Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (cHP) represents a severe lung disease often evolving to fibrosis with the subsequent destruction of the lung parenchyma. There are no approved therapies with confirmed efficacy to deal with this disease.
MethodsWe performed an open-label, proof of concept study, to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pirfenidone added to immunosuppressive drugs on the treatment of cHP. We included 22 patients assigned to two groups: Group 1, nine patients that received prednisone plus azathioprine and Group 2, thirteen patients, received prednisone plus azathioprine and pirfenidone (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT02496182). There were no significant imbalances in clinically relevant baseline characteristics between two study groups.
ResultsAfter 1 year of treatment, inclusion of pirfenidone was not associated with improved forced vital capacity (primary end-point). A not significant tendency to show higher improvement of diffusion capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO) was observed in the group receiving pirfenidone (p=0.06). Likewise, a significant improvement in the total score on the SGRQ was found in the group 2 (p=0.02) without differences in other two questionnaires related to quality of life (ATAQ-IPF and EQ-5D-3L). HRCT showed a decrease of the ground glass attenuation without changes in the fibrotic lesions and without differences between both groups.
ConclusionsThese findings suggest that the addition of pirfenidone to the anti-inflammatory treatment in patients with chronic HP may improve the outcome with acceptable safety profile. However, prospective randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trials in largest cohorts are needed to validate its efficacy.
La neumonitis por hipersensibilidad crónica es una enfermedad pulmonar grave que con frecuencia evoluciona hacia fibrosis, con la ulterior destrucción del parénquima pulmonar. No existen tratamientos aprobados con eficacia confirmada para el manejo de esta enfermedad.
MétodosLlevamos a cabo un estudio preliminar de eficacia, abierto, para evaluar la eficacia y la seguridad de la pirfenidona sumada a los fármacos inmunosupresores en el tratamiento de la neumonitis por hipersensibilidad crónica. Se incluyeron 22 pacientes, que se asignaron a dos grupos: grupo 1, 9 pacientes que recibieron prednisona y azatioprina; y grupo 2, 13 pacientes que recibieron prednisona, azatioprina y pirfenidona (identificador NCT02496182 en ClinicalTrials.gov). No se observaron alteraciones significativas en las características clínicamente relevantes iniciales entre ambos grupos.
ResultadosTras un año de tratamiento, la inclusión de la pirfenidona no se asoció con una mejora de la capacidad vital forzada (objetivo principal). Se observó una tendencia no significativa a mostrar una mayor mejora en la capacidad de difusión de monóxido de carbono (DLCO) por el pulmón en el grupo que recibió pirfenidona (p=0,06). Asimismo, se encontró una mejora significativa en la puntuación total del cuestionario SGRQ en el grupo 2 (p=0,02) sin encontrarse diferencias en los otros dos cuestionarios relacionados con la calidad de vida de los pacientes (ATAQ-IPF y EQ-5D-3L). La TAC de alta resolución mostró una disminución de la atenuación en «vidrio deslustrado», sin cambios en las fibrosis y sin diferencias entre ambos grupos.
ConclusionesEstos hallazgos sugieren que añadir pirfenidona al tratamiento antiinflamatorio en pacientes con neumonitis por hipersensibilidad crónica podría mejorar el pronóstico con un perfil de seguridad aceptable. Sin embargo, se necesitan ensayos prospectivos aleatorizados doble ciego y controlados con placebo para validar esta eficacia.
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is a complex syndrome caused by the repeated exposure and sensitization to a wide variety of antigens. The etiology is diverse with more than 100 different sources of antigens currently known to produce the disease .1,2 The clinical course is variable but a number of patients with chronic disease evolve to a fibrotic progressive disorder which is associated with substantial worse prognosis .1–5 In this context, a recent report indicates that patients with chronic HP (cHP) showed a 5-year mortality of 31.5%.6 Aging, persistence of the inciting antigen, and smoking have been associated with chronicity, but the mechanisms involved in the development of chronic fibrotic HP are unclear.
Since HP is considered an inflammatory-driven lung disorder, corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs are frequently used, mainly in patients with disease progression. However, there are no prospective studies to confirm this approach and there is no consensus on an optimal regimen.7 A recent retrospective study suggested that treatment with mycophenolate mofetil or azathioprine allowed the reduction in prednisone dose and was associated with improvement in diffusion capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO) after one year without effect of forced vital capacity in patients with fibrotic HP.8
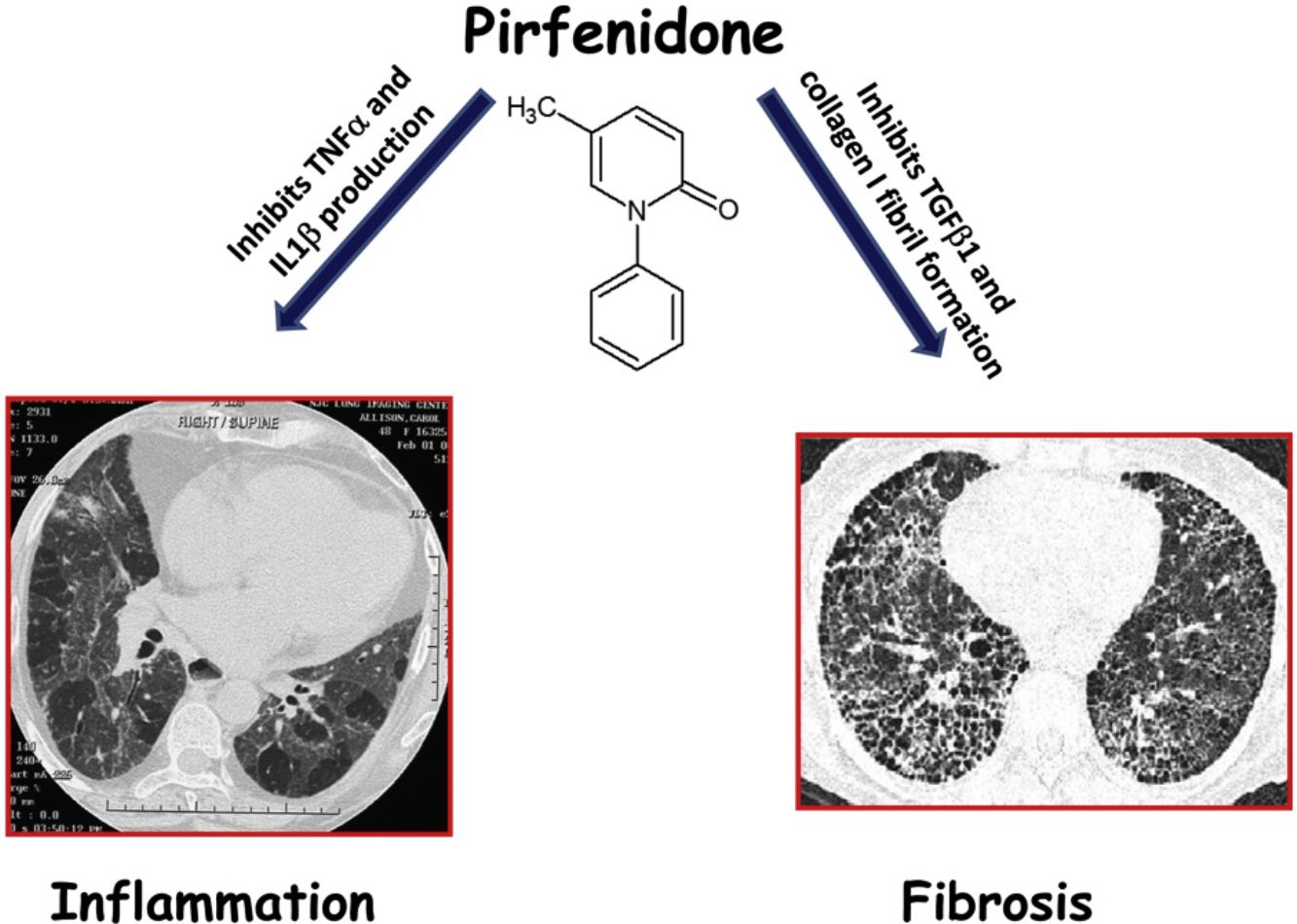
In 2014, two drugs, pirfenidone and nintedanib were accepted as anti-fibrotic therapy for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).9,10 In addition to anti-fibrotic effects, pirfenidone has also anti-inflammatory properties, such as down-regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and subsequent IL-1β secretion, and decreasing the expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα).11,12 These effects may be important in HP, since they are upregulated in this disease and seems to be involved in the pathogenesis.13,14
On these bases, we performed an open-label, proof of concept study, to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pirfenidone added to immunosuppressive drugs on the treatment of cHP.
MethodsStudy populationThe study was conducted at the National Institute of Respiratory Diseases in Mexico City. Diagnosis of HP was made as previously described,15 and confirmed by a multidisciplinary team.
Diagnosis of HP was based on a history of exposure to organic antigens and/or laboratory proof of exposure (serum specific IgG), BAL lymphocytosis (performed in most of the patients), characteristic HRCT findings including the presence of micronodules, ground glass attenuation and mosaic attenuation, and when available, histopathological features compatible with HP.
Chronic HP was defined as: (1) more than 12 months of symptoms before diagnosis; (2) HRCT displaying in addition to nodules and ground glass attenuation, fibrotic lesions (defined as the presence of reticulation, traction bronchiectasis and/or honeycombing); (3) when available, presence of fibrosis and architectural distortion in the histopathological evaluation of the lung biopsy affecting more than 10%.15 A pathologist and a radiologist, blinded to the clinical data, scored the lesions.
None of the patients had been treated with corticosteroids or immunosuppressive drugs at the time of diagnosis.
The exclusion criteria included: current infection, or acute exacerbation, liver disease, history of chronic nephropathy, coronary arterial disease or chronic heart failure, peptic ulcer disease, pregnancy or lactation, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus and physical limitation to perform pulmonary function tests (PFTs) at baseline. The protocol was approved by the Ethic Committee at INER (C27-15), and all patients provided written informed consent. The protocol was registered in NIH Clinical Trials (NCT02496182).
Study design and assessmentsThis was an open label study. Eligible patients were randomized in two groups. Group 1 was assigned to receive prednisone 0.5mg/kg for four weeks, followed by 0.25mg/kg for eight weeks and finally a maintenance dose of 0.125mg/kg, and azathioprine 1–2mg/kg per day with a maximal dose permitted of 150mg. Group 2 was assigned the same treatment scheme with prednisone and azathioprine plus pirfenidone with a maximal dose of 1800mg per day (900mg twice a day). Kitocell® (pirfenidone prolonged-release tablets of 600mg), was kindly donated by CellPharma (Grupo Medifarma S.A. de C.V., México) and was administered two times a day. This presentation of Pirfenidone was manufactured according to standard good manufacturing practices (GMPs), good laboratory practices (GLPs) and sanitary regulations enforced by the Federal Commission for Protection against Sanitary Risks (COFEPRIS) and it is currently approved for clinical use.
Physical examination and clinical laboratory assessment were performed at baseline, 1, 3, 6, 9 and 12 months. Spirometry and carbon monoxide diffusing capacity (DLCO) were achieved at baseline, 3, 6, 9, and 12 months following ATS recommendations.
Quality of life was examined at baseline and 12 months with three questionnaires St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ),16 A Tool to Assess Quality of life in IPF (ATAQ-IPF)17 and a visual analogue scale (VAS) from EQ-5D-3L (EA-5D-3L).18 These questionnaires have been validated in Spanish and used elsewhere.
HRCT study was performed at baseline and 12 months. To evaluate the extension of the interstitial lung findings we used a visual semi-quantitative score described for ILD by Goh et al.19 An expert radiologist calculated the total extension score, ground grass score and fibrosis score.
The primary efficacy end-point was the change of predicted value of the FVC in percentage and ml at 12 months.
The secondary efficacy end-points were the changes in the percentage of predicted value of the DLCO, oxygen saturation and walk distance in the 6MWT, SGRQ score, ATAQ-IPF score, VAS score, HRCT total extension score, HRCT ground glass score and HRCT fibrosis score from baseline to 12 months of treatment.
All the adverse events were reported according with the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities, version 18.0. Safety outcomes were reported as events that occurred in the period from baseline until four weeks after the last dose of the study.
Statistical analysisThe univariate analysis was performed with frequencies, interquartile ranges and standard deviation. The comparison of the groups was performed with the Chi-square test or Fisher's exact test for categorical variables. Continuous variables were compared by U Mann–Whitney.
To evaluate the efficacy of the inclusion of pirfenidone in the treatment, we calculated the delta difference between basal and 12 months determination of FVC (liters and predicted percentage) and DLCO (predicted percentage). To quantify the results of the questionnaires of quality of life, we also used the delta of median change of total score, from baseline to 12 months.
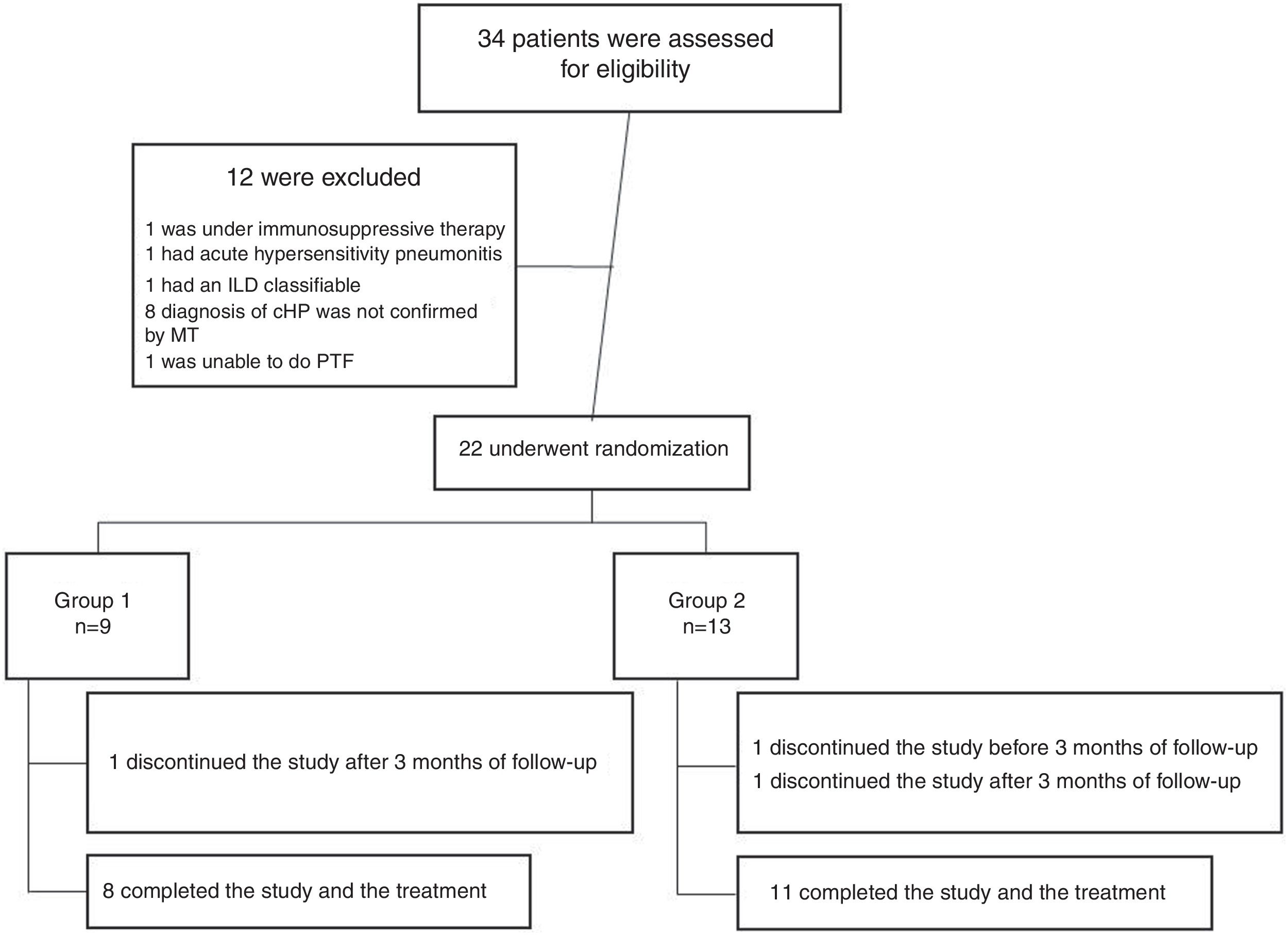
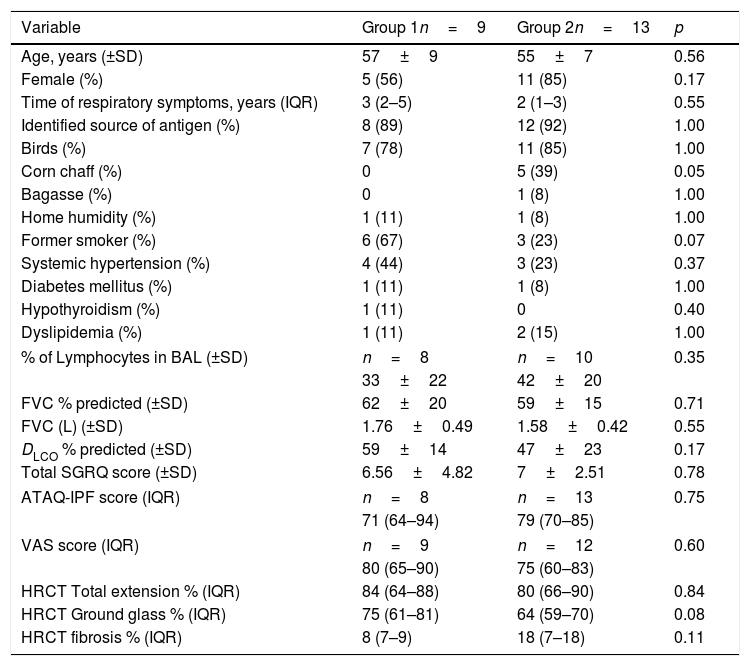
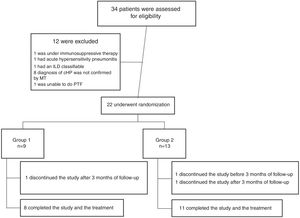
ResultsFrom July 2015 to March 2018, a total of 34 patients were enrolled for the study. Twelve patients were excluded for different causes, most of them because the diagnosis was not confirmed after multidisciplinary discussion (Fig. 1). Twenty-two patients were included in the study; nine were assigned to the Group 1 and thirteen patients were assigned to the Group 2 (Fig. 1). Demographic and baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 1. There were no significant imbalances in clinically relevant baseline characteristics between two study groups. Most patients were female (56% in group 1 and 85% in group 2) with a mean age of 57 (±9) and 55 (±7) years respectively. The proportion of identified exposure sources (mostly birds) was similar between the groups.
Characteristics of the patients at baseline.
| Variable | Group 1n=9 | Group 2n=13 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years (±SD) | 57±9 | 55±7 | 0.56 |
| Female (%) | 5 (56) | 11 (85) | 0.17 |
| Time of respiratory symptoms, years (IQR) | 3 (2–5) | 2 (1–3) | 0.55 |
| Identified source of antigen (%) | 8 (89) | 12 (92) | 1.00 |
| Birds (%) | 7 (78) | 11 (85) | 1.00 |
| Corn chaff (%) | 0 | 5 (39) | 0.05 |
| Bagasse (%) | 0 | 1 (8) | 1.00 |
| Home humidity (%) | 1 (11) | 1 (8) | 1.00 |
| Former smoker (%) | 6 (67) | 3 (23) | 0.07 |
| Systemic hypertension (%) | 4 (44) | 3 (23) | 0.37 |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 1 (11) | 1 (8) | 1.00 |
| Hypothyroidism (%) | 1 (11) | 0 | 0.40 |
| Dyslipidemia (%) | 1 (11) | 2 (15) | 1.00 |
| % of Lymphocytes in BAL (±SD) | n=8 | n=10 | 0.35 |
| 33±22 | 42±20 | ||
| FVC % predicted (±SD) | 62±20 | 59±15 | 0.71 |
| FVC (L) (±SD) | 1.76±0.49 | 1.58±0.42 | 0.55 |
| DLCO % predicted (±SD) | 59±14 | 47±23 | 0.17 |
| Total SGRQ score (±SD) | 6.56±4.82 | 7±2.51 | 0.78 |
| ATAQ-IPF score (IQR) | n=8 | n=13 | 0.75 |
| 71 (64–94) | 79 (70–85) | ||
| VAS score (IQR) | n=9 | n=12 | 0.60 |
| 80 (65–90) | 75 (60–83) | ||
| HRCT Total extension % (IQR) | 84 (64–88) | 80 (66–90) | 0.84 |
| HRCT Ground glass % (IQR) | 75 (61–81) | 64 (59–70) | 0.08 |
| HRCT fibrosis % (IQR) | 8 (7–9) | 18 (7–18) | 0.11 |
SD: standard deviation; IQR: interquartile range; BAL: bronchioalveolar lavage; FVC: forced vital capacity; DLCO: carbon monoxide diffusing capacity; SGRQ: St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire; ATAQ-IPF: A Tool to Assess Quality of life in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; VAS: visual analogue score; HRCT: high resolution computed tomography.
A total of 19 patients (83%) completed the study: 8 patients in the Group 1 and 11 patients in the Group 2. One patient was missed after 3 months of treatment in the Group 1, and 2 patients discontinued prematurely the treatment, one before and the other after 3 months in the Group 2.
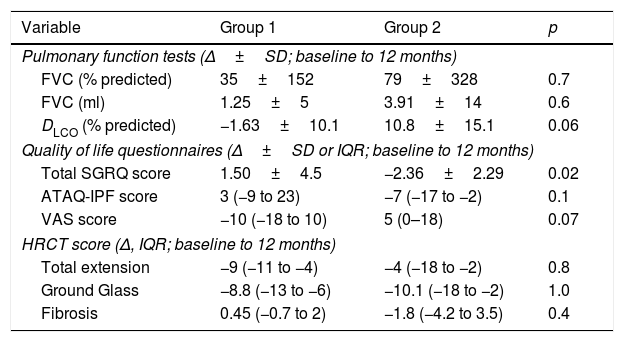
Primary efficacy analysisNo significant changes were observed in the predicted value of FVC (%) from baseline to 12 months in any of the groups. An improvement was observed in FVC in ml in both groups with a small (non significant) tendency to be higher in Group 2 (Table 2, Fig. 2A and B).
Primary and secondary efficacy outcomes.
| Variable | Group 1 | Group 2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pulmonary function tests (Δ±SD; baseline to 12 months) | |||
| FVC (% predicted) | 35±152 | 79±328 | 0.7 |
| FVC (ml) | 1.25±5 | 3.91±14 | 0.6 |
| DLCO (% predicted) | −1.63±10.1 | 10.8±15.1 | 0.06 |
| Quality of life questionnaires (Δ±SD or IQR; baseline to 12 months) | |||
| Total SGRQ score | 1.50±4.5 | −2.36±2.29 | 0.02 |
| ATAQ-IPF score | 3 (−9 to 23) | −7 (−17 to −2) | 0.1 |
| VAS score | −10 (−18 to 10) | 5 (0–18) | 0.07 |
| HRCT score (Δ, IQR; baseline to 12 months) | |||
| Total extension | −9 (−11 to −4) | −4 (−18 to −2) | 0.8 |
| Ground Glass | −8.8 (−13 to −6) | −10.1 (−18 to −2) | 1.0 |
| Fibrosis | 0.45 (−0.7 to 2) | −1.8 (−4.2 to 3.5) | 0.4 |
Δ: Delta change; FVC: forced vital capacity; SD: standard deviation; DLCO: carbon monoxide diffusing capacity; IQR: interquartile range; SGRQ: St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire; ATAQ-IPF: A Tool to Assess Quality of life in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; VAS: visual analogue score; HRCT: high resolution computed tomography.
A difference in the mean change of the predicted value of DLCO from baseline to 12 months was found with −1.63±10% in the Group 1 versus 10.8±15% in the Group 2, although it not reach statistical significance (p=0.06); Table 2, Fig. 2C).
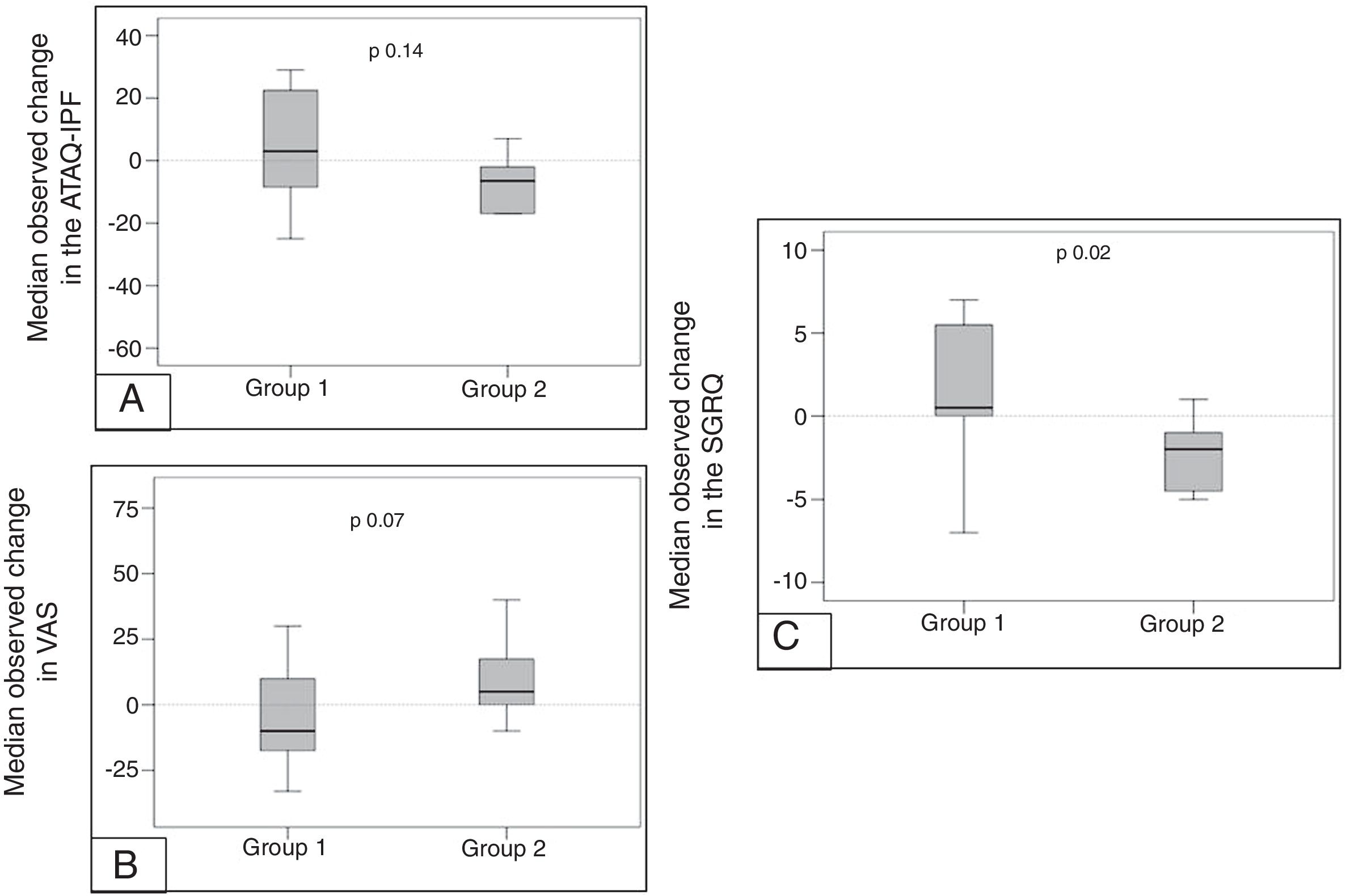
Quality of lifeThe median change from baseline to 12 months in total score on the SGRQ was 1.5±4.5 in the Group 1, and −2.36±2.29 in Group 2, p=0.02 (Table 2 and Fig. 3A). VAS score was −10 (−18 to 10) in Group 1 and 5 (0–18) in the Group 2 (p=0.07) (Table 2 and Fig. 3B). ATAQ-IPF score was 3 (−9 to 23) in the Group 1 versus −7 (−17 to −2) in Group 2 without statistical difference (Table 2 and Fig. 3C).
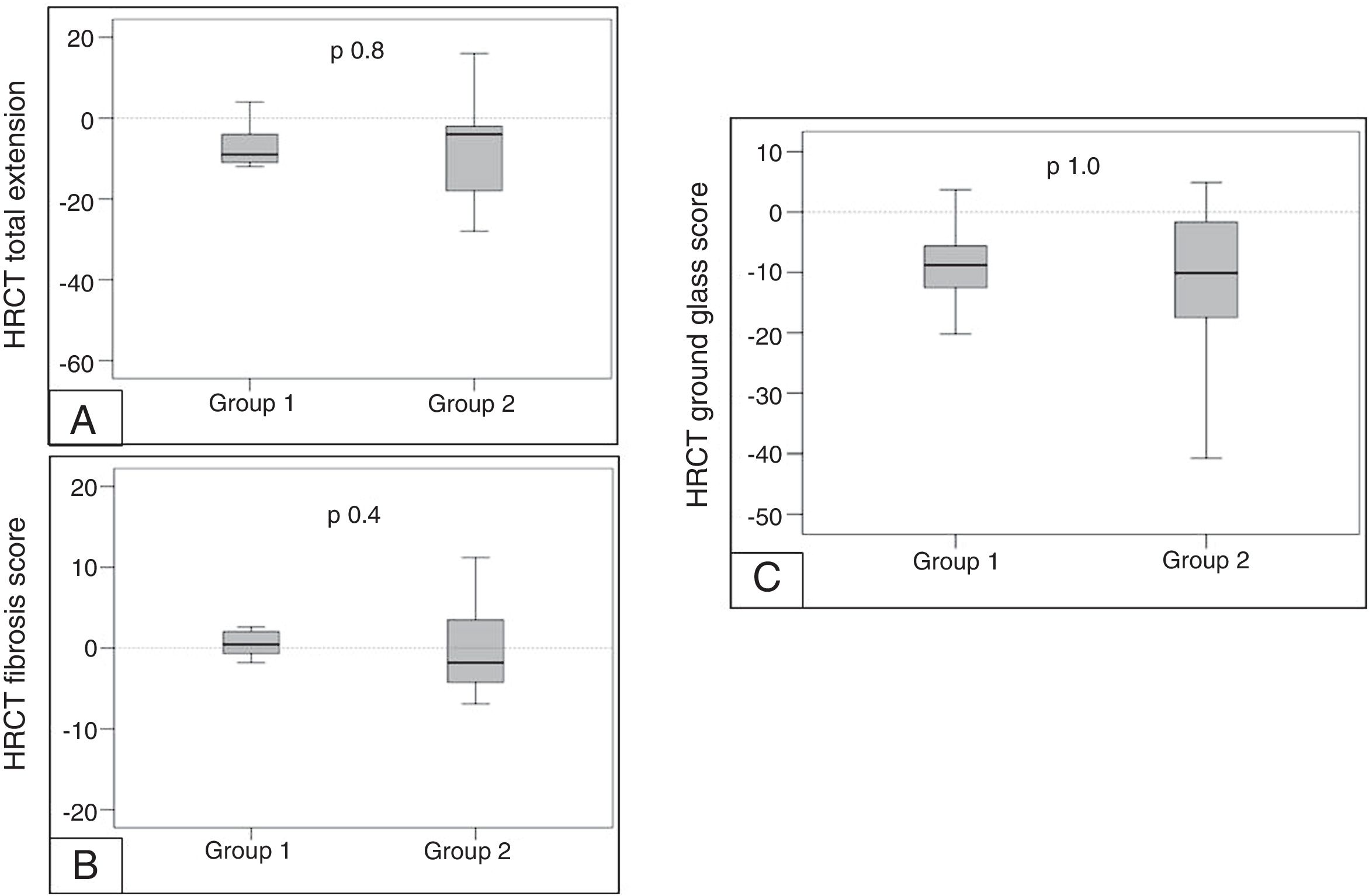
High resolution computed tomography (HRTC)The analysis of HRCT showed a slight/moderate decrease of the extent of the lesions, as well as of the ground glass attenuation without changes in the fibrotic lesions and without differences in both groups (Table 2 and Fig. 4).
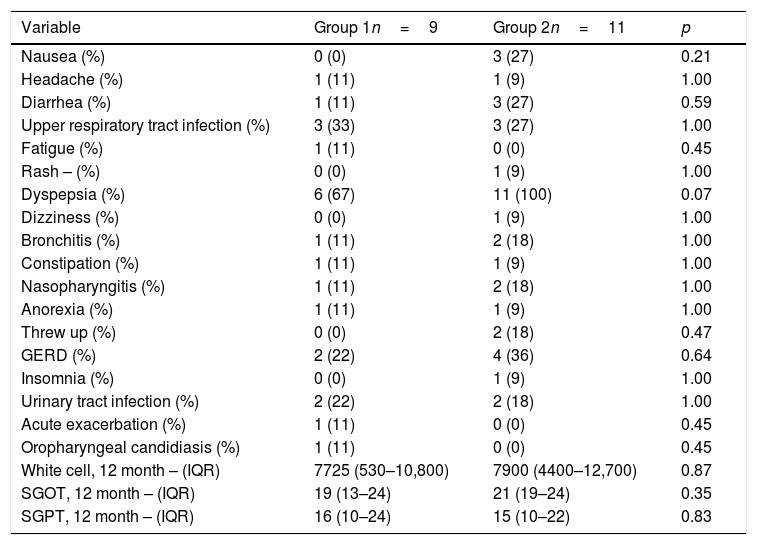
Adverse eventsNausea, diarrhea and dyspepsia were more frequent in the group that received pirfenidone (Table 3). Other adverse events included upper tract respiratory infection, and urinary tract infection; however, no differences between the groups were observed. There were not severe adverse events in the two groups of treatment and it was not necessary to withdraw the study treatment. There were not deaths during the study period.
Adverse events.
| Variable | Group 1n=9 | Group 2n=11 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nausea (%) | 0 (0) | 3 (27) | 0.21 |
| Headache (%) | 1 (11) | 1 (9) | 1.00 |
| Diarrhea (%) | 1 (11) | 3 (27) | 0.59 |
| Upper respiratory tract infection (%) | 3 (33) | 3 (27) | 1.00 |
| Fatigue (%) | 1 (11) | 0 (0) | 0.45 |
| Rash – (%) | 0 (0) | 1 (9) | 1.00 |
| Dyspepsia (%) | 6 (67) | 11 (100) | 0.07 |
| Dizziness (%) | 0 (0) | 1 (9) | 1.00 |
| Bronchitis (%) | 1 (11) | 2 (18) | 1.00 |
| Constipation (%) | 1 (11) | 1 (9) | 1.00 |
| Nasopharyngitis (%) | 1 (11) | 2 (18) | 1.00 |
| Anorexia (%) | 1 (11) | 1 (9) | 1.00 |
| Threw up (%) | 0 (0) | 2 (18) | 0.47 |
| GERD (%) | 2 (22) | 4 (36) | 0.64 |
| Insomnia (%) | 0 (0) | 1 (9) | 1.00 |
| Urinary tract infection (%) | 2 (22) | 2 (18) | 1.00 |
| Acute exacerbation (%) | 1 (11) | 0 (0) | 0.45 |
| Oropharyngeal candidiasis (%) | 1 (11) | 0 (0) | 0.45 |
| White cell, 12 month – (IQR) | 7725 (530–10,800) | 7900 (4400–12,700) | 0.87 |
| SGOT, 12 month – (IQR) | 19 (13–24) | 21 (19–24) | 0.35 |
| SGPT, 12 month – (IQR) | 16 (10–24) | 15 (10–22) | 0.83 |
IQR: interquartile range; GERD: gastroesophageal reflux; SGOT: serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase; SGPT: serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase.
A substantial number of patients with chronic HP evolve to fibrosis which leads to progressive clinical deterioration and worsened quality of life. Although there are no randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials, these patients are usually treated with prednisone, and more recently, with immunosuppressive therapy either azathioprine or mycophenolate mofetil, with controversial results.8,20 Some studies suggest that rituximab, a human/murine, chimeric monoclonal antibody, with specific affinity for the B-lymphocyte transmembrane protein, CD20, may be effective in selected patients that are refractory to other systemic immunosuppressive drugs.21,22 However, the experience is scanty.
In this context, there is an urgent need to identify new therapeutic approaches for this disease mainly focused on the fibrotic progressive phase.
In the last years, two anti-fibrotic drugs pirfenidone and nintedanib, have been approved for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, an epithelial-driven disease and certainly the most aggressive fibrotic lung disorder.9,10 More recently, these drugs are being explored for use in several inflammatory-driven fibrotic lung diseases such as systemic sclerosis, non-specific interstitial pneumonia and others.23,24 Importantly, some of the chronic fibrotic HP patients present a usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) like pattern, characteristic of IPF either in the HRCT or in the lung biopsy, and these patients can be indistinguishable and are often misdiagnosed as IPF.4,25
With these bases we conducted this open-label, proof of concept study, adding pirfenidone, which also has some anti-inflammatory properties, to the immunosuppressive therapy that we usually indicate in HP patients with chronic progressive disease.
Our results showed that after a year, the addition of pirfenidone to prednisone and azathioprine was associated with some improvement compared with the immunosuppressive treatment alone. Among all the primary and secondary pre-specified efficacy end-points, the addition of pirfenidone resulted in a marginal tendency to improvement in gas exchange (DLCO), a significant improvement in quality of life according to the total score on the SGRQ with a tendency to be significant in VAS. No effect was observed on lung mechanics and fibrotic opacities in HRCT. However, it is important to emphasize that in this proof of concept study, the sample size is too small and underpowered (0.506) to make a definitive conclusion. Nevertheless, we consider that these preliminary results are encouraging, mainly because the effect on quality of life a relevant aspect for the patients with chronic respiratory diseases.
Importantly, there was an acceptable safety profile. Actually, although gastrointestinal adverse events were more frequently observed in the group receiving pirfenidone, no differences were observed between both groups, and no serious AEs leading to discontinuation of pirfenidone were observed.
This study has several limitations to be considered. First, the sample size was small and all the patients were enrolled from one reference Center. Second, investigators were not blinded to treatment. Third, this was an uncontrolled open-label trial (without a placebo group).
In conclusion, combination therapy with immunosuppressive drugs (azathioprine and prednisone) plus pirfenidone seems to provide a benefit as compared with immunosuppressive drugs alone in patients with chronic fibrotic HP, and may improve the outcome with acceptable safety profile. However, further investigation of the effect of pirfenidone and other anti-fibrotic drugs through a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial is needed.
Conflict of interestOne of the authors: Jonathan Castillo-Pedroza serves partial time with Cell Pharma, the Company that gave us the pirfenidone. He did not participate in the interpretation/integration of the data.
None of the other authors have conflict of interests regarding this manuscript.


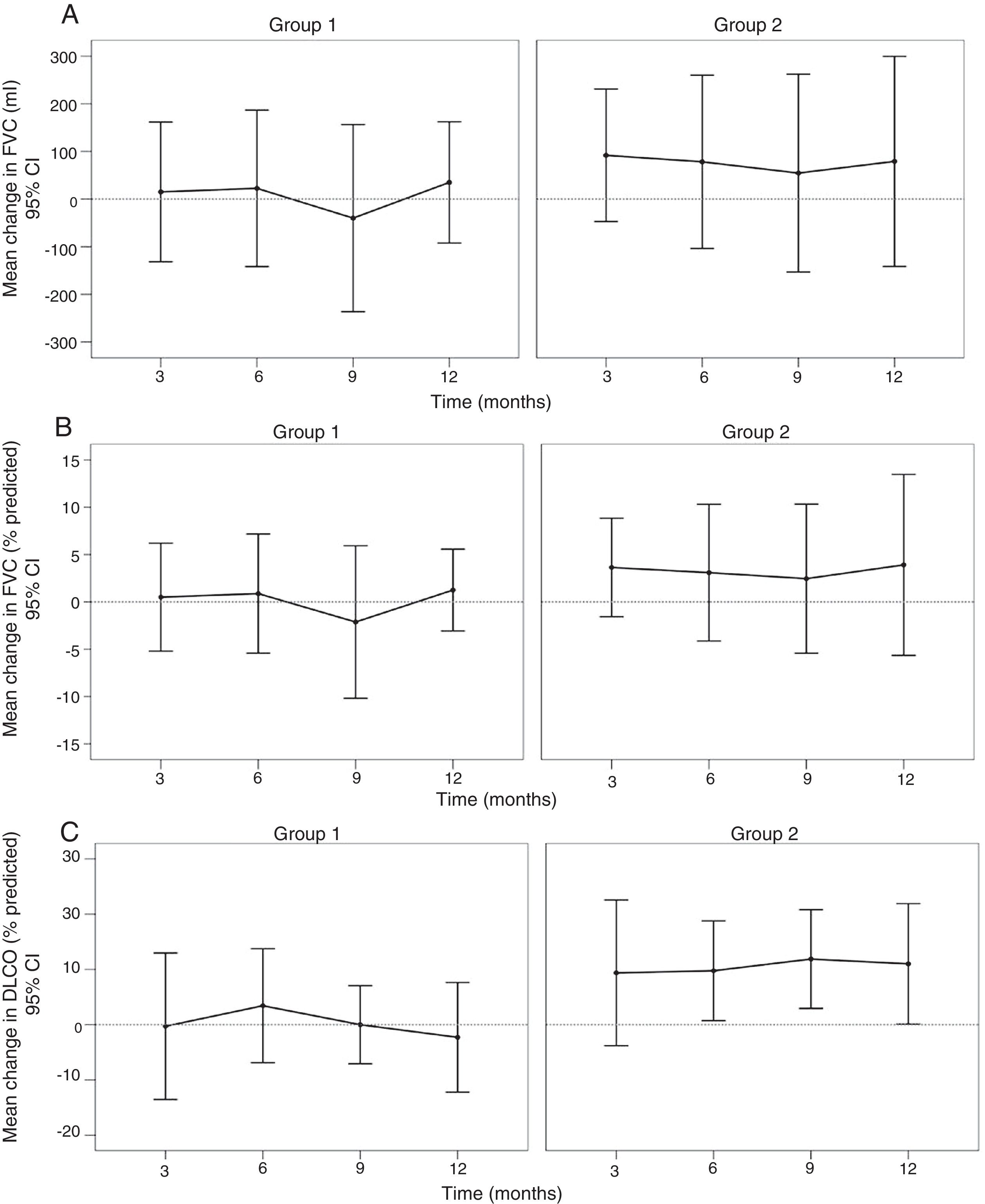
![No changes were observed in FVC (ml) [A], FVC (% predicted) [B] and DLCO (% predicted) [C] between both groups. No changes were observed in FVC (ml) [A], FVC (% predicted) [B] and DLCO (% predicted) [C] between both groups.](https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/03002896/0000005600000003/v2_202003070709/S0300289619303813/v2_202003070709/en/main.assets/thumbnail/gr2.jpeg?xkr=ue/ImdikoIMrsJoerZ+w98FxLWLw1xoW2PaQDYY7RZU=)
![Mean change in quality of life questionnaires scores in both groups from baseline to 12 months of treatment. [A] ATAQ-IPF score, [B] VAS score and [C] SGRQ score. Mean change in quality of life questionnaires scores in both groups from baseline to 12 months of treatment. [A] ATAQ-IPF score, [B] VAS score and [C] SGRQ score.](https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/03002896/0000005600000003/v2_202003070709/S0300289619303813/v2_202003070709/en/main.assets/thumbnail/gr3.jpeg?xkr=ue/ImdikoIMrsJoerZ+w98FxLWLw1xoW2PaQDYY7RZU=)
![Mean change in HRCT in both groups from baseline to 12 months of treatment. [A] Mean observed change in the HRCT total extension score. [B] Mean observed change in the HRCT fibrosis score. [C] Mean observed change in the HRCT ground glass score. Mean change in HRCT in both groups from baseline to 12 months of treatment. [A] Mean observed change in the HRCT total extension score. [B] Mean observed change in the HRCT fibrosis score. [C] Mean observed change in the HRCT ground glass score.](https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/03002896/0000005600000003/v2_202003070709/S0300289619303813/v2_202003070709/en/main.assets/thumbnail/gr4.jpeg?xkr=ue/ImdikoIMrsJoerZ+w98FxLWLw1xoW2PaQDYY7RZU=)







