronic respiratory failure due to slowly progressive NMD or CWD. Given the small number of studies that have addressed this question, and given the heterogeneity of published data regarding participants’ diagnoses and ventilatory modes used, we undertook a systematic review with meta-analysis of individual participant data (IPD).
MethodsThis systematic review and meta-analysis is reported according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of Individual Participant Data (PRISMA-IPD) statement.21 The study protocol was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO, CRD42021245121: www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/).
Search strategy and selection criteriaRelevant articles indexed between 1 January 2000 and 31 December 2020 were sought in Medline, Embase, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials. Search terms were chosen to identify studies that investigated any NIV-related intervention conducted in adult participants with slowly progressive NMD or CWD. Additional details regarding the search strategy are provided in supplementary material.
Study inclusion criteriaInclusion criteria were pre-defined in the registered study protocol and applied at the study level. They included: (i) controlled or non-controlled trials, and cohort studies that included individuals with slowly progressive NMD or CWD who were naïve to long-term NIV at the time of study enrolment, (ii) studies in which participants were treated either with pressure-cycled or volume-targeted pressure support modes (hybrid modes) and in which NIV settings were reported, (iii) studies with a timeframe of at least 4 weeks, (iv) studies that reported PaCO2 levels at baseline and study endpoint.
Study and data selection processThe titles and abstracts of studies identified from the search were independently screened by two investigators (MD and AL) using www.covidence.org. The selected full-text articles were then reviewed for eligibility by the same investigators and discrepancies were settled by discussion. If consensus could not be reached, a third investigator (J-CB) resolved the disagreement. The corresponding authors of each eligible study were contacted by email and asked if they would accept to share participant data. Authors were asked to complete a standardised datasheet that included the variables listed in Supplementary Tables 1 and 2, and Table 2. No aggregate data were sought.
The risk of bias of the studies included in the meta-analysis of IPD was assessed with the revised Cochrane collaboration risk-of-bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2),22 and with the Newcastle–Ottawa quality assessment scale for cohort studies.23
OutcomesOutcomes were defined a priori in the registered protocol. The primary outcome was diurnal PaCO2 level at study endpoints, as reported by the authors in the published materials. Diurnal PaO2, daily NIV usage, interface type, nocturnal oxygenation and sleep quality at study endpoints were planned to be considered as secondary outcomes.
Deviations from the study protocolAs PS and BURR were the primary interventions evaluated in this review, studies that reported interventions with volume-cycled modes were not planned to be eligible for inclusion. However, two selected studies reported data from participants treated with both pressure-cycled and volume-cycled modes, and individual participant data were provided.24,25 We therefore decided to include these data in the analysis. We processed them together with data from the hybrid modes, in which inspiratory support is also defined by VT. Hence, the level of VT setting, in mL/kg of predicted body weight (VT,PBW),26 was added to the data analysis.
Data synthesis and analysisAll analyses were conducted according to the predefined statistical analysis plan outlined in the protocol. Given the low rate of missing data, we performed a complete case analysis. One outlier with a baseline PaCO2 level>15kPa was excluded from the analysis of PaCO2 and two outliers with a PaO2 level>16kPa at study endpoints were excluded from the analysis of PaO2.
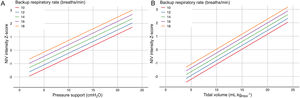
Diurnal PaCO2 level at study endpoints was analysed using a generalised linear mixed model with a random intercept for study. In the base model, baseline PaCO2, daily NIV usage at study endpoints, and disease category (NMD versus CWD) were included as fixed effects. Then, all other variables were tested one by one and included in the final model if p<0.2 and the rate of missing data was<10%. Lastly, the impact of ventilatory parameters (PS, VT and BURR) was tested. We defined NIV intensity as the product of PS and BURR for pressure-cycled modes, and the product of VT and BURR for volume-cycled and hybrid modes. We used the Z-scores of these values to obtain a unified measure of NIV intensity regardless of the NIV mode. By definition, mean NIV intensity of the whole cohort corresponds to a Z-score of 0. We defined the mean – 1SD, mean, mean+1SD, and mean+2SD of NIV intensity Z-scores as low, medium, high and very high NIV intensity. A conversion chart between ventilatory parameters and NIV intensity Z-scores is presented in Fig. 1. Interactions between NIV intensity, disease category and baseline PaCO2 level were also tested.
Values of NIV intensity Z-scores according to backup respiratory rate for pressure-cycled modes (panel A), and for volume-cycled and hybrid modes (panel B). Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) intensity was defined as the product of pressure support (PS) and backup respiratory rate (BURR) for pressure-cycled modes, and of tidal volume (VT) and BURR for volume-cycled and hybrid modes. Z-scores represent the number of standard deviations above or below the mean NIV intensity used in the included studies. For pressure-cycled modes (panel A), the combination of a BURR set at 14breaths/min and a PS set at 10cmH2O corresponds to a Z-score of 0 (medium NIV intensity). The combination of a BURR set at 14breaths/min and a PS set at 20cmH2O corresponds to a Z-score of 2 (very high NIV intensity). For volume-cycled or hybrid modes (panel B), the combination of a BURR set at 18breaths/min and a VT set at 5mLkgPBW−1 corresponds to Z-score of −1 (low NIV intensity). The combination of a BURR set at 18breaths/min and a VT set at 15mLkgPBW−1 corresponds to a Z-score of 1 (high NIV intensity). BURR, backup respiratory rate; NIV, noninvasive ventilation; PS, pressure support.
For secondary outcomes (PaO2 and daily NIV usage), the same approach was used for the construction of the final model. Finally, to investigate the relation between interface type and NIV intensity, we identified NIV intensity as the dependent variable, and we included interface type as a fixed effect in the base model, along with baseline PaCO2 level, disease category and daily NIV usage.
In the final models, the following assumptions were verified: linearity, absence of collinearity in the predictors, homoscedasticity, normality of residuals, absence of influential data points and independence. All statistical analyses were performed with R and Jamovi (Gamjl package), and R packages lmer4 and lmerTest.
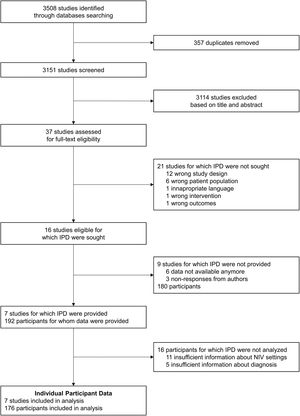
ResultsStudy selection and collection of IPDThe flow-diagram of study inclusions is shown in Fig. 2. Of the 16 eligible studies identified, 7 authors were able to share IPD.24,25,27–31 The main characteristics of the studies for which IPD were provided and of the studies for which IPD were not provided, based on the published materials, are displayed in supplementary Table 3. Of the 7 studies included in this meta-analysis, data from 192 individual participants who met the inclusion criteria were provided by the authors. We excluded 11 participants for whom insufficient data were provided for NIV settings at study endpoints, and 5 participants for whom information about diagnosis was not clear. Thus, the meta-analysis was carried out on data from 176 participants from the 7 studies: 113 with NMD, and 63 with CWD.
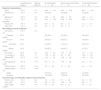
Study and participants characteristicsThe main characteristics of the studies included are reported in Table 1. The primary timeframe for PaCO2 evaluation was 3±1 months for three studies,27–29 6 months for three studies,24,25,30 and 12 months for one study.31
Characteristics of the included studies.
| Study | Location | Design | Population | Sample size included in the meta-analysis (n) | Primary outcome of the study | Primary timeframe (months) | Intervention/comparator |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nickol et al. (2005)27 | United Kingdom | Cohort study | NMD/CWDa | 19 | PaCO2 | 3 | Prospective follow up of patients initiated on long-term NIV |
| Pallero et al. (2014)24 | Spain | RCT (parallel groups) | NMD/CWDa | 40 | PaCO2 | 6 | Ambulatory NIV initiation vs. Hospital NIV initiation |
| Hazenberg et al. (2014)25 | The Netherlands | RCT (parallel groups) | NMD/CWDa | 38 | PaCO2 | 6 | Home NIV initiation vs. Hospital NIV initiation |
| Boentert et al. (2016)28 | Germany | Cohort study | NMD | 13 | Sleep disordered breathing | 3–4 | Prospective follow up of patients initiated on long-term NIV |
| Hannan et al. (2019)29 | Australia | RCT (parallel groups) | NMD/CWDa | 15 | PVA and arousal indices | 2–3 | Daytime NIV titration+PSG vs. control (daytime NIV titration+sham PSG) |
| van den Biggelaar et al. (2020)30 | The Netherlands | RCT (parallel groups) | NMD/CWDa | 40 | PaCO2 | 6 | Home NIV initiation vs. Hospital NIV initiation |
| Yüksel et al. (2020)31 | Turkey | Cohort study | NMD/CWDa | 11 | HRQoL | 12 | Prospective follow up of patients initiated on long-term NIV |
CWD, chest wall disorder; HRQoL, health-related quality of life; NIV, noninvasive ventilation; NMD, neuromuscular disorder; PSG, polysomnography; PVA, patient-ventilator asynchrony; RCT, randomised controlled trial.
The baseline characteristics of study participants are presented in Table 2. Mean PaCO2 level before starting NIV was 6.6±1.4kPa; 124 (70.5%) participants had a baseline PaCO2 level ≥6.0kPa, 65 (57.5%) with NMD and 59 (93.7%) with CWD. Mean FVC was 49.0±19.6%; 102 (58.0%) participants had baseline FVC<50% predicted, 52 (46.0%) with NMD and 50 (79.4%) with CWD. Additional information is provided in supplementary Tables 1 and 2.
Participant characteristics at baseline, NIV settings at study endpoints, and gas exchanges and daily NIV usage at study endpoints for individual participants and the groups with neuromuscular and chest wall disorders.
| N participants; n studies | Missing data (%) | All participants n=176 | Neuromuscular disorders n=113 | Chest wall disorders n=63 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline characteristics | |||||
| Age, y | 176; 7 | 0.0 | 58.4±14.7 | 56.3±13.8 | 62.4±15.4 |
| Female sex, n (%) | 176; 7 | 0.0 | 78 (44.3) | 44 (38.9) | 34 (54.0) |
| BMI, kg.m-2 | 176; 7 | 0.0 | 27.6±6.0 | 28.3±5.8 | 26.3±6.1 |
| FVC, % predicted | 175; 7 | 0.0 | 49.0±19.6 | 54.8±20.3 | 38.6±12.9 |
| PaCO2, kPa | 176; 7 | 0.0 | 6.6±1.4 | 6.2±1.1 | 7.3±1.5 |
| PaO2, kPa | 176; 7 | 0.0 | 9.2±1.9 | 9.8±1.7 | 8.1±1.7 |
| NIV settings at study endpoints | |||||
| NIV mode, n (%) | 176; 7 | 0.0 | |||
| Pressure-cycled | 82; 6 | 82 (46.6) | 53 (46.9) | 29 (46.0) | |
| Volume-cycled | 94; 4 | 94 (53.4) | 60 (53.1) | 34 (54.0) | |
| Volumetric modes | 40; 2 | 40 (22.7) | 14 (12.4) | 26 (41.3) | |
| Hybrid modes | 54; 3 | 54 (30.7) | 46 (40.7) | 8 (12.7) | |
| PS, cmH2O | 82; 6 | 0.0 | 12.4±6.3 | 10.9±6.3 | 15.1±5.6 |
| VT, mL.kgPBW-1 | 93; 4 | 1.1 | 10.8±4.0 | 9.3±2.9 | 13.6±4.4 |
| Backup RR, bpm | 157; 6 | 10.8 | 15.3±2.9 | 15.0±2.9 | 15.8±2.8 |
| NIV intensity Z-score | 157; 6 | 11.4 | 0.0±1.0 | −0.3±0.8 | 0.6±1.0 |
| EPAP, cmH2O | 138; 7 | 21.6 | 5.4±2.9 | 5.7±2.8 | 4.4±2.9 |
| Interface type, n (%) | 157; 6 | 10.8 | |||
| Nasal | 55 (31.3) | 24 (21.2) | 31 (49.2) | ||
| Oronasal | 102 (58.0) | 79 (69.9) | 22 (34.9) | ||
| Gas exchanges and daily NIV usage at study endpoints | |||||
| PaCO2, kPa | 176; 7 | 0.0 | 5.9±0.8 | 5.7±0.8 | 6.2±0.8 |
| PaO2, kPa | 174; 7 | 0.0 | 9.9±1.9 | 10.5±1.8 | 8.8±1.7 |
| Daily usage, h/night | 169; 7 | 4.0 | 6.5±3.0 | 6.4±3.1 | 6.8±2.7 |
Data are mean±SD or n (%). BMI, body mass index; EPAP, expiratory positive airway pressure; FVC, forced vital capacity; NIV, noninvasive ventilation; PS, pressure support; PBW, predicted body weight; RR, respiratory rate; VT, tidal volume.
The risk of bias assessment identified some concerns in five of the included studies,25,27,28,30,31 and the remaining two studies were found to have a low risk of bias.24,29 The most common concerns for the RCTs related to insufficient information about concealment of the intervention and/or the number of dropouts. Concerns for the cohort studies related to the lack of a control group. Details of the risk of bias analysis are provided in supplementary Fig. 1. The IPD provided were consistent with published aggregate data.
NIV settingsThe main NIV settings at study endpoints are presented in Table 2. Six of the included studies explicitly mentioned that the ventilatory parameter adjustment (PS or VT) was guided by a balance between the individual's tolerance and an effective reduction in daytime PaCO2 level or mean nocturnal TcCO2.24,25,27,29–31 The remaining study reported that adjustments were mainly driven by the presence of residual sleep-disordered breathing.28 Four of the included studies reported on the strategy used to adjust the backup respiratory rate; it was commonly set about two cycles below the individual's spontaneous awake respiratory rate.25,28–30
Ventilation for pressure-cycled modes was set with a mean PS of 12.4±6.3cmH2O (range: 2–28cmH2O). Volume-cycled and hybrid modes were set with a mean target VT of 621±159mL, corresponding to 10.8±4.0mLkgPBW−1 (range: 4.9–22.8mLkgPBW−1). Mean BURR was 15.3±2.9breaths/min, ranging from 8 to 24breaths/min. Overall NIV intensity Z-scores ranged from −1.7 to 4.2, and mean values were higher for the CWD (0.6±1.0) than the NMD (−0.3±0.8) group (supplementary Fig. 2).
Primary outcome: effects of NIV settings on PaCO2 levelThe results of the final multivariate models for PaCO2 are presented in Table 3. NIV intensity per se was not significantly associated with PaCO2 level at study endpoints. A lower PaCO2 level at study endpoints was independently associated with a lower baseline PaCO2 level and greater amount of daily NIV usage. These results held true when considering PS (or VT) and BURR separately.
Multivariate models for diurnal PaCO2 at study endpoints.
| Model (n participants; n studies)/covariates; [reference variable] | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Values | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base model with pre-defined variables (155; 6) | Final model for PaCO2, kPa (155; 6) | |||
| Baseline PaCO2, kPa | 0.42 (0.33, 0.52) | <0.001* | 0.48 (0.36, 0.61) | <0.001 |
| Daily NIV usage at study endpoints, hours/night | −0.06 (−0.10, −0.03) | 0.001* | −0.07 (−0.11, −0.03) | <0.001 |
| Disease category [CWD] | 0.07 (−0.19, 0.33) | 0.610* | 0.24 (−1.59, 2.07) | 0.800 |
| Variables added one by one to the base model | ||||
| Sex [male] (155; 6) | 0.18 (−0.03, 0.39) | 0.086* | 0.12 (−0.10, 0.33) | 0.278 |
| Age, y (155; 6) | 0.00 (−0.00, 0.01) | 0.235 | – | – |
| BMI, kgm−2(155; 6) | 0.00 (−0.02, 0.02) | 0.899 | – | – |
| FVC, % predicted (154; 6) | −0.00 (−0.01, 0.01) | 0.864 | – | – |
| Interface type [oronasal] (155; 6) | −0.16 (−0.44, 0.13) | 0.276 | – | – |
| Study design [RCT] (155; 6) | 0.40 (0.06, 0.74) | 0.020* | 0.26 (−0.10, 0.62) | 0.162 |
| Study duration, months (155; 6) | −0.02 (−0.11, 0.07) | 0.639 | – | – |
| Effects of NIV intensity on the final model | ||||
| NIV intensity Z-score | – | – | −0.18 (−1.16, 0.80) | 0.720 |
| (Baseline PaCO2 * Disease category [CWD]) * NIV intensity | – | – | −0.35 (−0.67, −0.02) | 0.035 |
BMI, body mass index; CWD, chest wall disorders; FVC, forced vital capacity; NIV, noninvasive ventilation; RCT, randomized controlled trial.
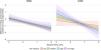
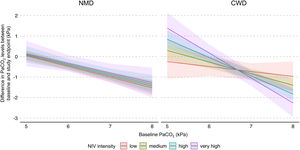
In addition, a multiple interaction associated with a lower PaCO2 level at study endpoints was identified, including a higher baseline PaCO2 level, diagnosis of CWD, and higher NIV intensity (Table 3). Indeed, as shown in Fig. 3, the reduction of PaCO2 between baseline and study endpoints was greater for higher baseline PaCO2 levels, and this reduction was associated with higher NIV intensity only in CWD.
Model of the difference in PaCO2 levels between baseline and study endpoints according to baseline PaCO2, disease category, and NIV intensity. The figure shows the difference in PaCO2 levels between baseline and study endpoints, and final marginal means of the model according to baseline PaCO2, disease category, and NIV intensity. The values presented were adjusted for variables included in the final model, i.e. daily NIV usage, sex, and study design. Low, medium, high and very high NIV intensity correspond to a Z-score of −1, 0, 1 and 2, respectively. CWD, chest wall disorders; NIV, noninvasive ventilation; NMD, neuromuscular disorders.
In a sensitivity analysis, we included only patients with baseline PaCO2≥6kPa and re-ran the final multivariate regression model. The results confirmed that NIV intensity per se was not associated with PaCO2 at study endpoints (supplementary Table 4).
Secondary outcomes: effects of NIV settings on PaO2, daily NIV usage, and interface typeA higher PaO2 level at study endpoints was independently and positively associated with a higher baseline PaO2 level and greater amount of daily NIV usage, but negatively associated with NIV intensity (supplementary Table 5). The multiple interaction between baseline PaO2 level, disease category and NIV intensity was also significant: the improvement in PaO2 level between baseline and study endpoints was more pronounced with lower baseline PaO2 levels, and this improvement was associated with higher NIV intensity in CWD. Unexpectedly, in CWD with elevated baseline PaO2 level, a higher NIV intensity resulted in a reduction in PaO2 between baseline and study endpoints (supplementary Fig. 3).
Daily NIV usage at study endpoints was not associated with NIV intensity. Greater amount of daily NIV usage was independently associated with being male, and with longer study duration (supplementary Table 6). No significant association was found between NIV intensity and interface type (supplementary Table 7). Finally, owing to the high rate of missing data, nocturnal oxygenation and sleep quality at study endpoints could not be analysed (supplementary Table 2).
DiscussionThe primary aim of this systematic review with meta-analysis of IPD was to evaluate the effect of NIV intensity on PaCO2 level in individuals with slowly progressive NMD or CWD initiated on long-term home NIV. We used an original method involving the Z-score principle, which allowed us, based on the included studies, to define the intensity of NIV regardless of the ventilatory mode. In the whole study sample, NIV intensity was not significantly associated with PaCO2 level at study endpoints. However, the effects of NIV intensity differed between the underlying disease categories: no significant effect of NIV intensity was found for NMD, whereas in CWD with the most severe baseline hypercapnia, higher NIV intensities were associated with greater reductions in PaCO2 levels. Neither daily NIV usage nor interface type were associated with NIV intensity.
The severity of the respiratory impairment at the time of NIV initiation could explain the discrepancy in the effect of NIV intensity on PaCO2 level at study endpoints between participants with NMD and CWD. Participants with NMD had moderate impairment of respiratory function and gas exchange at baseline. It is therefore conceivable that they had no major impairment of thoraco-pulmonary compliance or neural respiratory drive. Moreover, patients with NMD are often closely monitored in specialised centres; therefore, respiratory failure is managed early. Participants may have had other symptoms for which the use of NIV was indicated, such as nocturnal hypercapnia or hypoxemia, orthopnoea or reduced muscle strength.2 Consequently, the change in PaCO2 level was achieved even with low intensity NIV. These results contrast with those of a recent retrospective study by our group that suggested that higher levels of ventilatory support were associated with lower nocturnal TcCO2 in individuals with NMD.20 However, the participants in that study had been treated with NIV for more than 8 years on average and therefore likely had more advanced disease. Additionally, the analysis was based on nocturnal, rather than diurnal evaluation of PCO2, which may also explain the stronger relationship between NIV intensity and PCO2.
In the present meta-analysis, respiratory function and gas exchange at baseline were more impaired in the individuals with CWD than in those with NMD. In CWD, increasing NIV intensity could compensate for reduced compliance, which is a major determinant of alveolar hypoventilation in these disorders.32,33 Although the model showed that NIV intensity was associated with a greater improvement in hypoventilation in the individuals with CWD with the highest levels of hypercapnia, a paradoxical effect of NIV intensity might occur in those with moderate or no hypercapnia; in this situation, the benefits of NIV intensity may be limited.
It is noteworthy that the sensitivity analysis including only patients with diurnal hypercapnia (PaCO2≥6kPa) at treatment initiation did not alter the direction of the results of our main analysis, thereby supporting the validity of our findings regardless of baseline PaCO2.
Our results also support evidence that the amount of daily NIV usage is an essential determinant of improvement in daytime PaCO2 level.34–37 This finding highlights the importance of encouraging good adherence to treatment to obtain sufficient daily usage, at least during the first months, rather than immediately increasing NIV intensity to reduce PaCO2 levels. Close follow-up, for instance by telemonitoring or with specific procedures such as polysomnography-directed titration, could be useful to increase daily NIV usage in the initial phase of treatment.29,38
Finally, our results did not show any association between NIV intensity and the type of mask used (nasal vs. oronasal) in either NMD or CWD. This contrasts with the results of a recent meta-analysis in individuals with COPD or OHS that showed that the inspiratory positive airway pressure level tended to be higher (1.42 [−0.04, 2.88]cmH2O) in individuals fitted with an oronasal mask.39
This meta-analysis has several limitations. First, among the 16 studies that fulfilled our inclusion criteria, only 7 authors shared their IPD. The studies for which we did not obtain IPD were older, and alteration of FVC at the time of NIV initiation was significantly more pronounced, which likely reflects the current trend to introduce NIV at earlier stages of disease progression.2,3 Although these considerations may have induced a selection bias, it should be noted that very few studies restricted their inclusion criteria to our population of interest. Consequently, our research question could not be addressed with aggregated data, which made it necessary to obtain IPD. The resulting sample size was therefore limited and, even though this meta-analysis gathered one of the largest datasets analysed in such a population,16 it may have been underpowered and so the results must be interpreted cautiously, particularly the modelling of the highest NIV intensity levels for which the confidence intervals were quite large.
Second, we combined data from prospective cohort studies and RCTs, which could have led to heterogeneity in the results. However, in the multivariate models, study design was not significantly associated with any of the outcomes of interest. In addition, in the RCTs, we only used data from the individuals who received treatment, and no control groups were available in the cohort studies. Therefore, we cannot differentiate between the effect of the natural course of the diseases and the effect of NIV. Although we tried to minimize this bias by testing and adjusting for participants’ baseline characteristics (especially baseline PaCO2), we cannot exclude the presence of residual and unmeasured confounding.
Third, the data provided did not allow us to conclude on the effect of NIV intensity on nocturnal variables, especially nocturnal hypoventilation, which is a very common and important indication for ventilation in these disorders.2 The effect of NIV intensity on nocturnal symptoms should be evaluated in clinical trials, particularly in this population in which improving sleep quality (as well as health-related quality-of-life) is a major target of long-term home NIV.6
Finally, the NIV parameters by which we defined “high” levels of NIV intensity are notably lower than what is encountered in other aetiologies such as COPD.12–15,40 Nevertheless, these values reflect what is actually documented in the literature in this heterogeneous population, and should be further investigated.
ConclusionThis meta-analysis found no significant effects of NIV intensity on PaCO2 levels in individuals with NMD or CWD initiated on long-term home NIV. More specifically, the effects of NIV intensity at the time of treatment initiation are not uniform across populations; higher NIV intensities may be of benefit to individuals with CWD and the most severe levels of baseline hypercapnia. Importantly, the amount of daily NIV usage, whatever the settings, appears to be a decisive independent factor in determining NIV effectiveness on gas exchange. During the early period of NIV implementation, achieving sufficient therapy usage seems to be a consideration that likely should prevail over the intensity of settings to increase alveolar ventilation. Further prospective studies should be conducted to confirm these results.
Authors’ contributionsMD, AL, ML, CK and J-CB contributed to the conception and design of the study. All the authors have written or edited the manuscript.
AH, MP, AHN, LMH, MB, AY, MEH, NH and PJW provided complete IPD from their respective studies. Each co-author made substantial contributions to the manuscript; drafted sections of the manuscript and revised it critically for important intellectual content; provided final approval of the version to be published; agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the manuscript and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Patients’ consent for publicationNot required.
Data sharingNo data are available. All the de-identified individual participant data collected in this systematic review and meta-analysis must be requested from each author individually.
FundingThe authors do not declare a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflict of interestsMD reports personal fees from Air Liquide Medical Systems, Breas Medical AB, and ResMed SAS, outside the submitted work; AL reports consulting fees from Air Liquide Medical Systems, outside the submitted work; ML is a part time employee of Air Liquide Medical Systems, outside the submitted work; AH reports grants from ZonMw VIMP, outside the submitted work; WW reports grants and personal fees from Löwenstein Medical, Germany, grants from Philips Respironics, USA, and personal fees from Sentec, Switzerland, outside the submitted work: LH and MEH report in-kind support from Philips Respironics to his research institute, outside the submitted work; PJW reports personal fees from Philips Respironics, outside the submitted work; HP reports personal fees from ASV Santé, SOS Oxygène, ISIS Medical, Breas Medical, ResMed, Sanofi – Genzyme, and Sanofi – Biogen, outside the submitted work; J-CB is employed by AGIR à dom (French home care provider), outside the submitted work. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
We thank all the co-authors who contributed to the studies included in this meta-analysis, Nathalie SELLIER (from the AFM-Téléthon organization) for her contribution to the conception of search equations, and Johanna ROBERTSON, PhD for language editing.